Sometimes a correctly set ignition helps eliminate these defects. Therefore, set the ignition yourself (or with the help of a neighbor in the garage who knows everything) with the appropriate marks. For these purposes, you can look into a book about your car and read how to do it correctly.
It happens that problems arise with the spark or with the supply of air and fuel mixture. There may also be flaws in the operation of the engine (troits or jerks). All this is also checked if your car stalls during acceleration, and there is some kind of dip when you press the gas. Also, especially in very cold weather, the cause of dullness may be insufficient heating of the engine. In these cases, before driving, warm up the engine well to operating temperature, and then start driving.
Injection cars
If your car uses the injection principle, then you can check the malfunction using special diagnostic equipment. This is available at any service station that respects its reputation. Stuttering and jerking during acceleration can be associated with insufficient fuel pressure, failure of the air flow and throttle position sensors.
But with accelerating, smooth movement, jerking may most likely be due to the fact that the ignition system is acting up. In this case, it is also recommended to carry out computer diagnostics of the components and, if necessary, repair the ignition. If problems arise on the road, you can independently check the contacts with the wires on the ignition coils. Also, when starting the engine with the hood open, listen to the operation.
The crackling sound of electricity during a breakdown should be clearly audible, if any. And in the dark, a spark is also visible at the breakdown. You can move, but carefully, to the nearest service station.
If, in general, the engine power has decreased (it accelerates poorly, does not climb hills well), then perhaps you should listen to the sound of it idling. Signs such as a change in exhaust sound, engine shaking, increased fuel appetite, floating speed, jerking and dullness during acceleration may indicate that one of the engine cylinders has failed.
Naturally, the power decreases, operation becomes unstable and, as a result, the car picks up speed poorly. Here it smells like engine repair, and this is already very serious.
Results:
As you can see, there can be a lot of reasons why a car stalls during acceleration. They are different both in nature and in difficulty of elimination. In any case, if this happens to a car, it is not recommended to drive like this for a long time. It is necessary to understand the essence of the problem as quickly as possible.
Air leaks and sensors
As you know, the injection engine is equipped with an electronic engine control system (ECM), which completely controls the operation of the power unit. This system is actually multiple sensors and a controller (ECU). Based on sensor readings, the control unit adjusts the SOP, increases or decreases the amount of fuel supplied, prepares a fuel-air mixture that will be optimal for a particular engine operating mode, etc.
If the signal is incorrect, then fuel supply may not be implemented correctly. In this case, a failure appears, which the driver feels in the form of a delay in pressing the gas, that is, a failure. Note that such failures are especially relevant on those cars with an “electronic” gas pedal. In other words, there is no direct connection to the throttle body.
Let us also add that the throttle valve must be cleaned periodically, and also on many cars it is necessary to carry out the procedure for adapting the throttle valve after cleaning this element. To avoid problems, experienced drivers clean the throttle valve at least once a year. This procedure is performed for preventive purposes.
In garage conditions, when there is no diagnostic equipment, checking electronic sensors is carried out by elimination; a multimeter tester is used for diagnostics.
- As for air leaks, this phenomenon may well lead to jerks and failures during acceleration. If excess air is sucked in somewhere, then the ECU loses the ability to correctly determine the amount of air entering the engine.
As a result, the mixture of fuel and air will be prepared incorrectly; instead of a power-rich “rich” mixture, a lean working mixture will be supplied to the cylinders. The suction may occur at the intake, and problems in the fuel supply system are also possible. In any case, depressurization requires immediate detection of the problem area.
Why does a car accelerate poorly?
Owners of used cars often encounter the problem that the car stalls when accelerating. This can be expressed in different ways:
- From the very start, pressing the gas pedal to the floor, the driver hardly feels any feedback from his iron horse, the car either picks up speed very slowly or does it jerkily;
- The problem may occur when overtaking. Drivers often describe it this way: “when I try to overtake a car, I change lanes, press the gas pedal to the floor, but the car doesn’t move, it feels like someone is holding it by the rear bumper.”
The car does not accelerate
There can be a great many such descriptions, but the reasons for such behavior of the car are often the same.
First of all, this is, of course, the wrong job:
- Motor unit;
- Fuel system malfunction;
- Ignition system or electrical circuit.
The design of the car’s fuel system (injector or carburetor) is also important.
About illusions on car forums
On Internet forums, dialogues reach conclusions that are difficult to believe for a person even with little understanding of the work and structure of a modern imported internal combustion engine. The stories, due to naivety and technical illiteracy, create the illusion of some kind of home-grown help that does not bring benefit, but harm.
A cracking sound that appears in the engine compartment cannot be diagnosed in a car enthusiast’s personal garage. Its occurrence indicates serious technical, electrical, and mechanical problems in the engine. But it is the sovereign right of the owner of a car that growls - to deliver the car to a technical assistance station or to figure it out yourself and find the reason.
Fuel system problems
Too little fuel can cause your engine to run too rich, which slows combustion and reduces power output once the engine warms up. Excess fuel is unlikely unless you open the fuel injector or carburetor needle valve fully. Or your high pressure fuel pump or pressure regulator is faulty.
Reduced fuel delivery can occur due to clogged filters, a faulty pump, or clogged injector screens. A faulty injector is one that does not open or is constantly open. It will cause the cylinder to misfire. And this will subsequently cause a decrease in power and noticeable vibration of the engine at idle.
Jerks and failures during acceleration: causes and solutions
They sharply pressed the gas - and the car showed nothing. Or the acceleration is very sluggish and alternates with dips and jerks. In the most advanced cases, this manifests itself even during smooth acceleration, or the engine begins to “trouble” at idle. Today I propose to figure it out together why this is happening. And first, a little theory.
A little bit of theory
First, let's delve into the essence of the concept of "traction failure"
. Fuel flows from the gas tank into the engine, where, when burned, it pushes the pistons, which perform useful work - accelerating the car. And those same failures and jerks are nothing more than periodic omissions of the “pushing” stage. power stroke is not carried out (or is not carried out properly)
. That's sorted out. And now a completely logical chain of cause and effect begins: from the gas tank to the cylinder. In fact, there are only two global options: either there is not enough fuel, or the mixture cannot burn normally. But this is a theory, and we are interested in why this happens in practice.
Reasons and solutions
Let's look at the most common cases in detail. Let me make a reservation right away that the reasons for the behavior described above largely coincide with the reasons for high fuel consumption, which we have already discussed earlier. Moreover: “jerking” is usually accompanied by excessive engine appetite. But traction failures can also have other roots.
1) Insufficient pump performance
. Or, as an option: a clogged fuel receiver in the gas tank/dirty fuel filter (that is, any obstacles in the path of the fuel). This is perhaps the most common reason. As a consequence, there is a drop in pressure in the fuel rail and compensation for this drop by the duration of the opening of the injectors. As a result, the calculated composition of the mixture changes, which is why the car eats a lot and drives poorly. When there is frankly not enough fuel at peak moments (during acceleration), dips and jerks begin. We partially discussed this phenomenon in the article linked above and I will not go into details. Let me just say that the very first thing you need to do is remember the existence of the fuel filter and in what century it was last changed.
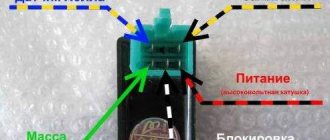
2) Problems with ignition.
But here we will look at the situation in more detail.
Option “A”:
tired candles
. Due to carbon deposits on the electrodes, its melting, cracks in the insulator and other reasons. In any case, the mixture is not ignited as expected. Diagnostics is simple - unscrew and look. Perhaps what you see will greatly surprise you.
Option “B”:
faulty ignition coils
. Here it is hardly possible to determine visually. But thank God, now any VAZ can self-diagnose and detect misfires without problems. He’ll even tell you which cylinder it’s in. There would be a scanner. Well, or an on-board computer with a screen - it’s inexpensive, but the thing is very useful.
Option “B”:
breakdown of the coil insulator.
That is, the device itself is working properly, but the rubber cover is torn, or has become stiff and cracked. Because of this, the spark escapes not to the spark plug electrodes, but to the wall of the spark plug well. By the way, the situation is absolutely similar with high-voltage wires - they should not be made of wood, and certainly not torn. As in the case of candles, checking your guesses is literally a matter of five minutes.
Actually, that's all the diagnostics are. Of course, there is always room for exceptions, but the general picture of jerks and failures in traction in 90% of cases fits into the reasons described above. Therefore, don’t be afraid to roll up your sleeves and help your car yourself. Believe me, this is the surest option.
I hope it will be useful to someone!
Strong acceleration and stable ignition to everyone!
PS: Friends, I will be very glad to like and subscribe to my channel OVER 9000!
This article is published by me exclusively on Yandex.Zen. If you read it on another resource without a link to my channel, know: it was simply stolen
Reduction - Power - Engine
A decrease in motor power also leads to a decrease in the relative inductance of the windings.
The decrease in engine power and, consequently, the increase in specific fuel and oil consumption by the end of the unit's overhaul period is explained by the development of cylinder liners and wear of the piston rings, which leads to a drop in compression pressure and an increase in the temperature of the exhaust gases. The appearance of significant ellipses and cones on the shaft journals causes an increase in clearances in the bearings and a drop in oil pressure, which can also cause a decrease in the power and reliability of the installation.
A decrease in engine power also occurs when ignition is too early, when the combustible mixture ignites prematurely and the force of the gases acts against the piston, which moves towards TDC.
The decrease in engine power by the end of the tests when operating on M3 motor fuel is explained mainly by coking of the injector nozzles and the general deterioration of the engine condition.
A decrease in engine power is observed in the presence of malfunctions that cause a decrease in compression (pressure at the end of the compression stroke) in its cylinders. Such malfunctions include: increased wear of pistons and cylinder liners, breakage or burning of piston rings, loss of elasticity, weak or uneven tightening of bolts (nuts) securing the cylinder heads, damage to the gasket.
The reduction in engine power occurs mainly due to the depletion of the combustible mixture. Reasons that can cause a decrease in power include narrowing of the gas passages, clogging of gas filters and gas channels of the evaporator, insufficient opening of the valves of the first and second stages of the reducer and economizer device, as well as a decrease in the flow area of the gas main, flow and main valves.
The reduction in engine power occurs mainly due to the depletion of the combustible mixture. Reasons that can cause a decrease in power include: narrowing of the gas passages, clogging of gas filters and gas channels of the evaporator, insufficient opening of the valves of the first and second stages of the reducer and economizer device, as well as a decrease in the flow area of the gas main, flow and main valves.
A decrease in engine power is caused by a decrease in compression as a result of: failure of the cylinder head gasket seal due to weak or uneven tightening of the fastening nuts or damage to the mounting, burning of rings in the piston grooves due to the deposition of resinous substances and carbon deposits; wear, breakage or loss of elasticity of rings; wear of the cylinder walls.
A decrease in engine power and an increase in fuel consumption occurs when the centrifugal and vacuum ignition timing regulators malfunction, unless this is caused by malfunctions of other engine systems and mechanisms.
To reduce engine power with a trapezoidal speed diagram, it is advantageous to adopt gear ratios slightly higher than optimal. The reduction in the performance of the mechanisms is insignificant, and the engine power is significantly reduced.
To reduce engine power with a trapezoidal speed diagram, it is advantageous to adopt gear ratios slightly higher than optimal. The reduction in the performance of the mechanisms is insignificant, and the engine power is significantly reduced.
The reasons for the decrease in engine power are as follows. A combustible mixture of gas and air has a lower calorific value than a mixture of liquid fuel and air. The filling coefficient, due to the high temperatures of the combustible mixture of gases and air entering the cylinders, is lower than when operating on liquid fuel. Due to the lower value of the coefficient of molecular change during the combustion of gaseous fuels compared to the combustion of liquid fuels, the average indicator pressure decreases.
A common reason for a decrease in engine power is the entry of a lean mixture into the cylinders.
This leads to a decrease in engine power and increased fuel and oil consumption. Wear of the oil scraper rings leads to increased carbon formation and the rings getting stuck in the piston grooves.
The latter entails a decrease in engine power, increased oil consumption and increased wear of parts. This leads to the need for premature disassembly of the engine and, consequently, to disruption of the normal operation of the mating parts. After each disassembly, oil loss usually increases.
The car jerks when accelerating: what to look for when diagnosing?
Sometimes the causes of car problems can be found out without expensive diagnostics and computer testing of the functionality of all components. Some symptoms can clearly and unmistakably tell which module of your car is not working properly. However, there are manifestations of problems that may indicate several types of breakdowns at once. If your car jerks during acceleration, you need to immediately respond to this manifestation, because the reasons can be quite serious.
Violation of valve timing
The main parts of the gas distribution mechanism (GRM) are the intake and exhaust valves. They are “obliged” to open and close only at the right moment so that the fuel mixture enters the cylinders on time and exhaust gases are removed. This process is called phase distribution. If it is violated, you will see that the power of the engine has disappeared, which will begin to “triple” and sometimes have difficulty starting.
Causes of valve timing violations:
- wear, as well as incorrect installation, displacement of the chain or timing belt (most often this is a jump by one tooth (link));
- play or deformation of the pulley on the crankshaft;
- wear of hydraulic compensators, camshaft and (or) its bed;
- burnout or rupture of the head gasket;
- Malfunction of the camshaft position sensor (DPRV).
To restore normal operation of the timing belt, it is necessary to set the position of the timing and crankshaft shafts according to the marks. If the chain is worn, replace it. The same applies to the camshaft with a bed, hydraulic compensators, gasket and DPRV.