The fuel pump overheats, reasons
The power supply system of the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 21081, 21083, 2109, 21091, 21093, 21099 vehicles uses a mechanically driven fuel pump.
Signs of an overheating fuel pump - The engine stalls while the car is moving
In most cases, this happens in hot weather when driving in city mode (traffic jams, prolonged idling).
— A hot engine cannot be started
Starting is possible only after 10-20 minutes of parking (after some cooling). After a short stay of a hot engine, the fuel mixture may become over-rich and, as a result, it may be difficult to start the engine. Over-enrichment occurs due to the forced opening of the needle shut-off valve of the float chamber due to the increased pressure of gasoline vapors in the heated gasoline pump and the supply line to the carburetor.
— There are dips, jerking and jerking when you press the gas pedal
Since an overheated fuel pump stops functioning normally and pumping fuel into the carburetor, the fuel level in the float chamber drops, there is simply not enough gasoline to operate the accelerator pump and gas pump, and the throttle valve opens to a large angle, causing the fuel mixture to become leaner with excess air. A failure or series of failures occurs.
Causes of malfunction: fuel pump overheats
— The “return” is faulty - the return line from the carburetor to the gas tank
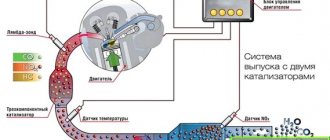
The fuel system of the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is equipped with a line for draining excess fuel into the gas tank (“return”). While the fuel pump is operating, fuel circulates freely through its body into the carburetor and is drained back into the fuel tank. The fuel pump is cooled by the fuel passing through it. See photo above.
The slightest malfunction of the “return”: clogging, deformation of parts, malfunction of the check valve leads to disruption of the fuel circulation through the fuel pump and its cooling. Vapor plugs appear in it and in the fuel supply line. The pump runs idle. The engine stalls. Hot weather and urban travel aggravate the situation, leading to a sharp exacerbation of the problem.
When the engine starts, the expansion of heated gasoline and its vapors in the overheated gasoline pump (they have nowhere to go since the “return” is blocked) slightly opens the needle shut-off valve in the float chamber and squeezes fuel out of the float chamber through the carburetor’s gas pump into the engine intake tract. The fuel mixture becomes richer during startup. The engine does not start.
— The fine fuel filter is located too close to the hot engine
The gasoline passing through the filter is intensely heated from the hot engine. Air pockets appear. the fuel pump refuses to work.
fine fuel filter for the carburetor engine power supply system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
What to do if the fuel pump (fuel pump) overheats?
- Stop and wait until it cools down. If possible, put a wet rag on it. This will speed up the cooling process.
— Move the fine fuel filter to a more ventilated place under the hood (away from the engine). Or remove it from the power system altogether.
Notes and additions
— On an engine with a fuel injection system (injection), overheating of the fuel pump is possible when the fuel level in the gas tank is low. Since the cooling of the electric fuel pump of the fuel system occurs at its expense. A fuel pump immersed in gasoline releases the heat generated during its operation. Often a critical decrease in the fuel level in the gas tank leads to failure of the electric fuel pump.
More articles on the fuel pump of the fuel system of the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Fuel pump overheating: is it dangerous to drive with a light bulb?
Does driving a car with a low fuel level in the tank cause the submersible fuel pump to overheat and fail? Popular rumor assures that yes. Professional repairmen in car service centers often say the same thing. Let's check if this is really true!
Riding on a light bulb
There is a very common garage superstition about the dangers of driving “on a light bulb” - this is what people call driving a car with a low fuel level. They say that the gas pump in the tank (we are talking about injection engines, of course) when the fuel runs out is not completely immersed in gasoline, which means it does not cool, overheats and quickly fails. The plastic anti-drip glass in which the fuel pump “cartridge” and the fuel level sensor are installed does not help: the “waterline” in it is the same as in the tank, the glass is intended only to protect against exposure of the pump intake during starts and maneuvers.
It seems that the problem of pump overheating looks quite real. However, if you think about it, you can reasonably doubt the danger described above. Yes, the pump has a submersible design, but who said that its most important task is to cool the pump? First of all, this arrangement reduces the noise level and provides large-scale modularity, and not at all heat removal.
The fuel pump motor has low power (50-70 watts) and is located as far as possible from heat sources. In other words, by pumping gasoline it cools itself with high efficiency and, most likely, does not need cooling with gasoline from the outside, along the outside of the body. At the same time, even when the fuel tank runs out, its operating conditions do not change: as in the case of a full tank, it continues to pump fuel through its insides with constant force, current consumption, rated performance and with continuous circulation through the “return” line.
However, the fact that the pump has enough cooling from the inside is a subjective confidence that requires verification. Either by complex engineering calculations, or by a simple and visual experiment. We will carry it out!
Does it get hot or not?
Let's repeat the introductory one. We assume that the submersible electric gasoline pump does not require actual cooling from immersion in gasoline and, without any damage to performance, functions until the last drop, which it can reliably suck in, relatively speaking, until the engine stalls on its own due to the pump sucking in air and subsequent drop in pressure in the fuel rail.
To check this, we will assemble a simple stand from a gas pump, a container with five liters of gasoline, a 12-volt power supply, a pressure gauge and a fuel pressure regulator. The pump will be installed “in air” and will suck in fuel through a short hose. Thus, it will have to be cooled exclusively by gasoline flowing through its insides.
It is clear that if the pump pumps fuel from container to container as it is, the experiment will be useless. Therefore, we will give the pump the required load - we will connect it through a pressure regulator: just as it is done in a car. The pressure regulator will provide the fuel with a stable “backup”, and the liquid will circulate in a circle in the same way as in the standard car power system.
For the experiment, we took a new pump from an inexpensive popular brand of the most common type, with a vortex discharge impeller. Specifications - 90 liters per minute, maximum pressure 6.5 bar, current consumption 5 amperes.
A small problem was the lack of an intake fitting on the pump. There is an outlet pipe onto which you can pull the hose, but there is no inlet pipe! Therefore, I had to quickly make a plastic cap from scrap materials that fits hermetically on the pump, and screw the hose fitting into it.
A plastic plumbing pipe plug was ideal as a cap. The inner diameter of the plug from the 32 mm pipe perfectly coincided with the outer diameter of the pump housing: the cap, heated by a hairdryer, was pressed on.
We start the system by first pouring fuel into the pump manually, through the removed hose, so that it does not thrash the air uselessly. The pump impeller chamber was filled with liquid, and the further process was already self-sustaining.
The pressure in our test system is approximately 4 bar. It is provided by the above-mentioned regulator, which is a fuel filter with a built-in pressure regulator from Volkswagen. The above-mentioned 4 bar is the filter’s nameplate pressure, the real one is about 0.4 bar less. Its use is convenient because the filter has standard fittings for connecting hoses, in contrast to independent pressure regulators, which are mounted on the injector ramp through a flange and bolts.
We connect the pump output to the filter input through a pressure gauge, the “return” output from the regulator is connected to drain into a container, and we simply turn off the filter output, which is normally directed to the injectors. As a result, gasoline circulates continuously, and operating pressure is maintained in the line after the pump, as in a fuel rail.
results
As part of the simple test bench we assembled, the pump worked continuously for an hour, which was more than enough to evaluate the result. You didn't even need a thermometer - when you checked it by hand, the fuel pump body was barely warm to the touch. Being washed with fuel exclusively from the inside and remaining dry from the outside, the pump did not experience even a hint of overheating.
Actually, we do not draw any far-reaching conclusions from this experiment - everything is “just for technical fun” and for the sake of love for accuracy in general and wording in particular. After all, there are a lot of references on various automotive Internet forums about pump failure due to overheating caused by driving with a low fuel level in the tank. They are systematically heard in the dialogues of car owners, and are often heard from car repair professionals. But, as can be seen, these fears are groundless.
Pumps certainly die sooner or later. True, mainly due to water and dirt in the tank and from natural wear and tear on the commutator, brushes and impeller. But the amount of gasoline in the tank for the pump to operate is not important.
You must be logged in to comment.
There is a slightly more obvious fact: at least on the Volga-3110, until some year the fuel pump was not in the tank, but under the bottom of the car. With exactly the same performance and pressure parameters. And, by the way, all the operating instructions warned against running “dry,” that is, when it started pumping air. Then, oh, maybe he’ll die. True, I didn’t check it personally, but the warning was still in some kind of paper form, and not in the form of “a neighbor in the garage said so.”
As a Volga driver, I responsibly declare: not only on the 3110, but also on my 31105 there is a so-called frame pump attached to the bottom of the car. BUT! The instructions for the car say that you should not drive constantly on the lamp, because this leads to premature wear of the pump.
Of course, there is no overheating, BUT! If the pump, under favorable conditions, is designed for 160,000 mileage (in particular, Pekar said this when I bought their pump), then premature wear can be 80,000. Again, I can’t help but take into account the fact that my pump is screaming wildly , when there is little gasoline in the tank and behaves much quieter than with the same half tank. PS: what overheating? what about the article? If the fuel pump overheated, the cars would explode, because... It is not gasoline that ignites, but its vapor. So it turns out that the vapors, coming into contact with the overheated element of the pump, would create a boom.
Look for the answer from those who use LPG, I have already changed three pumps on Kalina in one winter, until I understand. Moreover, for the first time they took out something extremely different from a pump, since it had melted very much
I believe there is more danger in the ability to grab air on bumps, turns and climbs
Denis, what is the operating temperature of your internal combustion engine? This is approximately the return temperature of the fuel. Test about nothing
So I’m not talking about the danger of overheating, but about a sharp jump in engine speed when air is grabbed and there is no lubrication with gasoline at this moment
The fuel pump overheats, reasons
The power supply system of the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 21081, 21083, 2109, 21091, 21093, 21099 vehicles uses a mechanically driven fuel pump.
Signs of fuel pump overheating
— The engine stalls while the car is moving
In most cases, this happens in hot weather when driving in city mode (traffic jams, prolonged idling).
— A hot engine cannot be started
Starting is possible only after 10-20 minutes of parking (after some cooling). After a short stay of a hot engine, the fuel mixture may become over-rich and, as a result, it may be difficult to start the engine. Over-enrichment occurs due to the forced opening of the needle shut-off valve of the float chamber due to the increased pressure of gasoline vapors in the heated gasoline pump and the supply line to the carburetor.
— There are dips, jerking and jerking when you press the gas pedal
Since an overheated fuel pump stops functioning normally and pumping fuel into the carburetor, the fuel level in the float chamber drops, there is simply not enough gasoline to operate the accelerator pump and gas pump, and the throttle valve opens to a large angle, causing the fuel mixture to become leaner with excess air. A failure or series of failures occurs.
Causes of malfunction: fuel pump overheats
— The “return” is faulty - the return line from the carburetor to the gas tank
The fuel system of the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is equipped with a line for draining excess fuel into the gas tank (“return”). While the fuel pump is operating, fuel circulates freely through its body into the carburetor and is drained back into the fuel tank. The fuel pump is cooled by the fuel passing through it. See photo above.
The slightest malfunction of the “return”: clogging, deformation of parts, malfunction of the check valve leads to disruption of the fuel circulation through the fuel pump and its cooling. Vapor plugs appear in it and in the fuel supply line. The pump runs idle. The engine stalls. Hot weather and urban travel aggravate the situation, leading to a sharp exacerbation of the problem.
When the engine starts, the expansion of heated gasoline and its vapors in the overheated gasoline pump (they have nowhere to go since the “return” is blocked) slightly opens the needle shut-off valve in the float chamber and squeezes fuel out of the float chamber through the carburetor’s gas pump into the engine intake tract. The fuel mixture becomes richer during startup. The engine does not start.
— The fine fuel filter is located too close to the hot engine
The gasoline passing through the filter is intensely heated from the hot engine. Air pockets appear. the fuel pump refuses to work.
fine fuel filter for the carburetor engine power supply system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
What to do if the fuel pump (fuel pump) overheats?
- Stop and wait until it cools down. If possible, put a wet rag on it. This will speed up the cooling process.
— Move the fine fuel filter to a more ventilated place under the hood (away from the engine). Or remove it from the power system altogether.
Notes and additions
— On an engine with a fuel injection system (injection), overheating of the fuel pump is possible when the fuel level in the gas tank is low. Since the cooling of the electric fuel pump of the fuel system occurs at its expense. A fuel pump immersed in gasoline releases the heat generated during its operation. Often a critical decrease in the fuel level in the gas tank leads to failure of the electric fuel pump.
More articles on the fuel pump of the fuel system of the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Gasoline pumps DAAZ vs Pekar
The other day I caught a vapor lock in the fuel pump. I was very surprised by this because I have a branded Pekar fuel pump in which there are no vapor locks. I decided to figure out what was going on. Having opened the fuel pump, I was somewhat shocked by its contents. which prompted me to write this article. So DAAZ vs Pekar.
First, some description of the pumps.
Left Pekar right DAAZ
Pekar - the words of the manufacturer. OPERATIONAL RELIABILITY — Oil- and gasoline-resistant membrane made from imported materials — Galvanic coating of parts protects gasoline pumps from the adverse effects of the environment REPAIRABILITY — For the first time in Russia, a modular design of gasoline pump units is used LEAK-TIGHT — Valve design that allows maintaining pressure and vacuum ensures quick engine starting ABSENCE OF VAPOR LOCK — Design fuel pumps, providing a minimum parasitic volume, eliminates the formation of vapor locks in the engine power system. PETROL PUMPS PROVIDE: - uninterrupted supply of fuel to the carburetor in various climatic conditions at temperatures from -40°C to +50°C - performance of the car engine in accordance with technical conditions
Pressure at zero supply, at a camshaft speed of 2000 rpm, (kgf/cm2) 0.22 - 0.35 Vacuum created by the pump, at a camshaft speed of 2000 rpm, not less (kgf/cm2) 0 ,4 Capacity for free draining at a fuel temperature of 20°C, at a camshaft rotation speed of 2000 rpm, not less (l/hour) 60 Suction (time from the start of pumping to the start of fuel supply), at a camshaft rotation speed of 200 rpm /min, no more (sec) 10 Valve tightness (pressure drop over 10 min), no more (kgf/cm2) 0.05 Outer diameter of the diaphragm (mm) 70 Pump weight, no more (kg) 0.5
DAAZ - the manufacturer’s words here, I must say, the manufacturer turned out to be more modest.
Capacity for free drainage, l/h 60 If you look at both pumps externally, you will notice that the DAAZ gasoline pump has a much larger cavity for gasoline, this is Pekar’s main move. because The baker does not have a dome-shaped lid, and this is what the buyer is attracted to. Thinking that a vapor lock will form under this very lid. But no, the fact is that this cover is nothing more than an INLET sump. and even if there is somehow air there, it will not affect the operation of the pump in any way. Just as the air in the gas filter does not affect the operation of the pump. The DAAZ dome is essentially an additional gas filter. Well, let's talk about everything in order.
Let's study the design of the Pekar fuel pump. So, the first thing we see in the Pekar fuel pump upon closer examination is that the outlet fitting is not flush with the pump, but is simply inserted into it. Of course, it fits tightly, but on the Internet you can find stories about how this fitting simply flew out of the pump. For example, here is a man’s story about how a fitting fell out of a baker and this led to a car fire https://www.azlk-team.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=17726&highlight=%E1%EE%EB%F2%E0%E5% F2%F1%FF
Opening the pump
Yes, the camera is really small, but what immediately catches your eye is the mark left by the exhaust valve on the diaphragm washer, this can be seen in the photo. There is only one diaphragm in the baker
If the diaphragm ruptures, gasoline will flow through the pusher hole straight into the engine crankcase
. Under the diaphragm there is a spring whose quality simply shocked me
that’s actually the whole design of the baker fuel pump
The fuel pump itself was purchased by me from the official dealer of TD Pekar and has a halographic sticker confirming its authenticity. Now let’s look at the design of the native Zhiguli DAAZ fuel pump. Both fittings on the DAAZ are tight, so you don’t have to be afraid that one fine day this fitting will come off.
Under the top cover of the pump there is a mesh filter with a sump that additionally filters gasoline at the inlet to the fuel pump. Once again, I want to note that the myth that steam locks form under the top cover of the DAAZ is complete nonsense. The top cover is an INPUT filter to the pump, so even if there is air in it, it cannot affect the operation of the pump.
What fuel pumps were equipped with classic VAZ models?
Classic VAZs include all models of the Zhiguli family, produced from 1970 to 2012 and their modifications:
- VAZ 2101;
- VAZ 2102;
- VAZ 2103;
- VAZ 2104;
- VAZ 2105;
- VAZ 2106;
- VAZ 2107.
Depending on the year of manufacture, the engines of these vehicles were equipped with different fuel systems. In all the first Zhiguli models, the fuel mixture was injected into the cylinders using a carburetor, and the fuel was supplied by a mechanical fuel pump. The latest modifications of the VAZ 2104, 2105 and 2107 had an injection system and an electric fuel pump.
Carburetor cars of the Zhiguli family were equipped from the factory with mechanical fuel pumps of the diaphragm type DAAZ 2101 (catalog number 1106010) produced by the Dimitrovgrad Automotive Unit Plant. Thanks to their simple design, reliability and maintainability, they have proven themselves well not only on the “classics”, but also on cars of the Sputnik and Samara families, which were equipped with their modified versions.
Injection Zhiguli models were equipped with domestically produced electric fuel pumps. They were produced by the Pekar and Utes enterprises under catalog number 21073–1139009. The latest modifications of the Zhiguli were equipped with products (catalog number 2112–1139009). The same devices were installed on all models of the Samara and Lada families.
Main causes of overheating
ATTENTION! A completely simple way to reduce fuel consumption has been found! Don't believe me? An auto mechanic with 15 years of experience also didn’t believe it until he tried it. And now he saves 35,000 rubles a year on gasoline! Read more"
Most likely, if there are no characteristic reasons for overheating, the pump has simply outlived its useful life. Simply replacing it can completely eliminate the problem. On the other hand, if the cause is not eliminated, the new pump will also heat up like the old one, and the money spent on the purchase can be considered lost.
However, this rarely happens. More often than not, problems are actually related to the pump.
Here are the main causes of overheating.
- Dirt. A device used for a long time will overheat faster. It is necessary to check all pump elements, including the filter mesh. Clean or replace consumables if necessary.
- External damage, such as a crack or something similar. The cause may also be wear of the device’s gears or rollers protected by hydraulic superchargers.
- Driving with Chek-Engin. Some motorists ignore the warnings that the car sends. They continue to drive, although the system notifies that there are problems, including those related to the fuel pump.
- Driving with a red light. It lights up on the instrument panel if the volume of fuel liquid in the tank is critically small. It is especially dangerous to travel with a half-empty tank in hot weather. The fuel pump will soon overheat.
- Refueling at questionable gas stations. Pumping low-quality fuel also negatively affects the operation of the pump. If the fuel contains a large amount of sulfur, the commutator will gradually become covered with a dark coating, contact with the brushes will deteriorate, and sparking will begin inside the device, which will lead to overheating.
- The main filter is clogged. This is a separate part installed in the section of the fuel line. It has the ability to retain small particles of debris that get into gasoline.
- Violations in the voltage circuit, short circuits. This is also a clear reason for overheating of a modern type electric pump. With such problems, the pump begins to turn on in starting mode, and as a result overheats.
Signs of an overheating fuel pump are:
- decreased engine performance;
- its unstable operation in all modes.
However, an accurate diagnosis is always made after a thorough check. If the pump is not placed inside the tank, but is located under the bottom of the car, diagnosing overheating is easier than ever. You need to remove the plastic protection of the device and drive it like this for several days. When the engine suddenly stops or performance decreases, get out of the car and put your hand on the pump. An overly hot case is evidence of overheating.
Where is the fuel pump located on 2106, 2107 and other models
The location of the fuel pump on carburetor and injection classic VAZs is different. In the first, it is installed on the left (as viewed from the passenger compartment) on the engine cylinder block on a special boss, and is attached to it using studs through a heat-dissipating ebonite spacer. The mechanical fuel pump is driven from the engine intermediate shaft through an eccentric and a pusher (rod).
In injection Zhiguli cars, the pump is included in the design of the fuel module. It is located inside the gas tank. The design of an electric pump consists of a DC electric motor and a specially shaped impeller mounted on its shaft. The electric motor is powered from the vehicle's on-board network. The electrical circuit of the device is protected by a separate fuse and relay.
Pump repair or replacement?
There are two ways to get rid of a fuel system malfunction. In the first place is expensive, but reliable - replacing the entire fuel pump of a carburetor VAZ 2107. In second place is installing a repair kit. What's better? If you have a full hand and can carry out all the work perfectly, then, of course, it will be cheaper to install only new internals. But if you are a driver who rarely encounters such difficulties, it is better to purchase a new device and install it on your car. Fortunately, this procedure is simple - you need to unscrew two nuts and loosen the clamps.
But it is necessary to mention the quality of the elements that are included in the repair kit. Although no, their quality can be excellent, but in terms of size they will not fit exactly into the places that are intended for them. In most cases, repairs help for a couple of weeks, after which time the pump begins to malfunction again. Therefore, if the fuel pump on a VAZ 2107 does not work, it is better to install a new one. Even if, of course, its value is high, but if a defect appears, it can be exchanged. And the new one will last for several years, you won’t even touch it.
Diagnostics and replacement of the electric fuel pump on cars of the Zhiguli family
In injection engines of classic VAZs, the fuel pump may lose its functionality both due to problems with the power supply to it and due to a malfunction of its electric motor. In the first case, the situation can be corrected by diagnosing and repairing the electrical circuit of the device. But if the electric motor of the pump fails, only replacing it will help.
Checking the protection devices for the electrical circuit of the fuel pump on injection VAZs of the Zhiguli family
If there is a problem with the electrical equipment of the fuel pump circuit, it usually does not turn on at all. Turn on the car's ignition without starting the engine and listen. First, you should hear a click from the relay, and then a characteristic “squeal” emitted by the pump’s electric motor. If you don’t hear anything like this, start diagnosing with the electrical circuit of the device.
The pump circuit is connected to the on-board network via a separate relay, and its protection is provided by a fuse. Both of these devices are located in the vehicle's optional mounting block. You will find it under the glove box. It contains 3 relays and 3 fuses. The fuel pump relay (indicated R2 in the diagram) is located in the middle, and the fuse (F3) is to the left of it. We pull the fuse out of its seat and check it by “ringing” it with a tester. If a malfunction is detected, we replace it, not forgetting to comply with the rating (15 A).
You can check the functionality of the relay by installing a known working device in its place. Instead, replace it with the relay located to the right of the one being diagnosed, which is responsible for the radiator fan circuit. If this option does not suit you, turn on the ignition and measure the voltage between the pink wire going to the relay and the vehicle ground. The device should show 12 V. This means that the device is powered. After this, you need to connect the pink wire with the gray one at the relay terminals. So we will connect the fuel pump directly to the battery. If it works (that same “squealing” sound will be heard), simply replace the relay.
Checking the fuel pressure in the system
The main indicator of the operation of a fuel pump is the pressure it creates in the system. If the device turns on, pumps fuel, but the engine runs intermittently, take the time to check the pressure. To do this, you will need a pressure gauge with a measuring range of 5–7, equipped with a gas-resistant hose and a threaded fitting (if there is no special one, you can use a regular tire pressure gauge). The sequence of actions is as follows:
- On the fuel rail we find a fitting closed with a plastic cap. Unscrew the cap and connect the pressure gauge hose to the fitting. If your device is not equipped with a special threaded fitting, the hose can be secured to the “nipple” using a small clamp.
Replacing the fuel pump on injection Zhiguli cars
You can replace the fuel pump either as an assembly (install a new fuel module) or separately (change only the pump). The cost of a new domestically produced module with a fuel level sensor is 2800–3000 rubles. The production pump itself will cost 500 rubles less.
Replacement Tools:
- slotted and Phillips screwdrivers;
- key to 10;
- key to 7.
Work order:
- Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Open the gas tank cap.
- Using a slotted screwdriver, remove the rubber apron from the neck of the tank. Disconnect the safety valve tube from it.
After installing the pump, it is advisable to check the pressure in the system as described above.
Replacing the fuel pump in cars of the Zhiguli family does not require the car owner to have extensive knowledge in the field of auto repair, and does not take a lot of time and money. It can be done without any problems in a garage, or right on the street. However, if you do not have the necessary tools or the desire to do this yourself, it is better to turn to specialists.
The pump does not turn off: nozzles overflow, faulty relay
During overheating, as mentioned above, the fuel pump may not turn off. That is, overheating in this case occurs due to prolonged operation of the device in vain.
This may occur due to malfunctions of the ECU or RTD sensor. Due to “glitches”, these controllers are able to influence the electric pump.
Another reason for the uninterrupted operation of the pump can be nozzles that “pour”. This does not allow the pump to create the necessary pressure in the ramp, i.e., to start the engine. You can test the condition of the injectors using the spark plugs. If they are flooded, then there may be a break in the injectors.
It is possible that the fuel pump relay has failed. A working element should click three seconds (or five) after starting the engine, which will indicate that the supercharger is turned off. If there is no sound, or there is a click, but the fuel pump does not turn off, it is recommended to remove the relay and check if the pump is working. If its rotation stops, then the relay needs to be replaced; it is faulty.
Often the electric pump simply sticks. In this case, it is enough to remove the relay and just knock on it. This must be done while simultaneously disconnecting the battery terminal.
In general, if the pump relay is “buggy”, then anything is possible. For example, this situation. Summer, hot. You are standing in a traffic jam, under a traffic light, the engine is running at low speed. Suddenly, for some unknown reason, it stalls and does not start. It’s good that there’s a traffic jam and there’s no need to move forward yet. After ten minutes, the vehicle’s performance is restored as the pump cools down. Such engine stalling can also occur when driving at low speed in the heat.
Mechanical pumps just need to be watered with cold water to restore the operation of the device. What about the electric pump that is located inside the tank? And often the reason for its overheating is not hot weather at all, but a relay that is faulty.
Many experienced motorists recommend driving without a relay in this case. As an analogue, install a pin jumper 30/87. True, this is not entirely convenient; each time before a trip you will have to insert the jumper, and then pull it out. But this way you can check whether the bug is repeated. If yes, then the relay should be excluded from the list of possible faults.
Source: ozapuske.ru
Why does the VAZ 2106 fuel pump get hot?
PS: Here’s another thing that might be the matter. The smell of gasoline appears periodically. I can’t determine where it’s coming from, but it smells like (spruce-spruce) in the cabin. Maybe it's sucking air?
Do I need to change anything when installing a VAZ 2140? My colleague’s machine died and I’m wondering if I should immediately install a baker for him? Do I need any gaskets or other extras? put?
I don’t remember the details - it’s been 8 years since I parted ways with AZLyK, but if you’re interested, I can take a look, since this unit is growing into the ground next to my parents’ house. : : Ilya.
Author:
JJConnect
Date:
18 Aug 2009 15:10
As I have previously dealt with the problem of fuel pump overheating. The following items were replaced: The pump itself, the pusher and the thermal gasket. Coolant All caps Replaced Carb Thermostat and pump were checked for proper operation The ignition was set During maintenance they set CO and said that the mixture was a bit too lean The gas tank vent was also cleaned and finally driving without a cap did not help!
But the problem did not go away. Now I was stuck in a traffic jam in the east and stalled ten times. You run out of the car with some water, start pouring water on the pump and back to quickly pump it into the main line until the carbic, pump it up manually and notice that at the same time all the gasoline leaves the fine filter made of Chinese plastic, we continue pumping and over time the full filter is pumped up again, I noticed that from under the cap The radiator is pressed by the antifreeze; I didn’t twist the caps out of harm’s way. At the same time, the temperature according to the sensor is 90 - 92 degrees. When the Carlson is turned on, it works constantly, but it only maintains the temperature and does not reduce it. I drove through a traffic jam and stood on the side of the road, removed the terminals from the fan so that it would not turn on, and I hope there is no overheating, although it could be a coincidence. This problem also reminds us of itself and when driving the temperature remains stable at 88 - 90 degrees. I looked at the radiator, not to say that it was shiny, but it wasn’t clogged either. I don’t see any point in changing everything anymore, and I don’t have the money. I would like to hear more reasons and your comments. Maybe change the oil? =) Trips to the service center yielded nothing except phrases: we need to take everything apart, change everything, and then when we figure it out, you’ll get a bill. I would be grateful for any thoughts and APs!
And yes, when I was still dismantling the benzoak ventilation, I noticed a hanging wire screwed to the top of the lid, it looked like a mass!
[Message modified by user 08/18/2009 15:18]
[Message modified by user 08/18/2009 16:14]
[Message modified by user 08/19/2009 15:06]
Author:
Valery Anatolyevich (Zufa_66)
(Send a letter) (About the user) Date:
18 Aug 2009 15:22
And yes, when I was still dismantling the fuel pump ventilation, I noticed a hanging wire screwed to the top of the lid, it looked like a ground!
The fuel pump has no ventilation. Maybe a gas tank? Try driving with the lid open.
Riding on reserve
What the modern pump doesn't like most is running on the reserve fuel tank. Why, one wonders? The fact is that current models of gasoline pumps are submersible in design. They are placed inside the fuel tank. One of the goals of this solution is to provide cooling to the pump due to the flow of circulating fuel liquid.
Obviously, if there is little fuel in the tank, you should not expect normal circulation. The fuel pump will not cool and will quickly overheat.
It is noteworthy that this driving style is typical of Russian drivers. The fact is that this is being done due to a lack of funds and the high cost of fuel. You fill the tank with several liters of gasoline at certain intervals when you have money on hand. Yes, this allows you to maintain financial liquidity, and there is no need to give up driving a car, but other difficulties arise, including overheating of the electric pump.
Let's look at the pump cooling principle in more detail. The liquid transferred by the fuel supercharger to the injector a priori serves as a coolant for the device. It absorbs heat, reduces the temperature of the pump, and prevents jamming of mechanisms. But if there are less than three liters of gasoline left in the tank, then when the car moves, the liquid moves along the edges of the fuel tank. In general, in this situation, the pump may not be washed by it, remain dry and only suck in fuel with its lower part.
It’s even worse when the device sucks in air instead of gasoline. This is possible if you drive over potholes and off-road conditions with a small volume of liquid in the tank. At the moment of suction, the liquid remaining in the tank may splash out to the side, which will lead to the absorption of gasoline vapors. This is extremely dangerous for the pump mechanisms, the risk of breakdown increases several times, and overheating occurs immediately.
What are the signs of a VAZ-2106 fuel pump malfunction?
The design of the VAZ-2106 car is clearly outdated today.
In addition, many “sixes” are at a fairly advanced age. Therefore, it is not surprising that they periodically experience certain malfunctions. One of the fairly common problems here is a breakdown of the fuel pump. To begin with, it should be noted that this part plays a very important role in the operation of the car. After all, it is the fuel pump that is responsible for supplying gasoline from the gas tank to the carburetor or injector. Accordingly, any problem in its operation disrupts this process. Well, if there is no gasoline supply, the car simply will not move. However, there are times when the fuel pump works, but not as it should. This situation will also lead to problems.
Reasons for lack of submission
The owner of a VAZ 2106 is faced with a choice - which path to take in order to restore the functionality of the pump.
The first option is the simplest and most reliable
, but expensive in terms of cost. Any decent service station has equipment that, in a minimum amount of time, will not only measure the pressure at the inlet and the vacuum at the outlet of the fuel pump, but also identify the part causing defects in the operation of the equipment.
Second
The option is not the simplest, not so fast, but practically free, except for the time spent on it - do all the diagnostic and repair work yourself in the garage.
Removing and installing the fuel pump
Removing and installing the fuel pump is a simple operation. The fuel pump, together with the gaskets, is mounted on two studs and secured with nuts, which must be unscrewed with a 13 mm wrench. To remove the fuel pump, you need to disconnect the supply and discharge fuel lines, unscrew the fuel pump mounting nuts, remove the spring washers, and then the fuel pump itself.
When removing it, be careful, as you can damage the thin gasket, which often sticks to both the pump and the thick heat-insulating gasket. The thermal insulation gasket itself, as a rule, can be easily removed by hand without the use of any tools. In the worst case, make it easier to remove by lightly tapping it with the handle of a screwdriver. Do not forget also that under the thick thermal insulation gasket there is another thin installation gasket, which is also a sealing gasket.
Installing a repaired fuel pump has its own characteristics. First of all, install a sealing gasket A with a thickness of 0.70-0.80 mm, and then a heat-insulating one. Next, install a thin gasket B with a thickness of 0.27–0.33 mm.
With such a set of gaskets between the fuel pump body and the cylinder block, the minimum output of the pusher (its inner end touches the back of the cam) should be in the range of 0.8-1.3 mm. This dimension (d) can be easily checked by installing spacers and a pusher (rod). If the pusher protrudes from the gaskets by an amount less than 0.8 mm, then gasket A is replaced with gasket B with a thickness of 0.27-0.33 mm.
In the case where the pusher protrudes more than 1.3 mm, instead of gasket A, it is necessary to install a thicker gasket type C with a thickness of 1.20-1.30 mm. It should be clarified that a gasket with a thickness of 0.27-0.33 mm should always be installed between the fuel pump body and the heat-insulating gasket.
Fan fault
Overheating can be caused by problems with the computer fan (cooler). All computers have a fan installed inside, one that starts when the device reaches a certain temperature. However, these components can fail for several reasons. One of the main reasons for problems with a cooler is the long period of its use. The fan, like any other electronic device, is subject to wear and tear. In addition, it can become clogged with dust and other small particles, causing it to work slowly or stop completely. As a result, the heating components of the computer are unsatisfactorily cooled, causing powerful heating of the case. Problems with the fan can be indicated by the presence of powerful noise from the system unit or the lack of air, which usually comes out through the ventilation holes.