Messages [1 to 20 of 29]
1↑ Topic by Gamez 03/16/2014 23:44:23
- Gamez
- Assistant
- Inactive
- Name: Pavel
- From: Ukraine Zhitomir
- Registered: 03-07-2013
- Messages: 213
- Reputation: 11
- Motorcycle: Dnepr 10-36
Subject: Lost spark
The spark on the motorcycle MT 10-36 suddenly disappeared. It was like this: I started it up, warmed up the carburetors (Min. 20), drove about 1 km and turned it off. I tried to start it, it wouldn't start (it tormented me for about 10 minutes), I removed the cap, I inserted the spark plug, I put it on the cylinder, there is no spark on the second one, the same thing. The current does not go to the coil (it does), but there is still no spark, I still don’t understand what the reason is, maybe someone connected. And yes, the contact was scraped with natfil.
(A huge request not to write something like BSZ, go there, no problem)
2↑ Reply from PATRIOT 03/16/2014 23:59:47
- PATRIOT
- Patriot IMZ
- Inactive
- Name: Ilya
- From: Krasnodar region, Krasnodar
- Registered: 18-02-2011
- Messages: 3 148
- Reputation: 176
- Motorcycle: No. Next will be the K750!
Re: Lost spark
That's right, all this is BSZ rubbish. All sorts of Sarumans, Shards.
In short, the most important thing is to check the current of the positive wire going to the coil (preferably with a test light) because you will see the strength of the current - the light will burn brightly or dimly. Maybe you have something wrong in the wiring, and the ignition simply doesn’t have enough current! Moreover, the contact current consumes a lot of current. We go further, if current flows to the coil, check the spark on the spark plugs - no, don’t rush to change the capacitor. Usually the capacitor produces a spark even if it is faulty. Also try setting the gap between the contacts smaller (by eye), maybe the gap is too large for sparking! Well, if you did all this and there is no spark, then you bought a shitty coil! Try another one, buy it, or borrow it from a friend. I also recently bought 2 new 6-volt ones. I put one on - no spark. I put the second one on - there is a spark. Good luck!
3↑ Reply from drakone 03/17/2014 11:54:58
- on drakone
- Elder
- Inactive
- Name: Albert
- From: Omsk region. Omsk city
- Registered: 07-12-2012
- Messages: 4 972
- Reputation: 125
- Motorcycle: Ural 8.103.10, GAZ 31029
Re: Lost spark
You came here for advice, and not to have bullshit shoved at you. You know what, check the simplest thing, maybe you have a blown fuse
4↑ Reply from ZED-m63 03/17/2014 14:55:48
- ZED-m63
- Pro
- Inactive
- Name: Evgeniy
- From: Amur region/Svobodny
- Registered: 10-03-2014
- Messages: 808
- Reputation: 39
- Motorcycle: URAL m-63
Re: Lost spark
5↑ Reply from Watto 03/17/2014 15:11:30
- Watto
- Elder
- Inactive
- Name: Vladimir
- From: Nizhny Novgorod region
- Registered: 22-09-2012
- Messages: 1 678
- Reputation: 236
- Motorcycle: ZiD-50, Honda CB750 Night Hawk, Dnepr MT 10-36
Re: Lost spark
The fuse, this is really probably the simplest thing - Gamez has probably already checked it. I'd also look at the battery. I had the following experience when operating the Pilot - a year-old battery (Chinese, of course) lost its charge literally before our eyes. Coming out of the garage, I started the engine with an electric starter, drove to the place, and after a short parking there was not enough charge even for the signal.
Edited by Watto (17-03-2014 15:14:49)
6↑ Reply from ZED-m63 03/17/2014 15:25:49
- ZED-m63
- Pro
- Inactive
- Name: Evgeniy
- From: Amur region/Svobodny
- Registered: 10-03-2014
- Messages: 808
- Reputation: 39
- Motorcycle: URAL m-63
Re: Lost spark
Yes, this can happen too.
7↑ Reply from drakone 03/17/2014 16:45:08
- on drakone
- Elder
- Inactive
- Name: Albert
- From: Omsk region. Omsk city
- Registered: 07-12-2012
- Messages: 4 972
- Reputation: 125
- Motorcycle: Ural 8.103.10, GAZ 31029
Re: Lost spark
apparently there was no mass
8↑ Reply from Gamez 03/17/2014 16:50:13
- Gamez
- Assistant
- Inactive
- Name: Pavel
- From: Ukraine Zhitomir
- Registered: 03-07-2013
- Messages: 213
- Reputation: 11
- Motorcycle: Dnepr 10-36
Re: Lost spark
Well, I tried it right away with the charger connected, I think if there was enough electricity, but I don’t have any for the fuse line
9↑ Reply from drakone 03/17/2014 16:52:14
- on drakone
- Elder
- Inactive
- Name: Albert
- From: Omsk region. Omsk city
- Registered: 07-12-2012
- Messages: 4 972
- Reputation: 125
- Motorcycle: Ural 8.103.10, GAZ 31029
Re: Lost spark
what about wire?
10↑ Reply from kilowatt3 03/20/2014 11:08:56
- kilowatt3
- Electrician
- Inactive
- Name: Alexander
- From: Belgorod region Alekseevka
- Registered: 24-03-2011
- Messages: 1 950
- Reputation: 197
- Motorcycle: Dnepr MT 11, but there were different ones and more than one!
Re: Lost spark
the topic is worn out to holes, there is even a video review so I’ll take it down soon, look for a plus on the reel or a dead reel or contacts can sit on the ground a movable cam there is no other option
11↑ Reply from Stierlitz 03/20/2014 18:22:24
- Stierlitz
- Elder
- Inactive
- Name: Sergey
- From: Tolyatti
- Registered: 21-12-2013
- Messages: 1 229
- Reputation: 126
- Motorcycle: Ural IMZ-8.1243 Voyage
Re: Lost spark
Regarding the purpose of the capacitor. It is not needed at all to create a spark on the candles, but just the opposite - so that the contacts do not spark or burn. So even in its absence, if other elements of the electrical circuit are in good working order, there will be a spark on the spark plugs, but the contacts on the cams will quickly burn out, and the resistance on them will increase.
12↑ Reply from Alexey2009 05/28/2014 14:32:03
- Alexey2009
- Newbie
- Inactive
- Registered: 28-09-2011
- Messages: 27
Re: Lost spark
The spark on the motorcycle MT 10-36 suddenly disappeared. It was like this: I started it up, warmed up the carburetors (Min. 20), drove about 1 km and turned it off. I tried to start it, it wouldn't start (it tormented me for about 10 minutes), I removed the cap, I inserted the spark plug, I put it on the cylinder, there is no spark on the second one, the same thing. The current does not go to the coil (it does), but there is still no spark, I still don’t understand what the reason is, maybe someone connected. And yes, the contact was scraped with natfil.
(A huge request not to write something like BSZ, go there, no problem)
Or maybe the wiring from the ignition switch just came loose?
Dnepr 11 no spark. Help
Dnepr 11 no spark. Help
Post by Demenchuk » June 11, 2011, 5:13 pm
Post by Andrey21 » June 11, 2011, 8:59 pm
Post by Demenchuk » June 11, 2011, 10:11 pm
Post by Garic » June 11, 2011, 10:43 pm
Post by Andrey21 » June 12, 2011, 06:36
Post by Sergeus » June 12, 2011, 11:16 am
————————— Let's start by checking the ignition system. Let's unscrew the spark plugs, inspect and check the gap between the electrodes. It should be 0.6 mm. If adjustment is needed, bend or bend the side electrode. If the gap is too large, the formation of a spark is difficult, and if it is too small, carbon deposits are deposited on the electrodes, which can bridge the spark gap. Then the spark disappears or is weakened, since part of the energy goes to the “ground” of the soot. In both cases, the engine will run intermittently.
Next you need to check and adjust the gap between the breaker contacts. The K-650 and K-750 have a DC battery ignition system with a voltage of 6 V, and the Dnepr MT10, MT11, Ural M67 have 12 V. Their distribution breakers are different in design: respectively PM05, which has ignition timing for control a shifter on the motorcycle handlebar, and PM302-A with a centrifugal regulator that provides automatic change in ignition timing depending on engine speed.
The procedure for adjusting the gap between the contacts is the same for both breakers. First, we inspect the working surfaces of the contacts. If they are dirty, oily or burnt, you need to clean them with a special abrasive plate or file, blow with air and wipe with chamois leather slightly moistened with clean gasoline. There should be no abrasive grains, fibers or other foreign particles remaining between the contacts that disrupt the electrical contact. It is not recommended to clean the contacts with emery cloth, which will release a lot of abrasive particles into the breaker.
The gap between the breaker contacts is checked and adjusted. By turning the engine crankshaft with the trigger lever, set the maximum gap between the contacts (the textolite rack of the movable should be at the top of the cam) and determine its value with a feeler gauge. It should be within 0.4-0.6 mm (rns. 1.a). If the gap is large, the spark on the spark plugs is weakened. When the gap is small, sparking occurs and the contacts burn.
To measure the gap, you should loosen the screw securing the fixed contact post in PM05 (Fig. 1.b), and the locking screw in PM302-A (Fig. 2, a). By rotating the adjusting screw, which has an eccentric head, in one direction or another, we set the required gap.
Checking and setting ignition timing. Untimely ignition of the mixture is very harmful to the operation of the engine, so special attention must be paid to ignition adjustment. If the ignition is too late, the spark occurs when the piston is at or even behind TDC. The mixture burns slowly until the exhaust valve opens and even in the exhaust pipe. This causes overheating of the engine, exhaust pipes and mufflers. Moreover, the pressure in the cylinder increases slowly and will be much lower than during normal ignition. Naturally, engine power decreases and fuel consumption increases.
If the ignition is too early (the piston has not yet reached TDC), the increasing gas pressure prevents the piston from moving, increasing the load on the parts of the crank mechanism. The maximum pressure in the cylinder can significantly exceed the pressure at optimal advance, which is associated with abnormal combustion of the working mixture. In addition, the temperature of the gases inside the cylinder increases sharply, and this, as a rule, leads to burnout of the piston bottom.
"Dnepr" K-650 and K-750 with PM05 breaker. In order to facilitate the installation of ignition timing, marks with the letters “B” (top dead center), “P” (late ignition) and “P” (early ignition) are placed on the outer surface of the engine flywheel, and a hole is made on the engine crankcase near the oil filler neck with tag. The adjustment sequence is as follows.
Remove the cover and the slider (rotor) of the breaker, turn the shifter to the “Early” position. We check and, if necessary, adjust the free play of the ignition timing control cable with a stop (see Fig. 1, c), which should be 2-3 mm. We connect the test light to ground to the low voltage terminal of the ignition coil (the wire coming from the insulated terminal of the breaker is attached to it).
Turn on the ignition and slowly rotate the crankshaft with the start pedal until the marks on the engine crankcase and the flywheel (with the letter “P”) coincide. If the control light comes on before the marks coincide or does not light up after they are aligned, the ignition must be adjusted. To do this, there is a screw 3 on the left side of the movable disk of the breaker (see Fig. 1 b), which fits into the cutout of the breaker body. Having loosened the lock nut, turn it with a screwdriver in one direction or another until the light turns on, signaling the beginning of the contacts opening. In this case, the maximum ignition timing on the crankshaft will be 32-36° BTDC.
Then set the ignition timing shifter to the “Later” position, turn on the ignition and turn the crankshaft in the direction of rotation until the marks on the engine crankcase coincide with the flywheel (with the letter “P”). If the light does not light up, set the ignition timing by rotating screw 6 until it turns on. Late ignition in this case will be equal to 4-8 degrees before TDC.
Motor with breaker PM302-A or PM302-01. Since 1982, Dnepr MT10-36 motorcycles have a new PM302-A breaker instead of the PM302-01 breaker. having a more modern and reliable design of the advance machine. In terms of seating, these breakers are interchangeable. In order to facilitate checking and setting the ignition timing, unlike motorcycles with PM05, there are only two marks on the flywheel: “B” - top dead center and “P” - early ignition. There is also a mark on the engine crankcase near the hole near the oil filler neck.
We check and adjust the ignition in this way.
We connect the test lamp to the low voltage terminal of the ignition coil and to ground. Rotate the crankshaft in the direction of rotation until the mark on the engine crankcase coincides with the “P” mark on the flywheel.
Turn on the ignition and slowly move the weights of the machine until they stop. The control light should light up when the weights touch the stops. If the light does not light up at all or flashes earlier, then the device needs adjustment.
To do this, loosen the fixing screws of the breaker and, with the weights of the machine fully extended, slowly turn the breaker body until the light comes on, which will correspond to the beginning of the opening of the contacts (the moment a spark occurs between the electrodes of the spark plug), and the ignition timing angle for the rotation of the crankshaft is equal to 32 - 36° (or 6.3-8.0 mm according to the piston movement) to TDC.
If there is no indicator light, the moment when the contacts begin to open can be easily determined as follows. Turn the engine crankshaft until the breaker contacts are completely connected. Turn on the ignition and apply a screwdriver or other steel object to one of the ends of the ignition coil core. When the breaker contacts are closed, the current passing through the coil winding magnetizes the core, which attracts and holds the screwdriver. Then, with light pushes of the kickstarter lever, we slowly turn the crankshaft until the screwdriver falls off, since when the breaker contacts open, the core is demagnetized.
It should be remembered that the springs of the machine cannot be bent or stretched, since violation of their special calibration will distort the operation of the machine, and, consequently, the ignition timing will not be optimal for a given engine operating mode.
How to adjust the ignition on a boxer
A correctly adjusted Ural or Dnepr should start with half a turn. If, despite the carburetor float chambers being filled with gasoline, you have to hit the kickstarter for a long time before the engine reluctantly starts to spark, then it’s time to adjust the ignition. This must also be done if the engine backfires when starting, and knocks during operation, overheats, or runs poorly, let’s turn our attention to the classic system with a PM 302A breaker, which is equipped with the vast majority of heavy motorcycles. Let's look at the whole process from the very beginning.
On a new motorcycle (if you were lucky enough to buy one), the contacts, as a rule, are skewed and touch at one point. Using small pliers, you need to slightly bend the contact fastenings so that the area of their contact is maximized. It is more convenient to bend the movable contact hammer; it is more pliable.
After this, the contacts should be cleaned with sandpaper, folding it in half and placing it between the contacts. You don't need to remove a lot of metal. Then the sandpaper should be replaced with a soft cloth soaked in clean gasoline, and the remaining abrasive should be thoroughly removed. After completing this operation, it will not be superfluous to lubricate the axis of the moving contact by dropping 1-2 drops of spindle or motor oil onto it. Apply a few drops of the same oil to the felt felt.
Let's install the breaker with the ignition timing machine in place (don't forget about the mark on the machine's leash!). Now let's adjust the gap between the contacts. Let's set the cam to the position where they are maximally open. Having loosened the screw securing the fixed contact, we will rotate the eccentric with a screwdriver, while simultaneously measuring the gap size with a 0.5 mm thick feeler gauge. When the probe begins to enter the gap with slight friction, carefully close the screw.
Turning the crankshaft using the kickstarter, we will find an arrow on the flywheel (for “Urals”) or a “TDC” mark (for “Dneprs”) and set it opposite the mark in the viewing window.
Now you need to turn on the ignition. Let's take an 8x10 wrench and apply it to the steel core of the coil. We will turn the breaker body in the direction of the arrow stamped on its cover until the key touches the core. In this position, lightly tighten the breaker mounting screws so that it can rotate, but with some effort.
Let's take a long thin rod, for example, an old knitting needle, rest one end of it against the breaker flange, and apply light blows to the second with a small hammer or a 19x22 wrench, thereby slowly turning the breaker in the opposite direction. At the moment the contacts open, the key, attracted to the ignition coil, will fall with a melodious ringing. In this position, the breaker mounting screws must be tightened.
It remains to check that the initial ignition timing we have set is correct. To do this, turn the crankshaft until the contacts close, hang the key on the reel again and, turning the crankshaft with light blows of your fist on the kickstarter, slowly bring the arrow on the flywheel closer to the mark on the crankcase. If the key falls when they match, everything was done correctly. If the arrow does not reach the mark, the ignition is early, and the breaker body needs to be turned slightly in the direction of the arrow on its cover. If the key falls after the marks coincide, turn the breaker in the opposite direction.
At first glance, the amount of work seems quite large. But in everyday use, all operations are not required, and besides, by adjusting the ignition once or twice, you will learn to do this in a matter of minutes, and this system will no longer cause you trouble.
Motorcycles Ural and Dnepr
I have ELECTRONIC IGNITION! After the fall, the diesel engine stopped starting! He really stood in traffic police on the street for 2 weeks! I have electronic ignition! no spark! the light rang from the battery to the generator! We changed the coil! It lights up everywhere it needs to! but there is no spark! what to do? Anyone who lives in Moscow and understands electrics can help (it won’t rust after me) write to [email protected] ! The motorcycle is in Mitino!
[Edited 7/22/2003 graff]
[Edited 7/22/2003 graff]
Maybe change the spark plugs first? ;-))
connect the positive wire directly to the coil. (the wire on the left from the ignition cover next to the spark plug) turn on the ground so that the minus goes along the frame. try to kick. and watch the spark on the candles. if there is no spark: 1-check the battery 2-the coil could be damp (throw it out and put another one in) 3-check the gap on the cams (0.6 mm in the open position) 4-change the capacitor (shiny cylinder in the ignition)
5- if all else fails, shoot yourself or buy a Japanese one (because the Urals will break down all the time and without knowledge of how to repair it, it’s better to hang yourself right away so as not to suffer)
Having received a spark, try to connect everything as it was. if the spark is gone 1 - check the fuses 2 - check the operation of the ignition switch (maybe it’s broken) 3 - check the stop engine remote control (right)
4 - if it doesn’t help, rip out all the wiring and assemble it yourself according to the diagram.
I’ll complement Boxer: with a 5 W 12V lamp, first start checking the coil.. turn on the ignition, engine.. look at the breaker contacts, they are open - connect the lamp between them, the lamp should light up.. well, follow the wiring in sequence if it doesn’t light up. if there is voltage on the coil, look at the coil itself, the gaps, the conduit
What the fuck contacts. The guy writes in Russian - electronic ignition.
The ignition is like Stary Oskol, Tyumen or Uktus. Turn on the ignition, check with the light so that the plus goes to the coil and the switch. If it comes, first remove and ring the coil or temporarily switch to another, working one. If it doesn’t help, then the switch has received 3.14 zdets (or the Hall sensor).
No spark causes and solutions.
When there is no spark after an unsuccessful attempt to start the engine, or the spark on the spark plugs suddenly disappears and, of course, the engine does not start, then some novice drivers do not know where to start to get rid of this malfunction. This article will describe the reasons why a spark may be absent or appear every once in a while, and will also discuss methods for simple diagnostics (troubleshooting) of the ignition system.
I have already written about repairing the ignition system and you can read about it in detail in this article. It describes in detail the testing of all components of the ignition system, both the modern contactless electronic and the more ancient contact ignition system.
But this article will describe when there is no spark, the reasons and specific actions to ensure that a spark appears on the spark plugs.
No spark causes and solutions.
- 1. Let's start with the simplest and gradually move on to more complex reasons. The first and most common reason is a discharged battery. Of course, this can be determined without a voltmeter, since a discharged battery will not crank the crankshaft with an electric starter of a car or motorcycle. But many drivers, after an unsuccessful attempt to start with an electric starter, try to start the car with a pusher, hoping that the energy of the discharged battery is not enough for the starter, but is quite enough for the ignition system. In most cases this is not the case.
And if the energy of a discharged battery for a contactless electronic ignition system in most cases is enough to cause a spark and a successful attempt to start the engine from the pusher, then for an older contact system, the energy of a discharged battery will not be enough to cause a spark (especially if the contacts are burnt, and this happens often) . Therefore, in order not to guess and not waste human energy on pushing the car, we simply bring the battery back to normal using a charger. Beginners can read how to properly charge the battery here.
- 2. Another simple and banal reason why there will be no spark on the spark plug is simply a failure of the spark plug or it is simply necessary to clean the spark plug (read how to check and properly clean the spark plug here). Of course, the spark plugs don’t all fail at once, and if one of the spark plugs fails, the four-cylinder engine will simply start to stall. Therefore, this reason is only suitable for single-cylinder motorcycle engines, but still it was worth mentioning, let’s move on.
But before checking and cleaning a non-working spark plug, try swapping the high-voltage wires and if a spark appears on a previously non-working spark plug, then the reason is not in the spark plug, but in the spark plug wire, which should be replaced.
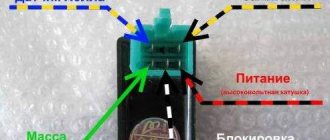
- 3. The third reason for the loss of spark, which often happens on used cars and motorcycles, is there is no voltage at the ignition coil terminal after turning the ignition key. Using a tester set to voltmeter mode (measuring direct current), you should measure at the coil terminals whether a voltage of 12 - 13 volts is supplied to terminal B+ of the coil (see figure) when the ignition switch is turned on. If it doesn’t, then you should check the integrity of the wire going from the lock to the coil (or from the mounting block to the coil - GP wire in Figure 1), and also check whether the terminals are oxidized.
- 4. If voltage comes to terminal B+ of the coil after turning on the ignition switch, but there is still no spark, then you should check the integrity of the wire and the cleanliness of the terminals of the wire coming to the distributor from the coil (the black wire marked with the letter C in Figure 1) and in general check all the wires and terminals of the low-voltage circuit of the ignition system (check the wires marked with the letters G and K, as well as GC and K. It also wouldn’t hurt to check the operation of the ignition switch itself 8 and the ignition switch relay 7, which rarely fail but still fail. And of course, we check the integrity of the fuses responsible for these circuits (in general, I advise beginners to check all the fuses at the very beginning).
- 5. On a contactless electronic ignition system, use a voltmeter to check the presence of a voltage of 12 volts (after turning on the ignition switch) at terminal B+ of the ignition coil, as well as at terminal 4 of the switch and check the integrity of the wire marked with the letters GP in Figure 2. We also check the integrity of the wire and the cleanliness of terminals K of the coil and terminal 1 on the switch and the integrity of the control wire of the gearbox connecting them. We also check the integrity and reliability of the connection (cleanliness of the terminals) with the car body of the black wire marked with the letter H in Figure 2, which connects terminal 2 of the switch to the car body. What can happen on the car due to poor contact of a lot of other wires, I advise you to read this useful article.
- 6. Next, we check the integrity of the wires and the reliability of the connection between terminals 3, 5, and 6 of the switch and the Hall sensor (wires marked with the letters Z, P and BC in Figure 2). If the terminals are securely connected and not oxidized, and the wires are intact, then we check the functionality of the hall sensor itself (read how to do this here). Well, you can find out how to check the functionality of the switch and ignition coil by clicking on the very first link at the beginning of this article, in the article about repairing the ignition system).
- 7. Having checked the low-voltage circuit of the ignition system, as described above, if everything is in order and a spark has not appeared, then we check the high-voltage part of the system. If there is no spark on any spark plug, then first of all we check the central high-voltage wire G (see Fig. 2), connecting ignition coil 5 and distributor 1. The tips of this wire must be clean and must be tightly inserted into the mounting sockets of the distributor cover and the ignition coil . We check the wire itself for integrity using a tester set to ohmmeter mode.
- 8. If there is no spark on only one spark plug out of four, then we check the high-voltage wire of the non-working spark plug (you can swap the wires, as described above, or check the wire of the non-working spark plug using a tester). Also, having removed the distributor cover, we check it for integrity (there should not be even the slightest cracks) and the cleanliness of all contacts inside and outside the cover, and the integrity of the carbon (graphite cylinder) in the center of the cover.
No Spark on Ural Chainsaw
Ignition of the Ural chainsaw
The Ural chainsaw ignition is a fairly common device, but quite reliable in operation. We will discuss how to repair the chainsaw ignition system with our staff a little below. The ignition system of the Ural.2T Electron chainsaw consists of a non-contact magneto of the EM-1 type, an ignition wire, a flywheel, an insulator with an interference suppression device and a spark plug.
Photo-1. Schematic electronic circuit of the magneto.
Magneto electronic circuit
In photo 1 you can see the electronic circuit diagram of the magneto of the Ural chainsaw
:- EM-1.
Photo-2. Design of the EM-1 magneto of the Ural-2T Electron chainsaw.
Magneto suit EM-1 for Ural-2T Electron chainsaw.
The chainsaw magneto consists of a generator coil-1, a control coil-2, a high-voltage transformer-3, a magneto base-4, a VVT. high-voltage terminal-5, an adjustable advance angle hazard-6, an electrical unit-7, a capacitor-8. Semiconductor elements of non-contact magneto EM-1 (thyristor, capacitor and resistor, also 5 diodes) are mounted in the magneto base chamber and filled with a special sealing compound.
Thus, the magneto works as a single unit and if one of the installed parts fails, it cannot be repaired. It is simply thrown out and a new magneto is installed in its place.
We recommend reading articles on this topic on our website https://stroivagon.ru:
Ignition of the Ural chainsaw, operating mechanism of the EM-1 magneto.
The EM-1 magneto ensures that spark formation begins on the spark plug at a chainsaw flywheel speed of 400-600 rpm. Therefore, the magneto is checked for sparking only with the use of an installed starter. The starter rotates the crankshaft of the chainsaw motor. With all this, you should know and take into account when checking that the chainsaw magneto produces a spark at an occupied temperature significantly higher than the temperature of the spark generated by the contact magneto.
READ Chainsaw device Shtil 361
With all this, the spark is difficult to see in the brightest sunlight. You should also know and take into account the fact that the magneto of a chainsaw works normally at a temperature of the magneto body up to 85 degrees. For which the design is designed to exceed the temperature of the body, the magneto can break. Therefore, during operation of the chainsaw , purposefully take breaks in work that ensure cooling of the magneto.
Repair of a Russian chainsaw.
Disassembly and assembly of the Ural chainsaw
. Magneto change.
Repair of ignition of a walk-behind tractor
My blog: VK Group: Triacs: .
Magneto EM-1 is installed in the chainsaw crankcase on two studs and secured with nuts (see photo 2). If the passage when the magneto breaks, it should be replaced with a new one. In all this, the ignition timing is set in this way: against risk - 6 on the magneto is put at risk 6 on the chainsaw crankcase (see photo 2). Spark
in the spark plug, in other words, between its electrodes occurs just when the chainsaw piston does not reach T.M.T. by 3.66 mm.
The occurrence of a spark corresponds to the angle of rotation of the chainsaw crankshaft by 29 degrees to T.M.T., which is actually the ignition timing angle. Therefore, when carrying out other routine repair work and additionally removing the EM-1 magneto, the indicated dangers should always be combined.
READ Husqvarna Doesn't Start Spark Yes
Ignition of the Ural chainsaw, removing the flywheel
The chainsaw flywheel is four-pole and is mounted on the crankshaft of the chainsaw motor.
Photo-3. Four-pole chainsaw flywheel.
The appearance of a four-pole chainsaw flywheel.
It is fixed on the crankshaft with a key and secured with a nut. The ratchet is attached to the flywheel hub and is used to start the engine. Let's look at how you need to remove the flywheel if you set a goal to get to the magneto and repair it. The flywheel can be removed without much expense and simply using a ratchet, but how is this I will show you a little below.
Photo-3.1. Blocking the rotation of the crankshaft.
We block the rotation of the crankshaft.
If you set a goal to remove the flywheel, you need to first unscrew the ratchet. The ratchet rotates together with the crankshaft, so while unscrewing it, you should block the rotation of the crankshaft. We block the rotation of the crankshaft if you are unfamiliar with the installation of the drive clutch.
Photo-4. Insert the washer into the ratchet.
Ratchet Removal Method
Our next step after blocking the crankshaft is to remove the ratchet. Next, insert a regular washer into the ratchet and screw the ratchet back.
Photo-5. We twist the ratchet with the installed washer back.
Inserting a wrench to tighten a ratchet
To tighten the ratchet, we block the rotation of the crankshaft
and use a wrench. Immediately after tightening the ratchet, the flywheel itself is removed from
crankshaft. The flywheel can only be removed using this method, in other words, using a ratchet!
READ Engine for Chainsaw Shtil 180 Video
Removing the flywheel from the crankshaft
We remove the flywheel and proceed to repair the magneto. As I already reported a little above, the magneto cannot be repaired, so it is removed and thrown away. And a new one is installed in its place and the dangers are combined.
Source
Lost spark at BSZ
Captain1977 Mon, 04/28/2008 — 08:38
Udavski, in fact, neither the ignition nor the coil should have died. More likely, when you shorted one of the wires to ground, either the wiring or the fuse in this circuit burned out. I had the same crap yesterday: I pushed the coil coil into its regular place, so the leads of the low winding rested on the crankcase, and after a short drive, obviously, the whole thing overheated, the insulation was pierced, the + 12V wiring from the ignition burned out, and everything died. I took the coil out, reconnected it - everything is OK. In your case: 1. Check the coil. Disconnect her from the switch, stick candles, and run wires from a guaranteed charged battery along her legs. If OK, move on to
2. Everything is the same, only with a switch, respectively, instead of striking, we flash a screwdriver in front of the Hall - like imitating a curtain. If everything is OK, we look for a burnt wire or fuse, or a dead battery. Keep in mind one more thing: if something shorted out somewhere and it burned out, then the insulation of what was nearby, that is, other wires in the harness, could melt.
maxuit, Quote: then most likely the khan to the switch I don’t agree even once! If the switch is dead, then it constantly puts pressure on the coil, then the on-board network sag, but not by the same amount! This means we have a ground fault along the path from the switch to the ignition, or somewhere else, or a dead battery. And the most unlikely option - the gasket between the transducer and the switch body is broken, is a hundred times less common than an honest screw. Another option is that the switch (or rather, the power transducer in it) is broken, then turn it on, don’t turn it on, there will be no reaction. Even if we assume that there was a short circuit in the power supply in the switch, the traces there are thin - they will evaporate in half a second, and that’s all. And in order to guarantee that the ignition/switch will burn out, you must either confuse the plus and minus (which is unrealistic with simple fiddling), or apply a very large voltage to a couple of batteries in series.
Reasons why a motorcycle won't start
Problems with carburetors, causes:
- Lack of fuel in the carburetor.
- Flooding (especially when the engine is hot).
- Clogged faucet sump.
- Illegal supply to the carburetor.
- The carburetor jets are clogged.
- Water getting into gasoline.
- The float needle valve is dirty or leaking fuel.
- The float is leaking.
- The carburetor jet is not tightened properly.
When a motorcycle sits for a long time, it may not start. And they say: the Ural won’t start after winter. It may also have difficulty starting in cold weather. These reasons cannot be avoided, since this is an old motorcycle and everything in it is done according to the old system. There is still a solution to this problem - you just need to dig it thoroughly and then warm it up for at least 15 minutes. And do this in winter from time to time. Then it will start better
Problems with candles. There may be no spark or vice versa.
When there is no spark at the spark plug due to:
- Candle breaking.
- Incorrect marking of the gap between the contacts of the breaker, oiliness or burnt contacts of the breaker.
- Lack of contact at the battery terminals.
- Wire terminals are dirty.
- Ignition coil malfunction.
- Broken low voltage wire.
Many people ask the question: the Ural won’t start, but there is a spark?! Then it’s worth addressing the situation with no or weak compression in the engine:
- No clearance in the valve mechanism.
- Faulty piston rings.
- Looseness in the fit of the valves due to burnout of the plates or the formation of carbon deposits on them.
It is not uncommon to experience interruptions in engine operation, where the main reasons are: Leaning of the mixture:
- Illegal supply to the carburetor.
- The carburetor jets are clogged.
- Water getting into gasoline.
- The float needle valve is dirty or leaking fuel.
- The float is leaking.
- The carburetor jet is not tightened properly.
Also common problems:
- Weak terminal tension on the battery.
- Burnt or incorrect breaker contact gap.
- There is no contact or the capacitor is broken.
Does not start. What to do?
It depends on what the symptoms are and whether they exist.