SR2015 › Blog › What is the difference between a two-stroke engine and a four-stroke engine?
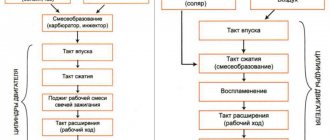
A two-stroke engine, an internal combustion engine in which the operating cycle is completed in one revolution of the crankshaft, i.e., filling the cylinder with a combustible mixture (or air), compression and combustion, as well as expansion and release of gases occur in two strokes of the piston.
Disadvantages of two-stroke engines: The disadvantage is the high thermal load of the piston group, which reduces the reliability of the engine, and the difficulty of purging.
Advantages of two-stroke engines: In two-stroke engines, all operating cycles (processes of inlet of the fuel mixture, exhaust gases, purge) occur within one crankshaft revolution in two main strokes. Engines of this type do not have valves (as in four-stroke internal combustion engines); their role is played by a piston, which, when moving, closes the intake, exhaust and purge windows. Therefore, they are simpler in design. The power of a two-stroke engine with the same cylinder dimensions and shaft speed is theoretically twice that of a four-stroke engine due to the greater number of operating cycles. However, incomplete use of the piston stroke for expansion, poorer release of the cylinder from residual gases and the expenditure of part of the generated power on purging lead to an increase in power by only 60...70%.
A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine whose operating cycle consists of four strokes (piston strokes) occurring in two revolutions of the engine crankshaft. During its first revolution, intake and compression occur. The intake of the working mixture (for a carburetor engine or spark-ignition engine) or air (for a diesel engine) occurs when the piston moves from top dead center (TDC) to bottom dead center (BDC). Compression of the working mixture or air is carried out when the piston moves from the bottom. m. t. to v. m.t. During the second revolution of the crankshaft, a power stroke occurs (the piston moves in the same way as during intake) and an exhaust stroke (the piston moves in the same way as during compression). The working stroke (combustion - expansion) is carried out under the influence of pressure on the piston of fuel combustion products. Release is the last beat; during it, spent combustion products are removed from the engine cylinder.
Disadvantages of four-stroke engines: All idle strokes (intake, compression, exhaust) are accomplished by the kinetic energy stored by the crankshaft and associated parts during the power stroke, during which the chemical energy of the fuel is converted into mechanical energy of the moving parts of the engine. Since combustion occurs in fractions of a second, it is accompanied by a rapid increase in the load on the cylinder cover (head), piston and other engine parts. The presence of such a load inevitably leads to the need to increase the mass of moving parts (to increase strength), which in turn is accompanied by an increase in inertial loads on moving parts. They are inferior in power to two-stroke ones. Minor disadvantages that are more than offset by advantages include work on adjusting the thermal clearance of the valves and the acceleration time of the scooter from a standstill, which is slightly longer than that of two-stroke mopeds.
Advantages of four-stroke engines: - fuel efficiency; -reliability; - ease of maintenance; -the four-stroke engine is quieter and more stable.
Unlike a two-stroke engine, in which the crankshaft, crankshaft bearings, compression rings, piston, piston pin and cylinder are lubricated by adding oil to the fuel; The crankshaft of a four-stroke engine is in an oil bath. Thanks to this, you do not need to mix gasoline with oil or add oil to a special tank (on models of two-stroke scooters with a separate lubrication system).
Also, significantly less carbon deposits form on the piston mirror and the walls of the muffler and exhaust pipe. In addition, in a 2-stroke engine, the fuel mixture is released into the exhaust pipe, which is explained by its design.
Source
Features and device
This type of power unit has become the basis for various types of devices and equipment due to its simplicity and reliability. The operating cycle of such a motor has only two strokes, unlike the 4-stroke engines that are installed on most cars. This pair of bars is compression and expansion. The reader may quite rightly wonder: where does the inlet and outlet of the working mixture go? The fact is that they are combined with the compression and expansion mentioned above.
Unlike a 4-stroke engine, in a 2-stroke engine the entire working cycle occurs in just one revolution of the crankshaft. This makes it possible to increase the power quality of the engine by 1.5 times or more with an equivalent displacement. However, this leads to a decrease in efficiency, otherwise all self-propelled mechanisms without exception would be equipped with such power units. But in shipbuilding they have found the widest application. A single-cylinder two-stroke engine is also an integral component of every small-engine scooter that roams our roads with might and main.
Another important feature of such mechanisms is their tendency to overheat. This is due to the release of large amounts of heat during operation. To solve this problem, forced cooling may be required. But there are also advantages to such a motor: the work of the piston is limited to 2 strokes, which means that it makes half as many movements. Due to this, wear on key parts of the power unit is reduced.
slavarespekt › Blog › Four-stroke engine
The four-stroke engine is the most common type of internal combustion engine in a modern passenger car.
The internal combustion engine was supposed to be an alternative to the industrial steam engine, but enthusiastic inventors immediately sensed its potential. They managed to find a way to increase engine power without increasing its weight. Nikolaus Otto played a key role in this, creating the first four-stroke engine in history.
History of Otto engine development
The motor, developed by the inventor Alphonse Beau de Rocha and embodied in metal by the German Nikolaus Otto in 1867, was the height of perfection at that time. It was cheap to operate, compact and did not require constant monitoring. The engine operated according to a special algorithm, widely known today as the “Otto cycle”. In 1875, Otto's company was producing more than 600 engines per year. It was Gottlieb Daimler and his fellow engineers who brought Nikolaus Otto's attention to the advantages of the four-stroke engine.
Otto’s team included a talented engineer named Gottlieb Daimler, who was fired up with the idea of building a car. Nikolaus Otto did not consider it necessary to improve the existing engine, and Daimler, who understood how the engine could be used in the design of a car, had to leave. Together with a like-minded person named Karl Benz, in 1889 Daimler managed to create the first car with a gasoline four-stroke internal combustion engine operating on the Otto cycle.
What are engine “cycles”
A four-stroke engine differs from a two-stroke engine in that the valve timing has separate intake and exhaust phases. They are controlled by the intake and exhaust valves located in the cylinder head, respectively. They are opened by a camshaft driven by the engine crankshaft.
The first stroke is called "inlet". At this moment, the piston begins to move down from top dead center, creating a vacuum. At the same time, the intake valve opens and the air-fuel mixture is sucked into the cylinder. When the piston reaches bottom dead center, the valve closes and the intake phase ends.
Injecting fuel in one portion at a strictly defined moment at the modern stage of development of four-stroke engines has ceased to be a dogma.
The second stroke is called "compression". The piston begins to move upward, both valves are closed. At this moment, the air-fuel mixture is compressed, heating up. This is necessary for more complete and efficient combustion of fuel.
The third stroke is the “working stroke”. A little before reaching top dead center, with the help of a spark from the spark plug (or due to compression, if we are talking about a diesel engine), the air-fuel mixture is ignited. At this moment, the gases expand sharply, pushing the piston down, thereby doing useful work.
The fourth measure is called "release". When the piston has completed its stroke and is at bottom dead center, and it is necessary to remove exhaust gases from the cylinder, the exhaust valve opens. The exhaust gases are pushed out through it by a piston that begins to move upward.
The operating procedure of a diesel engine differs only in that during the compression stroke only air enters the cylinder, and fuel is injected into the combustion chamber at the end of the compression stroke using an injector.
New mechanisms - old principle
From its invention to the present day, engineers have constantly improved the four-stroke engine. Most of the innovations came from the gas distribution mechanism. For example, if previously there were only two valves per cylinder, then on modern engines their number reaches five. In addition, many manufacturers use variable valve timing systems. The most famous are VVT-i from Toyota and Valvetronic from BMW. The variable phase system allows you to change the timing and height of valve lift depending on engine operating modes. After 150 years, the principle, called the Otto cycle, remains relevant. Physicists say that further progress requires a new type of fuel
The food system has also changed. On almost all modern engines, the carburetor has given way to distributed fuel injection. Ignition, dosage and fuel supply are now controlled by electronics.
How does a four stroke engine work?
Structurally, the working cycle of a typical four-stroke unit is ensured by the operation of the following elements:
- cylinder;
- piston - performs reciprocating movements inside the cylinder;
- intake valve – controls the process of supplying the air-fuel mixture to the combustion chamber;
- exhaust valve – controls the process of exhaust gases expelling from the cylinder;
- spark plug – ignites the resulting air-fuel mixture;
- crankshaft;
- camshaft - controls the opening and closing of valves;
- belt or chain drive;
- crank mechanism - translates the movement of the piston into rotation of the crankshaft.
Operating cycle of a four-stroke engine
The operating cycle of such a mechanism consists of four strokes, during which the following processes are implemented:
- Intake (fuel and air injection). At the beginning of the cycle, the piston is at TDC. At the moment when the crankshaft begins to rotate, it acts on the piston and moves it to BDC. This leads to the formation of vacuum in the cylinder chamber. The camshaft acts on the intake valve, gradually opening it. When the piston is in its extreme position, the valve is completely open, resulting in intense injection of fuel and air into the cylinder chamber.
- Compression (increasing the pressure of the combustible mixture). In the second stage, the piston begins to move back to the top dead center of the compression stroke. The crankshaft makes another turn and both valves are completely closed. The internal pressure increases to 1.8 MPa and the temperature of the combustible mixture rises to 600 C°.
- Expansion (working stroke). When the piston reaches the top position in the combustion chamber, the maximum compression is set to 5 MPa and the spark plug is fired. This leads to combustion of the mixture and an increase in temperature to 2500 C°. Pressure and temperature lead to an intense impact on the piston, and it begins to move back to BDC. The crankshaft makes another turn, and thus the thermal energy is converted into useful work. The camshaft opens the exhaust valve, and when the piston reaches BDC, it is fully open. As a result, the exhaust gases begin to gradually leave the chamber, and the pressure and temperature decrease.
- Exhaust (removal of exhaust gases). The engine crankshaft turns and the piston begins to move to the top point. This leads to the expulsion of exhaust gases and an even greater decrease in temperature and a decrease in pressure to 0.1 MPa. Next, a new cycle begins, during which these processes are repeated again.
During each stroke, the engine crankshaft rotates 180°. During a full working cycle, the crankshaft rotates 720°.
The four-stroke engine has become widespread. It can work with both gasoline and diesel fuel. The difference between the operating cycle for a diesel engine is that the ignition of the air-fuel mixture does not occur from a spark, but from high pressure and temperature at the end point of the compression stroke.
What is the difference between a two-stroke engine and a four-stroke engine and what are 4mix and 2mix
Almost every owner of a private home has gasoline-powered assistants that make it easier to perform various tasks - cutting grass, sawing trees, removing snow. The units under consideration are dominated by internal combustion engines created by Etienne Lenoir in 1860. Modern petrol tools are equipped with internal combustion engines, which are divided into two main types - two-stroke and four-stroke. We will learn in detail from the material what is the difference between a two-stroke engine and a four-stroke engine, and what other types of gasoline engines are there.
What is an internal combustion engine on gas-powered tools?
An internal combustion engine is a unit that transforms fuel into mechanical energy. Today, internal combustion engines are used everywhere - from tools to cars and other types of equipment. The principle of operation of the internal combustion engine is due to the fact that a combustible mixture based on gasoline with air is supplied to the design. The carburetor is responsible for creating the desired consistency of the combustible mixture.
The combustible mixture is fed into the cylinder, where it is ignited. The combustion of the mixture creates useful energy that is removed from the crankshaft in the form of rotational movements. The main advantage of the internal combustion engine is that it has high power when compared with electric motors. Most gas-powered tools—trimmers, brush cutters, walk-behind tractors, chainsaws, etc.—are equipped with two-stroke internal combustion engines. More powerful petrol tools are equipped with a four-stroke internal combustion engine. What is the difference between two-stroke and four-stroke engines, what operating principle do they have, as well as their pros and cons are described in the material.
Two-stroke or four-stroke?
First, let's figure out what type of engine to choose for a boat - two-stroke or four-stroke? Disputes about this do not stop, and we will tell you that it is not easy to give a definite answer: a lot depends on the situation and your preferences and capabilities. Still, in most cases one can and should lean towards the first type.
Two-stroke: pros and cons
A two-stroke internal combustion engine is a design in which the working cycle is completed using two piston strokes. Motors of this type are classics, time-tested and have the following advantages:
Gasoline two-stroke engines are not without their disadvantages:
It is clear that there are more advantages and they are much more significant than the disadvantages. You can buy excellent boat engines here.
Four-stroke engine: pros and cons
A four-stroke internal combustion boat engine is a design in which work is completed based on four strokes of the piston. Its advantages are also attractive:
conclusions
You can't go wrong with a good two-stroke engine.
Four-stroke engines are heavier and more expensive than their counterparts. It would be good to ask: will the savings on fuel pay for the high cost of the engine itself? Does a four-stroke weigh less than its two-stroke cousin with extra fuel?
In most cases, you can safely buy a two-stroke engine. But, if you fish by trolling, you can consider a 4-stroke, because you need both good speed and silence. But remember that good two-stroke models can handle this well.
We advise you to consider two types of motor depending on your fishing style and catch.
And don’t forget that it is important not only to buy a good motor, but also to install it correctly.
Useful video regarding which motor is better for a boat - two-stroke or four-stroke:
What is called a stroke in an internal combustion engine?
A stroke on an internal combustion engine is an action that takes place inside the mechanism. Moving the piston in the upper or lower direction is the stroke. Moreover, one stroke is when the piston moves upward, performing the corresponding work. The downward movement of the piston, which returns from the force generated by the combustion of fuel, is called the power stroke.
The first stroke from which the engine begins to operate is filling the cylinder with the fuel mixture. The next stage is the compression of the incoming mixture into the engine. Next, ignition occurs, and finally the removal of burnt gases. These are the four strokes that are performed in four-stroke engines. The crankshaft in four-stroke units makes two revolutions with one ignition of the fuel.
Two-stroke engines operate in two cycles - transporting the fuel mixture into the cylinder with its subsequent ignition, and removing exhaust gases from the cylinder. In two-stroke units, the crankshaft makes one revolution when burning one portion of the fuel mixture.
This is the main difference between the units under consideration and each other.
2-stroke and 4-stroke internal combustion engines are available in gasoline and diesel fuel types. To find out in detail what advantages and disadvantages are available in the 2- and 4-stroke engines under consideration, let us consider their design and operating principle.
Dry residue
So, when asked why we should overpay for four cycles, we can answer: “It’s quiet and economical.”
Now let’s decide whether this “quiet and modest girl” is worth the cost of a wedding?
It’s easy to talk about “silence” to a person who is not familiar with the subject under discussion. Yes, at low speeds, up to 1000-1200, the four-stroke engine is quiet, and at idle it’s almost inaudible - I remember a couple of times, at first, when I tried to start the already running engine with the key.