2 Design features of turbocharging systems
A moped or motorcycle with a turbocharging system has an increased supply of fuel and air to the cylinders. The engine power of a motorcycle or moped increases due to the fact that the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders releases more energy during combustion, and thus the gas pressure increases.
Traditionally, the turbocharger system equipped with a motorcycle or scooter includes the following components:
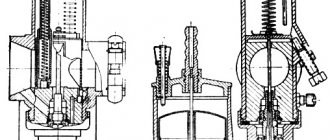
The turbine is the main component of the system. The result of modernizing the moped engine largely depends on its choice. The type of turbine is determined by the design of the bearing assembly. Bushing turbines are characterized by the fact that the impeller shaft is fixed in a bushing, which is lubricated with oil under pressure. A ball-type turbine has a shaft that rotates in a ball bearing assembly and is lubricated by oil spray. The ball turbine provides less friction and faster spin-up of the turbine. In addition, such a turbine requires less oil to operate. Compared to a ball turbine, a bushing turbine has a lower cost and overall dimensions of the cartridge. The geometry of the impellers is determined by the power requirements of the scooter or motorcycle engine and volumetric efficiency. To calculate the necessary parameters, it is necessary to construct a turbo map, on the basis of which you can select the appropriate turbine model for a particular motorcycle or other vehicle.
The turbine is connected to the scooter motor using manifolds. The intake manifold supplies the air-fuel mixture from the turbine to the engine. The design of the intake manifold includes connecting pipes, a receiver and other elements. Receiver parameters (volume) are determined based on instantaneous air flow rates. The exhaust manifold provides exhaust gas removal. The shape of the assembly connecting the manifold pipes affects the efficiency of the turbine installed on the motorcycle engine.
The intercooler is designed to cool the air after the supercharger. This is necessary so that the effect of inflation in the scooter engine is not weakened. The turbocharger uses water or air intercoolers. The air cooler has a simpler design and is characterized by a high rate of heat exchange between the environment and compressed air. The disadvantages of the air cooler include its large size, which leads to delays in creating pressure in the turbocharged system. A water intercooler has a more complex design, but it gives better results after stopping the motorcycle for a short time - the air in the engine cools the water during idle time, and after the engine starts moving, the cooled water cools the air.
READ How to set an avatar in telegram
A scooter or motorcycle equipped with a turbocharged system has bypass valves that allow excess pressure to be released. Wastegate is installed inside the turbine itself and controls its excess boost. Blowoff is designed to prevent accidents when increasing boost and can be adjusted to specific pressure characteristics.
A turbocharged motorcycle or scooter is equipped with a boost controller to control the boost. This programmable device provides adjustment of the pressure increase parameters in different gears. A motorcycle with a boost controller is characterized by “smooth” engine operation.
A turbocharged motorcycle or scooter has a special oil supply and drainage system. The parameters of the oil supply tube are selected in accordance with the required oil flow and the available pressure in the connection unit. Oil draining in a turbocharged scooter occurs under the influence of gravity. Incorrect installation of the drain tube leads to increased oil consumption and improper engine operation. A motorcycle, scooter, moped and other motorized vehicles have a specific design, so the drain must be installed above the oil level. To do this, use either a pump-out pump or an additional tank.
Turbine for motorcycle Dnepr
Triumph Thruxton R turbocharged motorcycles
English moto]Triumph[/anchor] built two motorcycles specifically to participate in the Essenza race, held at the Glemseck 101 festival in Germany.
The custom racing bikes “White Bike” and “The Bulldog” are built on the basis of the production Thruxton R motorcycle.
The White Bike reflects the symbiosis of modern racing trends with the classic T120 engine. “Bulldog” is a “charged” urban cafe racer with impressive sporting potential.
For “White Bike” the classic blue and white color scheme was chosen
Triumph's mechanics have done some serious work to boost the engines of the motorcycles: custom Rotrex superchargers were installed, a radiator and overpressure relief valve were added, new injectors were installed and an updated ignition control program was installed. Engine compression dropped to 10.0:1. For each bike, engineers created a unique exhaust system. Changes also affected the chassis - a MotoGP sports rear swingarm and Öhlins shock absorbers were installed on both motorcycles.
Installing a supercharger made it possible to increase power by 70 hp.
According to engineers, the maximum power of the 1200 cm3 two-cylinder in-line engine has increased by 60% and is 140 hp. Maximum torque increased to 157 Nm.
Exclusive handmade exhaust installed on a White Bike motorcycle
The White Bike features a custom Daytona 675 body kit, Triumph racing team colors and a hand-crafted MotoGP exhaust system. A boost pressure sensor has appeared on the stylish blue and white dashboard.
Separate direct-flow exhaust of the motorcycle “The Bulldog”
For the “The Bulldog” motorcycle, they created body kit elements stylized as a café racer. The motorcycle is painted in an exclusive black and red matte color scheme. New LED optics and a custom minimalistic dashboard were installed. A single leather seat and spoked wheels are accessories from the official Triumph catalog available to any owner.
Minimalistic design of the dashboard of the motorcycle “The Bulldog”
During the Glemseck 101 festival, the Essenza race took place - a 1/8 mile drag race. The Triumph team was represented at the competition by four-time World Superbike champion Carl Fogarty, who rode a White Bike and took first place.
Four-time World Superbike champion Carl Fogerty took first place at the Essanza. Photo by Carlfogarty
Recently, Triumph broke its own speed record on Lake Bonneville. English pilot Guy Martin, flying a Triumph Infor Rocket Streamliner, reached a speed mark of 441 km/h.
And on the first weekend of September, the Triumph representative office in Nottinghamshire organized the largest Triumph motorcycle rally, in which 668 motorcyclists took part! Organizers and participants are awaiting confirmation from representatives of the Guinness Book of Records.
Apparently, the British strive to maintain the company's sporting image by actively participating in various competitions and events.
All this is part of Triumph’s marketing strategy aimed at popularizing motorsports, supporting riders, as well as attracting new customers and increasing interest in the brand.
Subscribe to Omoimot magazine updates on VKontakte, Facebook, Twitter or Google Plus to be the first to know about the most important news of the motorcycle world.
Photos – 1000ps.ch
Operating principle of an electric turbine
According to dealer promises, the turbine forces air into the injection system (carburetor) and leads to an increase in engine power. Place the turbine on your scooter, instead of the standard (or no longer standard) air filter (installed directly on the carburetor), place the system activation button on the steering wheel (supplied in the kit). Ideally, when your scooter's engine spins up to medium or higher speeds, turn on the turbine and get an increase in power in the engine.
READ How to install radio on your website
In addition, the electric turbine can also be used as an auxiliary energy source for charging the battery or for use for the needs of the on-board electrical network at a time when the engine speed is insufficient for normal operation of the scooter’s electrical equipment.
This is ideally what sellers promise us...
Can an electric turbine increase engine power?
Turbocharging has thoroughly taken root in engines with fuel injection, both gasoline and diesel. A strong union of turbocharging with a carburetor engine did not work out due to problems with the organization of air flows, which guarantee the flow of gasoline from the jets into the intake manifold. In theory, turbocharging can also be installed on an engine with a carburetor power system, but in practice an infinite number of problems arise.
Firstly, in order to prevent the fuel-air mixture from becoming too lean, you will need to install new fuel jets (with an opening of a larger diameter). It is not so easy to choose jets for various carburetor systems so that the engine operates intelligently in all modes.
Secondly, the boost pressure at different speeds must be different, otherwise due to an excess of air in the intake manifold, the air flow passing through the diffusers will significantly slow down, which can lead to a reduction or even a stop in the supply of gasoline.
In factory turbocharged carburetor engines, which were produced in small numbers and quite a long time ago, the carburetor was originally designed to work with a turbine. Ordinary carburetors for naturally aspirated engines are not prepared to work with a turbine.
Thirdly, the compression ratio of turbocharged engines is lower than that of atmospheric engines - for example, not 9-10, but 8.1-8.6. Thanks to this, the pressure in the cylinders on the compression stroke is reduced to safe values and the possibility of detonation combustion of the fuel is reduced. Therefore, with this reconstruction, it is desirable to reduce the compression ratio and increase the size of the combustion chamber by placing an extra gasket under the cylinder head.
There are also a number of other disadvantages, due to which the operation of a carburetor engine with a “foreign” turbine will bring a lot of problems. And the motor life can be significantly reduced.
Based on this, we can conclude that installing an electric turbine on a carburetor engine, and even more so on a carburetor scooter engine, is not profitable. Homemade electric turbines, which folk craftsmen make with their own hands, are no exception.
Source
Turbine on motard
A couple of days ago the post office brought me everything I needed, and the guys from the Baza motorcycle service and I started installation.
My motorcycle, Yamaha WR250X, belongs to the motard class. These are lightweight motorcycles with high suspension and city tires, which allow you to ride recklessly both on asphalt and on hills, stairs and off-road, and even in the subway. The motorcycle police and some motorcyclists do not like motardists, and I must say for good reason (HAHA!).
The turbine itself is very small, with a tiny impeller, and will only blow half an atmosphere into a 250cc engine. However, this will give a 75% increase in power, peaking at 54 hp.
The first step of the instructions sounds something like “Remove everything you can remove from the motorcycle.” The instructions themselves, by the way, consist of 25 steps, including installation/disassembly, soldering, tuning, filing and engine surgery. The help of a qualified workshop is necessary here, since some actions are simply impossible to perform in a garage environment.
After removing all the plastic, the instructions tell you to install a filter for the vacuum system. This in itself is a two-minute task, but in order to get to the right bolts and correctly lay the vacuum line, I had to spend about an hour pulling out the plastic box from the motorcycle frame that holds all the electronics and air system.
By the way, after installing the turbine, nothing remains at all from the vacuum system and the air intake system into the engine; all pipes, valves and filters are completely dismantled. In order to get to the required holes, you also need to remove the tank and a bunch of plastic.
It took about 40 minutes to remove the plastic box for the air filter, which is almost impossible. I wouldn’t be surprised if in hell it would be necessary to endlessly install and remove such boxes. Hint: it is better to halve it right inside the frame and pull it out in parts.
At the same time, all technical fluids are changed, including, of course, the oil. Turbine bearings require lubrication and cooling during operation. In our case, the turbine oil circuit will be embedded in the engine oil circuit, transferring heat from the turbine to it.
Then we use a punch to make a mark in the center and at low speeds we begin to drill a hole, gradually increasing the diameter of the drill. By the way, I had to order inch drills and a tap especially for this operation.
Let's start carving. There is no automation here anymore, everything is very neat, slow and manual. To prevent the tap from leading and tearing up the metal, add plenty of oil during the cutting process.
We clean, rinse and polish the finished product, coat the threads with Teflon sealant and install it on the motorcycle.
The turbine will be held on the exhaust elbow, which is screwed to the engine. Exhaust gases flow through this elbow into the turbine, spinning its impeller up to 100 thousand revolutions per minute. A second impeller is installed on the same shaft, which pumps clean air into the system and creates pressure. Exhaust gases after the turbine go through a flange into a direct-flow muffler. Of course, the flange didn’t want to fit into the exhaust pipe of the muffler right away, and I had to work on it a little.
Almost installed turbine, visible rotor impeller and blow-off mechanism. When the pressure in the charge pipe exceeds the design value, a valve opens, allowing exhaust gases to bypass the turbine and the pressure drops.
Several control devices are connected to the intake system at once. There is a sensor on the steering wheel that shows the current pressure.
A vacuum sensor is installed next to the power commander, which is soldered to the gas sensor power supply. The signal wire from it goes to the analog input of the power commander.
Then all this electronic goodness is isolated and hidden in the air filter box, that is, where it once was.
Finally, launch. The turbine works great. The motorcycle itself has become much quieter, especially considering that before it had forward flow and full exhaust. After several tests we put back the tank, plastic and seat and the turbocharged motard is ready.
A small FAQ from the owner of a turbocharged motorcycle.
How much did it cost?
Without the cost of the motorcycle and including delivery - about 80,000 rubles.
Well, is it going?
Of course, my motard was doing well before, but riding with a turbine is incomparably cooler. Around 4000 rpm, the turbine begins to pick up and all that remains is to hold on to the steering wheel more tightly, the motorcycle pulls forward very strongly.
What is the service life and when will the engine melt?
The manufacturer says some have driven up to 10,000 miles with the turbo installed, which is pretty cool. Since the engine volume is very small and there is a lot of metal on it, it has a good margin of safety. However, the oil will now have to be changed twice as often.
Source