Ask in the comments. We will definitely answer!
A malfunction of the knock sensor causes the engine control unit (ECU) to no longer detect the detonation process when the fuel mixture is burned in the cylinders. This problem occurs as a result of too weak or, conversely, too strong an outgoing signal. As a result, the “check engine” light on the dashboard lights up, and the car’s behavior changes due to engine operating conditions.
To understand the issue of malfunctions of the knock sensor, it is necessary to understand the principle of its operation and the functions it performs.
How does a knock sensor work?
The operating principle of the unit is based on the piezoelectric effect. The DC signal comes to it from the controller. Inside the sensor there is a special resistor designed to reduce the voltage. After the voltage is reduced by 2 times, it is supplied to the controller again. The electric current at this time already has a variable value. The return signal is transmitted through a circuit that reproduces the reference voltage. This becomes possible due to the fact that the impulse comes in the form of a direct electric current and returns in the form of an alternating current.
The signal is reproduced in the engine during a detonation flash. Its amplitude depends on the detonation power. If the motor operates in normal mode, a 2.5V return signal is sent to the controller. In this case, the controller does not change the operating mode of the motor. If the signal value is different, the ignition timing will change. This is done to partially extinguish detonation. At this moment, the motor switches to safe mode - thanks to the same sensor.
Design and operating principle
Components that make up the DD device:
- mechanism body;
- contact washers;
- disc spring;
- screw for fixing the sensor;
- inertial mass;
- piezoelectric sensing component;
- electrical output equipped with contacts.
Device design
The detonation regulator functions as follows:
- A voltage is generated on the piezoelectric element as a result of exposure to mechanical impulses. This parameter increases due to an increase in the intensity of oscillations.
- As soon as the voltage exceeds the permissible value, the regulator sends a pulse indicating the need to change the ignition timing.
- The controller transforms the mechanical action into a constant impulse. The latter is fed to the microprocessor module, as a result of which the system performs injection optimization. This allows you to set the ignition later.
- Ultimately, the car engine begins to function as efficiently as possible. The power parameter of the power unit allows you to reach the highest level. Accordingly, DD directly affects the control of the fuel injection system.
How to check different types of knock sensors with a multimeter and other methods
Sometimes while driving, a car's gasoline engine begins to make a suspicious metallic knock. Drivers call it "tapping fingers."
This sound is a sign of detonation, a highly undesirable phenomenon that can lead to engine failure and costly repairs.
To prevent this from happening, a knock sensor is installed on the cylinder block. If it breaks, you can check it with your own hands.
How the sensor works
The phenomenon of detonation occurs for various reasons. This includes the use of low octane gasoline, a high compression ratio, and many other factors. What matters is driving in certain gears, the degree of soot, and the presence of certain components in the working mixture.
The knock sensor is an accelerometer that analyzes the mechanical vibrations of the cylinder block and converts them into electrical impulses.
The principle of operation is simple: the device constantly sends signals to the electronic control unit of the power unit. That, in turn, changes the composition of the mixture and the ignition timing depending on these signals.
The result is proper use of resources and engine operation at optimal power.
Appearance and diagram of the knock sensor
How to understand that it is out of order
The product is installed in cars with an electronic control circuit. Diagnosing faults in such machines is simple - if everything works correctly, the sensors on the dashboard remain inactive. The main sign of a malfunctioning knock sensor is the appearance of the inscription “Check engine” (CHECK). It can burn constantly, or it can appear and disappear.
If the sensor breaks down, acceleration performance deteriorates. The car starts, but works worse - it accelerates poorly, vibration occurs at rpm below 1000, power drops and fuel consumption increases, and the amount of smoke from the exhaust increases.
Why is this happening? Sensor malfunctions are related to automotive electronics. The following reasons are possible:
- the signal wire is broken;
- a short to ground has occurred;
- there was a short circuit in the on-board network of any wire of the device;
- the shielding braid is damaged;
- the power unit control unit has failed;
- something is damaged inside the sensor itself.
Checking the knock sensor
Since breakdowns occur for various reasons, you will have to check several elements of the system. Inspect the condition of the sensor wires, check the harness sockets and sensor plugs. Evaluate the reliability of their connections.
If everything is in order here, check the contacts of the socket. Found damaged components? Replace them. It is also recommended to examine the condition of the tourniquet. Turn off the ignition, disconnect the harness from the sensor and check it with an ohmmeter.
This way you will know if the chain is intact.
Sometimes the problem lies in the condition of the shielding braid. In this case, we proceed as follows.
- We look to see if the harness sockets and plugs are securely connected;
- We study each of their components;
- We check whether the shielding braid is intact.
If the cause of the malfunction is a short to ground, you must proceed using another method:
- We disconnect the entire block from the harness, along with the knock sensor;
- We check the integrity of the chain, look for heavily worn places;
- Turn off the ignition and, using an ohmmeter, examine the place where the engine mass is connected to the harness circuit.
We find and dismantle the sensor
Checking parts for one or two wires using a multimeter
The first thing to do is to find out what resistance is typical for a properly functioning sensor in a particular car. The figure varies greatly among different manufacturers.
We recommend: Types of car signals, criteria and nuances of choice
This is interesting: resistance indicators can be the most unexpected. So, in VAZ cars with injection engines it is almost impossible to measure it because the indicators are too high. In Nissan and Subaru the figures are about 550 kOhm, in Hyundai - about 5 MOhm (megaohm).
To carry out the tests, you will need a multimeter, and a fairly sensitive one, as well as a socket wrench of size “13” or “22”, depending on the size of the installed sensor.
To test resistance, switch the tool to kOhm resistance mode and attach it to the probe.
If a two-pin sensor is installed in the car, the connection is made to the terminals; in the case of a single-contact model - to the contact and the body.
Now lightly tap the sensor with a metal object - a screwdriver or bolt. Pay attention to the multimeter readings. If there are deviations from the values specified in the instructions, a breakdown has occurred.
It is recommended to check whether there is voltage at the electrical ends. Disconnect the electrical connector of the sensor and remove it from the engine. Switch the multimeter to millivolts and connect the “+” probe to the signal pin. The “—” probe must be connected to the sensor ground. This part is easy to recognize - it is a hole through which the mounting bolt to the motor passes.
Hold the sensor in your palm and lightly tap it on a surface. The result should be a voltage - typically between 30 and 40 mV. If no potential difference occurs, then the sensor has failed.
There are no particular differences in testing for broadband and resonant sensors.
We connect the sensor to the multimeter and knock it on a hard object
Diagnostics with a dial tester or voltmeter
- In addition to a multimeter, you can use a pointer tester - the actions are similar to working with a multimeter.
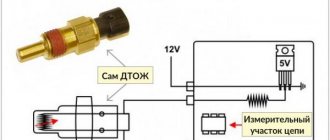
- There is another way. With the engine idling, connect an AC voltmeter to the sensor. Tap the knock control component with a hard, non-metallic object. If the voltmeter shows that the signal amplitude from the device is below 0.1 V, the device is faulty.
Repair or replacement?
You decide. The cost of the product depends on the car model and the manufacturer of the component - for a replacement you will need to pay an amount approximately equal to its price. You can change the device yourself; for this you will need a room with a pit. Self-repair is also possible: if you are well versed in cars, it will take no more than an hour.
Checking the knock sensor is an easy task that doesn't require expensive tools. Of course, a computer check at a service station will be more accurate, but if you don’t want to spend money, you can do it yourself.
Where is the sensor located?
To prevent detonation, a controller based on a piezoelectric element is mounted between the second and third cylinders of the block. This placement of the device allows for the most accurate debugging of the functioning of all cylinders. To understand where the DD is located, you need to refer to the service manual. But usually it is located between the indicated cylinders, since this place is the hottest in the engine compartment. When an engine begins to detonate, this process begins in the combustion chamber.
The DD is always installed on a flat surface to prevent possible distortion of sound waves or the impact of acoustic resistance. The regulator body is fixed to the cylinder block using a pin connection. This guarantees maximum adherence to the installation site. The controller itself can be found just below the intake manifold.
Replacing the sensor
Although the impact of the knock sensor on engine operation is not actively expressed, if it breaks down, measures must be taken to avoid more serious problems. It cannot be repaired, so if it fails it must be replaced. The main problem is getting to it, since the sensor is often located in a difficult to access place, below or behind the block, which requires removing the protection.
Directly replacing the device is very simple, you need to disconnect the negative battery and the contact chip. Depending on the design, the mounting bolt or the sensor itself is unscrewed, then a new one is screwed in and connected to the wiring. When working, you need to pay attention to the integrity of the wires and insulation, clean the contacts from plaque, otherwise the new part will not work correctly.
Signs of trouble
If the meter begins to work incorrectly, the following “symptoms” may indicate this:
- as a result of poor-quality formation of a combustible mixture, the power unit overheats, this happens quite quickly;
- The engine power and throttle response are significantly reduced;
- in the operation of the internal combustion engine, glow ignition occurs;
- acceleration parameters of the vehicle deteriorate;
- fuel consumption increases;
- Significant carbon deposits appear on the spark plugs.
The World of Matizov channel spoke in detail about the problems with the operation of such sensors.
Diagnostics
Before checking the knock sensor, you need to know exactly the normal resistance value of the controller; it depends on the make of the vehicle.
Before using a multimeter, you need to visually check the quality of the contacts, as well as the electrical circuit itself for possible damage. The block must be intact; defects on the conductors are not allowed. If they are present, the device will not function correctly.
The regulator diagnostic procedure is performed as follows:
- The multimeter is being prepared; it must be set to operating mode with a range of thousandths of a volt (up to 200 mV).
- The contacts on the connection block are diagnosed after disconnecting the regulator. The positive probe of the tester is connected to the control output, and the negative probe is connected to the ground of the device being tested. The use of twisted cables or worn chains as a conductor is not allowed. It is desirable that the length of the probe be minimal.
- The controller connected to the measuring device is clamped in the hand; the essence of the test is to determine the voltage. To influence the regulator readings, you need to hit the surface or any object several times without much effort. This will allow the tester to determine the absence or presence of voltage. Ideally, the readings obtained will be around 40-150 mV. If, as a result of diagnostics, there is no potential difference, then the controller must be changed.
Disconnecting the contacts from the detonation device on the engine
Diagnostics of the main regulator connector for integrity
Checking the sensor using a tester
Features of V-shaped internal combustion engines
In the event of an error on one of the knock sensors, their connectors must be swapped. If the sensors are difficult to access, study the electrical diagram. It is likely that the wires from the sensors come to a common connector. By disconnecting the connector, you can fool the engine ECU by installing appropriate jumpers between male and female.
Clear errors from the ECM memory, start and warm up the engine. Perform a test drive to see if the DTC returns (the Check Engine light will illuminate on the dashboard).
If the error from Bank 1 changes to Bank 2 and vice versa, it means that there are no problems with the wiring from the meter to the control unit, but the fault is in the sensor itself. If the error persists for the same cylinder head, you should check the wiring for a break. To do this, use a multimeter in ohmmeter mode. Connect one of the probes to the connector wire on the sensor side, and the second to its counterpart coming to the ECU. Check to see if the signal wire is shorted to ground. To test, connect one of the probes to the signal terminal of the sensor connector, and touch the battery ground terminal with the other. The resistance of the open wire must be greater than 20 mOhm.
Determining a fault using a multimeter
You can check the functionality of the knock sensor with a multimeter or any other tester that has a voltmeter. To do this, you should follow the instructions below.
- Remove the sensor from the car.
- Connect the probes of the device to the terminals.
- Apply small blows to the working part of the sensor with a metal object.
- Check the instrument readings. If voltage does not appear at the sensor terminals, it is unfit for further use.
Part of the car has a single-contact resonant sensor. In this case, one of the contacts should be connected to its body.
How does a knock sensor work?
Car engines can use one of two types of knock sensors: resonant and broadband. But since the first type is already outdated and is rare, we will describe the operation of broadband sensors (WS).
The design of a broadband DD is based on a piezoelectric element, which, when subjected to mechanical action (that is, during an explosion, which, in essence, is detonation), supplies a current with a certain voltage to the electronic control unit. The sensor is configured to perceive sound waves in the range from 6 Hz to 15 kHz. The design of the sensor also includes a weighting agent, which enhances the mechanical effect on it by increasing the force, that is, it increases the sound amplitude.
The voltage supplied by the sensor to the ECU through the connector terminals is processed electronically and then a conclusion is made whether there is detonation in the engine, and accordingly, whether the ignition timing needs to be adjusted, which will help eliminate it. That is, the sensor in this case is only a “microphone”.
We recommend: DIY windshield heating
Operating principle of DD
The operating principle of most knock sensors is based on the use of the piezoelectric effect. The working element of the meter has the ability to form a potential difference when exposed to external forces. The DD device of different designs is shown in the image below.
The knock sensor is designed to be sensitive to external influences. Thanks to this, it detects the slightest change in the operation of the motor. Detonation is always accompanied by vibration, which the DD picks up.
What is the knock sensor responsible for and what does it affect?
The part is installed on cars with engines running on gasoline. This is one of the main links of the management system. The purpose of the sensor is to control the level of detonation. The use of the component allows you to significantly save fuel, while the power unit begins to operate at full capacity.
Etonation is the pulse of electricity that is created during ignition. If there had been no detonation, the car would have been impossible to start.
In carburetor engines, to prevent detonation, the distributor is turned by hand, which somewhat slows down the ignition process. In modern motors, manual adjustment is not possible, since the electronic system is responsible for this. The control sensor is set to a certain range and operates on the basis of the piezoelectric effect.
The device controls the engine starting system and is responsible for its correct operation. The components of the mechanism are:
- vibration plate;
- electrical component - like a piezo;
- control wire;
- winding.
Effect of detonation on the system
The detonated mixture accelerates the spreading flame, instantly accelerating it to a speed of 2500 m/sec. This is incomparably higher than the flame speed of clock combustion, the value of which does not exceed 30 m/sec.
The walls of the cylinder chamber are the first to receive the shock of the wave. However, they are unable to neutralize the full power of the wave, the energy of which goes beyond the cylinder block, leaving a destructive trail behind it. Nearby structural elements gradually extinguish this energy, taking on an increasingly weakening blast wave.
There are knocks, noises and an increase in temperature in the engine. It is subjected to repeated impact deformation and overheating. Components and parts located in close proximity also suffer, their structure becomes loose, and they become covered with a layer of soot, which ultimately leads to accelerated wear.
Knock sensor: description, types, device, principle of operation
Detonation (detonation combustion) is a deviation from the norm in engine operation, expressed in the explosive nature of ignition of the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders.
Normally, the flame front propagates at a speed of 30 m/s, while during detonation the speed can reach 2000 m/s.
This phenomenon is undesirable, since due to the impact on the cylinders, pistons, cylinder head and due to the very high speed of flame propagation, it can cause serious damage after 4-6 thousand kilometers, and sometimes much earlier.
So, during detonation, the gas distribution mechanism and the cylinder-piston group are the first to be hit. To prevent this, a special sensor is used.
Types of sensors
There are two types of knock sensors:
- Broadband.
- Resonant.
The most common are broadband knock sensors, the design and principle of operation of which were described above. As a rule, they have a round shape with a hole in the middle for attachment to the block.
Resonant ones are similar to oil pressure sensors with mounting in the form of a threaded fitting. They are tuned not to the level of vibration, but to the frequency of micro-explosions in the combustion chamber. If they are detected, an electrical signal is transmitted to the controller. Each engine has its own micro-explosion frequency, which largely depends on the diameter of the pistons.
What is detonation combustion and its consequences
Engine detonation is an uncontrolled combustion of the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders, leading to a “mini-explosion”.
During normal fuel combustion, the flame propagation speed is about 30 m/s, but during detonation it increases significantly and can already reach 2,000 m/s.
Such loads on the cylinders and piston group can lead to serious damage after only 5-6 thousand kilometers. To prevent and control this phenomenon, a knock sensor is used.
Normal fuel combustion and combustion with detonation
What determines the occurrence of detonation?
The appearance of detonation combustion is often based on three main factors:
- Gasoline quality and octane number. The higher the octane number, the greater its resistance to detonation.
- Design features of the engine, which are expressed in the geometry of the combustion chamber, the compression ratio of the air-fuel mixture, the position of the spark plugs, etc.
- Motor operating conditions. In this case, the influence is exerted by the current load on the engine, carbon deposits and the degree of wear of the engine as a whole.
What is a knock sensor used for?
In carburetor engines, to prevent detonation, the distributor is manually turned, which slightly delays the ignition timing. In modern gasoline units, it is impossible to manually adjust the advance angle, since electronics are responsible for this.
In order to prevent detonation between the second and third cylinders, a sensor is provided on the block, used as a control device operating on the basis of the piezoelectric effect. To avoid false signals, it is configured to perceive noise in the range of 25-75 Hz.
The middle position of the sensor on the block allows for high-precision debugging of the operation of all cylinders. The location for it is determined by the dislocation of the most heated combustion chamber, from which the spread of detonation combustion begins. Whether the engine is transverse or longitudinal, the sensor is installed slightly below the intake manifold and operates as follows:
- mechanical impulses create a voltage on the piezoelectric element, which increases as the intensity of vibrations increases;
- when the voltage exceeds a safe threshold, the device sends a signal to adjust the ignition timing;
- the sensor transforms the mechanical effect into a constant electrical signal sent to the main control unit, after which the system optimizes injection and ensures later ignition;
- As a result, the power plant operates more economically, and the power reaches its intended maximum.
Design and principle of operation of the knock sensor
As mentioned above, the sensor is used to prevent detonation by changing the ignition timing and returning the system to controlled combustion of the mixture. It is used on injection engines.
During detonation combustion, strong vibration is transmitted to the engine. The sensor is designed in such a way that it picks up these vibrations and converts them into an electrical impulse.
Its main elements include:
- piezoceramic sensing element;
- steel weight;
- control resistor;
- insulator.
Inside the case, a piezoceramic element is connected to wires leading to contacts and a steel weight. An adjustment resistor is located at the output. When the weight vibrates, it acts on the piezoelectric element, thereby increasing the electrical impulse.
The sensor is installed on the engine block housing. It is usually located between the second and third cylinders. Since the engine has its own operating level of vibration, it begins to operate in the noise range of 30-75 Hz.
This position of the sensor allows you to more accurately adjust the operation of all cylinders. It is also placed in the area where detonation is most likely to spread. The operation of the knock sensor includes the following steps:
- Mechanical vibrations create an electrical voltage on the piezoelectric element, which increases as they increase.
- When the voltage reaches a threshold level, the sensor sends a signal about the necessary adjustment of the ignition timing.
- The engine control unit optimizes fuel supply and makes ignition earlier.
- As a result, the engine returns to normal operation with controlled combustion of the mixture.
We recommend: Restoring the panel after airbag deployment
Knock sensor operation
- During this time, the knock sensor is called upon to transmit signals about the occurrence and strength of detonation.
- There are two groups of knock sensors:
- — resonant-detonation
- - broadband
- The components of the device are: vibration plate, piezo element, signal wire and braid.
The dimensions of the device do not exceed the size of a matchbox. Always placed on the engine housing. Installed only in injection engines.
It is equipped with a sensitive piezoelectric element (most often a plate), on which voltage occurs at the moment of detonation. It varies depending on the amplitude and frequency of the blast wave.
Constantly changing wave characteristics lead to voltage fluctuations on the plate. All information, in a continuous stream, is transmitted to the on-board computer ECU, which constantly analyzes them.
When the permissible detonation threshold is reached, the ECU begins adjusting the ignition parameters, reducing the ignition angle.
How to recognize knock sensor malfunctions
On all cars, the coordinated interaction of systems and the uninterrupted operation of units and individual parts are ensured by many sensors. They are built into all elements included in the overall electronic monitoring and control system of the on-board computer.
The malfunction of these devices is determined during diagnostic procedures using professional equipment of service centers.
However, this does not deprive you of the obligation to obtain a minimum understanding of the operation of the components and assemblies of your car.
This knowledge will help you respond in a timely manner to various malfunctions, understand the essence and location of the problem, thereby ensuring road safety for yourself and other road users.
- The reasons for failure may be:
- - damage to the sensor itself
- - problems with wiring
- — breakage of braid or signal wire
- — malfunction of the engine control unit
- When the knock sensor stops functioning normally or fails altogether, the driver can feel it by several signs:
- — poor acceleration of the car;
- — unstable idle speed;
- — a characteristic noise is heard in the engines (car enthusiasts say “knock fingers”);
- — black smoke appears in the exhaust gases;
- - more fuel is consumed;
— “Check Engine” is displayed on the dashboard. But if there is no open circuit and the sensor is faulty, the check will not pop out.
The effect of a faulty knock sensor on individual processes
A huge danger lies in the fact that even a complete breakdown of the sensor does not cause the engine to stop. It continues to work, but according to distorted parameters, causing irreparable damage to the entire structure. Parts quickly wear out, lines and sensitive elements become covered with soot, and many parts involved in the process fail.
As soon as you have any suspicions, check the functionality of the sensor.
Checking the serviceability of the knock sensor
Using sensors from VAZ models as an example, let’s consider the process algorithm.
- You can get to the installation site of the device from below, so lift the car onto the inspection pit platform. Find the sensor, unscrew the fastening to the cylinder, remove it from the stud and remove it from under the module.
- Disconnect the wires from the car by pressing the latch.
- To begin with, arrange a visual inspection of the signal wire and eliminate breaks (if any). Then check the shielding braid and connect the broken sections. Finally, test the socket for the presence of current in it and the strength of its fastening.
- Connect to the voltmeter, observing polarity.
- Detonation can be simulated by lightly tapping the sensor body. Voltage surges should be recorded on the meters. If the arrow does not respond to tapping, it means the sensor is broken.
- Additionally, measure the resistance; it should be infinitely high if the sensor is working properly.
- Based on the test results, make a decision to replace or restore the sensor. After which, we put it back in place, connecting it to the stud, screwing in the nut and connecting the wires.
- Take the choice of a new sensor seriously. Remember that this is an important part responsible for the durability of your car's engine. Choose a high-quality manufacturer brand that suits your car.
- In foreign models, the sensor is placed in the engine cooling tract and filled with this liquid. Before dismantling, the coolant must be drained. Only after this is it unscrewed from its seat and the battery is disconnected.
- Make sure the engine is cold enough. Connect the battery.
- Screw the new part, the threaded part, into its standard place. Do not overdo it by screwing in as you may damage the sensor.
- Fill in the missing fluid and turn on the ignition to check for possible leaks.
Is detonation really that dangerous and what causes it?
Ideally, the fuel mixture begins to ignite even before the piston reaches its uppermost position at an ignition timing angle of 2-3°, and the final stage of ignition occurs at the moment when the piston begins its return movement, past top dead center. Detonation is characterized by premature spontaneous combustion of the mixture already in the middle of the compression stroke, even before a spark occurs between the electrodes on the spark plug. This puts a powerful force on the piston, causing the power plant to lose power and increasing gas mileage.
In cases of small-volume internal combustion engines with relatively high power and significant torque, detonation is detected at low speeds and soon disappears. In forced engines, it can occur under noticeable loads at high speeds and cause damage to the engine in literally a matter of seconds.
Detonation is explained by a number of factors, which include:
- octane number does not match the recommended one;
- features of the engine design (compression amount, position of spark plugs, geometry of the combustion chamber and piston bottom, presence of blower, etc.);
- operating conditions (ignition timing, loads, combustion chamber condition, etc.).
The nature and cause of the detonation phenomenon
The optimal combustion mode in a gasoline engine directly depends on the octane number of the fuel and the ignition timing. If at least one of the conditions is not met, detonation combustion occurs, leading to serious problems and even breakdowns.
Engine detonation is a phenomenon where the gasoline in the cylinder ignites on its own before the spark plug produces a spark and thus the fuel-air mixture ignites spontaneously ahead of time while the piston is still moving upward. This leads to melting or burning out of the piston group, failure of the valves, and this is an expensive overhaul of the engine. There may be several reasons why an engine knocks:
- Poor quality gasoline with a reduced octane number.
- Problems during engine operation - changes in compression ratio, faulty spark plugs, broken ignition timing, carbon deposits on spark plugs, unsatisfactory quality of the fuel-air mixture.
Why does detonation occur?
Here we can distinguish three main reasons due to which the engine begins to operate unstably:
- octane number of fuel: the higher it is, the less likely it is for this unpleasant phenomenon to occur (fuel quality is also important);
- design features of the engine: units with a high compression ratio are more prone to detonation, and therefore they must use fuel with an octane rating no less than that specified in the instructions;
- engine operating conditions: incorrectly selected gear, excessive load on the engine, incorrect composition of the working mixture - all this also leads to detonation.
Voltage measurement at idle
The performance of the motor can be determined by measuring the voltage at its contacts with the engine running at idle speed. The table below shows approximate voltage values that can be used to identify a malfunction of the knock sensor.
Table - Approximate voltage values
| Voltage, V | Sensor status |
| 0-0.01 | Unusable, voltage too low |
| 0.2-4.5 | Knock meter is OK |
| Over 5 | Sensor broken, voltage too high |