Almost any modern vehicle in its design includes the presence of such an element as a rear stabilizer. If we talk about the front support unit, then it is present in all cars. Manufacturers install this device in order to significantly protect the car from tipping over when cornering and in case of high-speed maneuvering. Of course, not every car enthusiast has an idea of what a stability stabilizer is, on what principle the mechanism works, and what it is generally used for. That is why this detail should be considered in more detail, as well as focusing on the key points and the most important nuances.
Operating principle of the support mechanism
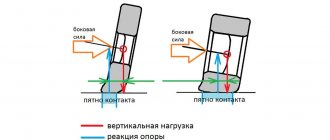
First of all, it is necessary to talk about the immediate tasks of this structural element. In particular, in a car, the anti-roll bar redistributes the load between the present suspension components. Every motorist has the idea that the moment you enter a turn, the car begins to roll. If the body is tilted excessively to the side, the car may even roll over. That is why manufacturers have provided for the installation of stabilizers. The main working element here is the rod, which rotates during the process, creating the necessary tension. In this case, when the body is aligned with the road, one support post is moved upward, and the other is pulled down. Also, this operating principle does not allow the driver and passengers to experience excessive loads when turning and making sharp maneuvers.
How it works
First, it’s worth taking a look at the principle of operation of the element. This will largely make it clear the essence of the device and its role in the suspension of a vehicle.
The main task of the SPU is to redistribute the resulting load between the elastic components of the vehicle suspension structure. You all know that when entering a turn, the car begins to roll. It is at this moment that the stabilizer begins to perform its functions. The racks begin to gradually shift, moving in opposite directions. That is, one goes down, and the other, on the contrary, begins to rise. There is also a middle structural element called the core. At this moment he is spinning.
What does this give in practice and how does the behavior of the car change? From the side where the car began to collapse, the stabilizer helps raise the body. On the other hand, the opposite effect occurs, that is, the body begins to lower.
The stronger the tilt, the stronger the resistance from the stabilizer. This aligns the car relative to the horizontal plane of the road surface. This reduces roll and improves traction.
What does the rear stabilizer consist of?
As a rule, the rear support mechanisms, as well as the front stabilizers mounted on modern cars, have a fairly simple design, consisting of the following components:
- durable steel pipe or special metal rod;
- two rods or racks;
- fastening components including clamps and rubber bushings.
It is noteworthy that the rod itself is made in a special U-shape in order to resist loads as effectively as possible, and in addition, not to come into contact with other parts of the car.
Kernel
First of all, we need to talk about the rod, since it is the main component of the mechanism. In particular, we are talking about an elastic transverse strut, which is made of spring steel. This element is located across the car body, both in the case of the front and rear support units. It is necessary to understand that for stability and resistance to heavy loads, this product has a rather complex shape, for the simple reason that at the bottom of any modern car there are a lot of other elements, whose location is taken into account by manufacturers when they strengthen the car’s suspension system.
Traction
In this case, we are talking about a structural element that is used to connect the ends of the rod with the arms or shock absorbers of the car’s suspension struts. If we consider the rods or stabilizer struts, then externally they look like standard rods with a length of 5 to 20 centimeters. At the edges, these elements have special hinges for fastening, which are protected by appropriate anthers. It is noteworthy that it is the hinges that provide the mobility of the fastening, which is why the load is distributed evenly. During movement, impressive pressure is created on these components, which is why the hinges collapse over time. In practice, rods most often fail after a mileage of 30-50 thousand kilometers, after which they are completely replaced, since the products cannot be repaired.
Fasteners
As a rule, the anti-roll bar is mounted in a modern car using rubber bushings and special clamps. Typically, the mounting of the support unit is carried out directly to the vehicle body in two opposite places under the bottom of the car. Rubber bushings are used here for a reason. They allow the rod to rotate with minimal resistance. These elements, like the traction rods, must be replaced periodically, as they fail quite quickly, especially on models that are often used in off-road conditions.
Everything ingenious is simple
Despite all the responsibility of the anti-roll bar, its design is outrageously simple.
In essence, it is a metal rod of complex shape that connects opposite wheels on an axle. The stabilizer is attached to the wheels (more precisely, to the suspension arms) by rods, or struts, also called links; in its middle part it is attached to the body elements using special bushings that allow it to twist like a torsion bar, preventing excessive body roll.
Available types of stabilizers
Depending on the mounting of the support unit, these products can be divided into two types, namely front and rear anti-roll bars. Some vehicle models do not have a rear strut brace. If we talk about the front stabilizer, then it is always present here, since the safety of the driver and passengers in the car largely depends on it.
Also worth highlighting separately is the active anti-roll bar. This element in the car is controllable for the simple reason that it is capable of changing its own rigidity depending on the type of road surface on which the car is moving, as well as taking into account the nature of the movement and the maneuvers performed. Such cross members are a way to provide maximum rigidity when entering a sharp turn. Medium hardness is intended for soft dirt roads. If a car with an active stabilizer is driven off-road, the function is usually turned off completely or operates at minimum settings.
The stiffness of the anti-roll bar provided by the manufacturer in modern cars is changed by several available methods, namely:
- use of hydraulic cylinders instead of standard racks;
- installation of an active drive on a vehicle;
- the use of hydraulic cylinders instead of rubber bushings.
Provided that a hydraulic system is installed on the vehicle, the hydraulic drive is responsible for the rigidity of the support unit.
It is noteworthy that the design of the hydraulic drive may differ depending on which hydraulic system is installed on the vehicle. It is worth noting that modern car models are often equipped with different anti-roll bars, while a more complex and reliable mechanism is mounted on the front of the car, while a simpler version of the support unit is mounted at the rear. This is due to the fact that the front wheel axle bears the main load when moving.
How does the anti-roll bar work?
When the car turns, one rack rises and the second lowers, that is, they move in opposite directions, the middle part of the stabilizer, which is called the rod, begins to twist.
As a result, on the side where the car “listened” to its side, the stabilizer raises the body, and on the opposite side, it lowers the body. The greater the tilt, the greater the resistance of the stabilizer. Then the car is leveled, the roll during turning is reduced and the quality of wheel grip on the road improves.
If you want to understand the operation of the anti-roll bar in more detail, this information will be useful to you.
To create vehicle roll resistance, a torsion bar is used, which is mounted in the wheel hub assembly.
The torsion bar works to twist, creating resistance to the vehicle's roll. The torsion bar is attached to the hub assembly of the left wheel, then passes in the direction of travel to the hinge attachment to the body, then in the lateral direction to the opposite side of the car, where it is mounted in a mirror image similar to the first side. The torsion bar sections running in the direction of movement act as levers when the suspension operates in the vertical direction. In the absence of roll, both segments rotate at the same angle, the torsion bar does not twist and rotates in the attachment points to the body as a whole. When the car rolls, the left and right sections of the torsion bar rotate at different angles, twisting the torsion bar and creating an elastic moment that resists the roll. On dependent rear suspensions this is often absent, instead the trailing arms are attached to the beam by a rigid connection capable of transmitting torque. Thus, the entire beam assembly with trailing arms acts as a torsion bar.
On McPherson-type front suspensions, “lever” sections of the torsion bar are often used as one of the 2 lower suspension arms, also transmitting longitudinal (in the direction of travel) forces from the hub to the body.
Stabilizers can be installed either on both axles, or only on one (usually the front).
Main disadvantages of the mechanism
Despite the fact that this device, at first glance, gives only a positive effect to the car, upon a more detailed review, a number of shortcomings can be identified. In particular, due to the presence of anti-roll bars, the travel of the suspension itself as a whole is noticeably reduced. This negatively affects the vehicle's maneuverability. Very often, due to the presence of anti-roll bars, SUVs with high ground clearance simply cannot cope with a significant obstacle. It should also be noted that such elements when traveling off-road can contribute to the hanging of the wheel, which loses contact with the surface and is completely inactive when trying to move off. Today, automobile manufacturers have solved this problem by installing an active suspension system or by installing an adaptive anti-roll bar, which can change its stiffness depending on the type of surface and the condition of the road surface.
Disadvantages and tuning
There are practically no shortcomings, unless you consider an SUV. The stabilizer greatly reduces the suspension travel, which is extremely important for SUVs. To solve such problems, there are active stabilizers. Passenger cars benefit on all fronts from this design.
A simple tuning is to install an STC if your car did not have one, the benefits of which you will immediately feel. If you are thinking about installing a thicker and stiffer rod, then it is better to reconsider.
Due to the strong compression of the rigid stabilizer, you will turn your independent suspension into a dependent one, thereby completely killing the car's handling. The manufacturer has calculated everything for you.
The main advantages of the stabilizer
Without a doubt, these design elements have some disadvantages, which appear mainly during off-road travel. However, the situation is such that most motorists simply do not go beyond the city limits, which is why they do not notice certain disadvantages, but, in turn, highlight a number of advantages of such support units. In particular, a car with anti-roll bars holds the road more confidently. At high speeds and when turning, the body does not sway. If you have this element in your car, you don’t have to worry about tipping over and can take turns at a higher speed. Due to anti-roll bars, during sudden lane changes and cornering, the driver and passengers do not experience excessive loads inside the car.
Conclusion
The rear or front anti-roll bar itself is a fairly simple mechanism that performs quite complex tasks. The presence of this element is reflected in almost all aspects associated with traveling by car. The presence of a stabilizer affects the comfort in the vehicle interior and also guarantees a high level of safety. However, we should not forget that such elements, despite all their strength, do not last forever and periodically it is necessary to carry out preventive maintenance by changing consumables, including stabilizer struts, as well as bushings. The rod itself is a reliable and strong component that can fail only under excessive and intense everyday loads, and this happens after a run of 100 - 120 thousand kilometers. Author: Oleg Mokrov