- Description of the causes of error P0300
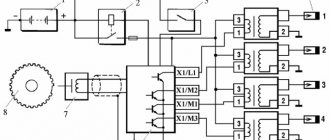
- Connection diagram
- Ride in test mode
- Check sequence when error P0300 is output
- Check for other dtcs (besides P0300 misfire related dtcs)
- Take handheld scan tool readings (misfire rpm and misfire load)
- Check the crankcase ventilation hose connections
- Check the number of misfires (all cylinders)
- Perform active test diagnostics using a handheld scan tool (fuel cut #1 to #4)
- Check the spark plugs
- Perform an ignition and spark test for ground.
- Check compression pressure in cylinder with misfire
- Check for normal spark plug and check for spark in misfired cylinder
- Check misfire cylinder ecm contact (voltage #10, #20, #30, #40, #50 or #60)
- Check wiring harness and connector (injector - ECM)
- Check cylinder injector misfiring
- Check the intake system
- Check valve timing
- Check fuel system pressure
- Take a portable diagnostic tool reading (coolant temp)
- Take portable diagnostic tool (maf) readings
What does the P0300 code mean?
Trouble code P0300 indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring. If the last digit of the code is not zero, such as P0302, then the number 2 means that cylinder No. 2 is misfiring.
A cylinder misfire causes engine speed instability. If the frequency change increases, the crankshaft position sensor senses this and the engine control module (ECM) may detect that one of the cylinders has just misfired.
Crankshaft sensor
Misfire means incomplete combustion of the fuel-air mixture inside the cylinder. When the situation worsens, the machine begins to jerk and performance drops significantly. These misfires are what cause the P0300 code.
avtoexperts.ru
Low prices and the ubiquity of OBD scanners have led to the fact that many car owners have them today. It seems like a great idea, connect the device and diagnose the car yourself, it will show everything itself. True, novice diagnosticians often encounter a problem. The car shows errors in non-obvious codes and it is not clear what to do with the received data. Error P0300 is one of the most common (and for some car models it is even a traditional “sore”). It’s easy to find its decoding on the Internet: “random multiple omissions across cylinders.” But not everyone can imagine what to do in practice if they see the combination P0300 on the scanner screen. Let's try to tell you briefly.
Car diagnostics
Where does it come from?
Identifying the problem that leads to the P0300 error code usually does not create difficulties - on the vast majority of cars the check light comes on. Sometimes this does not happen (depending on the ECU settings), but then something is wrong by the car’s behavior: loss of power, shaking at idle, uncertain start.
It is generally accepted that if there is “misfire on the cylinders,” then the problem is necessarily in the ignition system. But this is not entirely true - the ignition may be one of the reasons, but the problem may be elsewhere. If it was not possible to ignite the air-fuel mixture in a certain cylinder, it means either there is nothing to ignite, or there is nothing to ignite, or the conditions in the cylinder are unsuitable for ignition. There are a huge number of potential problems that can lead to this. We will disappoint those who want to get the result right away - not a single scanner will show the reason for the omission, you will have to look for it yourself.
Error P0300
The only way the device can help is to localize the problem by cylinder. If misfires occur in all cylinders, then the device will show error P0300, and if in just one, then instead of the last digit there will be a cylinder number, namely P0301, P0302, P0303 and so on. This makes further search for the problem somewhat easier.
Misfire in the first cylinder
What to check
It’s worth starting with the ignition system, namely the spark plugs. The easiest way to diagnose is to install a known-good set (this is where old, but definitely serviceable spark plugs come in handy, which are wise not to throw away after replacement). If nothing has changed with the other spark plugs, you need to dig further - to the coils and high-voltage wires. You can inspect them visually and try to look for current leaks or breakdowns, which will be clearly visible by sparking in the dark. It is convenient if there is information about which cylinder the problem is, because in this case there is no need to check all of them.
Old and new spark plugs
If everything is fine with the ignition, then the next step is checking the fuel system. The easiest way to start is with the fuel pump - check with a pressure gauge whether it creates the required pressure. On cars with a separate fuel filter, you can check it or even replace it - if it is very clogged, it can restrict the flow of gasoline. Another potential problem area is the fuel injectors. They may also be heavily soiled, but this is difficult to determine by eye. You can either wash and clean them preventively, or try to look for injectors for temporary installation and testing.
Checking the fuel pump with a pressure gauge
Another group of reasons are difficulties with the motor itself. Here you won’t be able to do without serious diagnostics and disassembly, because the problem could be stuck or incorrectly functioning valves, a clogged catalyst, timing belt jump, air leaks, or even low compression. It is no coincidence that we mentioned this only as the third point - it is worth delving into such “depths” only when simpler and more obvious options have already been excluded.
Valve burnout
Finally, you should not discount glitches of the ECU itself, as well as any of its sensors. There may either be no problem at all (the control unit is simply glitchy), or an incorrect signal may come from the crankshaft position, mass air flow sensor, detonation and other sensors, which the “brain” incorrectly interprets. To eliminate this problem, you need to arm yourself with a multimeter and check manually.
Cases from practice
Several interesting examples from practice related to error P0300.
The Lada Largus suddenly began to jerk sharply during acceleration. The incident happened on the highway; the driver did not have a scanner with him, but an LPG system was installed. Switching from gasoline to gas and back showed that the car behaves the same on both types of fuel, which means the problem is something else. As we have already said, the owner of the car did not have a scanner with him, but he had an old set of spark plugs, which he installed. The car drove smoothly and without failures. It’s interesting that before replacing the spark plugs, when the car was twitching, the “check” did not light up, but after the replacement it came on and did not go out until the error was reset by the scanner. The error was precisely P0304.
At one point, the Chevrolet Lacetti's "check" started to light up continuously. The scanner inexorably showed P0300, after resetting the error appeared again. Despite the fact that the appearance of the error did not particularly affect the behavior of the car, the owner turned out to be a passionate person and set himself the goal of getting to the bottom of the truth. He changed spark plugs, coils, high-voltage wires and even the battery, then flushed and cleaned the fuel line. But the error still appeared.
Ignition coil Chevrolet Lacetti 1.8
Finally, one auto mechanic advised him to drive several tens of kilometers in low gear with an engine speed of 5000 per minute. After which the check went out and the error no longer appeared. With a high degree of probability, the valves on this car were heavily coked, working at high speeds helped burn off excess carbon, the engine breathed more calmly and the ignition process began to proceed as normal.
These are just two stories, but there can be as many of them as possible with error P0300, because its very appearance is an excellent illustration of the thesis that even the presence of a scanner does not free you from manually searching for problems when you need to connect a multimeter, tools for assembly and disassembly, and most importantly - logic and common sense.
Causes of P0300
Trouble code P0300 is caused by many things. Here are some of them.
- Worn spark plugs.
- Faulty wires.
- Ignition coil malfunction.
- Oxygen sensor malfunction.
- Malfunction of fuel injectors
- Burnt out exhaust valve.
- Faulty catalytic converter.
- The throttle position sensor is faulty.
- Faulty engine control module (PCM/ECM).
- Leak in the cylinder head gasket.
- Intake leakage.
Error classification
The difference in numbers at the end of the error codes allows you to identify the serial number of the cylinder in which the ignition sequence failed. That is, code p0301 shows that the misfire occurred in the first cylinder, p0302 in the second, and so on. Depending on the brand of engine and the number of cylinders in it, the code may even be designated p0306 or p0312.
Thus, error code p0300 is the initial error for any engine, indicating a violation of the ignition sequence in the cylinder block.
In what cases does the computer generate error p0300?
The car owner should know that error code p0300 will be recorded only in cases where ignition failures are detected in two or more cylinders at the same time. That is, the system does not consider a one-time misfire in one specific cylinder a violation, so it does not send a signal about this error to the dashboard.
It is important that with repeated passes, Check Engine with code p0300 is displayed on the instrument panel. If the system has accurately identified the source of the problem, the number of the “problem” cylinder will appear - for example, p0303.
Troubleshooting P0300
- Replace faulty spark plugs.
- Check and repair broken wires.
- Replace the faulty ignition coil.
- Replace or repair the oxygen sensor.
- Inspect the fuel injectors.
- Replace the catalytic converter.
- Replace the faulty head gasket.
- Eliminate air leaks.
- Diagnostics and repair of a faulty engine control unit.
Diagnostics and repair
By carrying out diagnostic measures, you can detect malfunctions and understand why exactly the P0300 error code appeared.
Experts advise adhering to this sequence.
- Check the condition of high-voltage wires. You will need a multimeter set to resistance measurement mode. If the insulation is intact, the resistance will be from 4 to 10 kOhm.
- Check the ignition module or coils. A stand or multimeter will help here. The easiest way to test is by mounting the coil on a properly functioning cylinder. After this, the engine starts and the code is read into the ECU again. If the code has not changed, then the coil is working. We are looking for the reason further.
- Test the spark plugs. They should be dismantled and inspected for carbon deposits and damage. If necessary, cleaning is performed and the gap is set. If the spark plug fails, it should be replaced.
- Compression in cylinders. If it is low or there is no compression, this provokes difficulties with ignition. If compression is normal, move on.
- Injector condition. You can’t do without a diagnostic stand here. One of the options without involving a service station would be to refuel with high-octane gasoline. You need to drive it for 10-20 km at high speeds, and then check the error again.
- Check the fuel filter. This is a consumable that changes periodically. If the filter is dirty or bad fuel is used, the injectors become clogged and misfires occur. Hence P0300.
- Inspect the condition of the gasket on the intake manifold. Sometimes, due to its wear, gaps form and the error in question appears. The gasket should be replaced.
- It would be a good idea to check the EGR valve. It can jam, which leads to the problems in question. To do this, long-term fuel correction is checked in specific suspect cylinders. Differences from optimal indicators should be no more than 1-3%. You can easily find out about the reference values from the manual. With deviations of more than 7%, excess air intake occurs. The valve should be repaired or replaced.
Not all problems can be solved on our own. But it is absolutely impossible to ignore the symptoms that appear with P0300.
How to Diagnose DTC P0300?
Once a P0300 code is detected, a professional auto mechanic will perform the following steps. You can do the same thing yourself.
Connect your car charger
The charger is extremely important when diagnosing the P0300 code. Because troubleshooting requires that the ignition remain on, and this can lead to battery discharge. As a result, additional error codes will appear, which will complicate the search. A car charger will help preserve battery charge.
Connect OBD2 scanner
An OBD2 scanner is required to scan and resolve the P0300 code. With the help of it, you can track the issues related to the error and also troubleshoot them easily.
For cars manufactured before 1996, an OBD1 scanner is used. If the car was manufactured after 1996, use an OBD2 scanner.
Check wiring
Before replacing any part, first make sure all wires and connections are in good condition. Visually inspect the wiring, check for corrosion and correct if necessary.
Check the spark plugs
Spark plugs do not wear out quickly. But if a cylinder is misfiring, it's a good idea to check the spark plugs and notice any signs of trouble.
If the spark plug appears to be faulty, replace it. As part of regular maintenance, you should change the spark plugs every 30,000 km. You should also check the ignition coils!
Inspect the distributor cap
If you replaced the spark plugs, but the problem persists, check the fuel injectors for defects. If you have an old car, check the ignition distributor cap.
Check other error codes
If the OBD2 scanner detects more than one fault code, take the necessary measures to diagnose and resolve them. After doing this, check if the P0300 code returns.
Replace engine control unit
If you have checked everything above, but the error does not go away, there is a possibility that the problem is related to the control unit (PCM). It may need to be re-flashed or replaced.
What are these errors?
Codes p0300, p0301 and p0302 indicate failures in the ignition sequence. Their characteristic stands for “random multiple misses in cylinders.” If you use a special device for engine diagnostics, it will display the phrase “Random cylinder misfire detection system.”
Why is an ignition failure dangerous for a car? This question can only be answered after a brief examination of the operation of the engine as a whole. After starting, the engine operates in four-stroke mode:
- Inlet of the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel compression.
- Ignition (directly at this stage the working stroke occurs).
- Exhaust gas release.
Accordingly, if there is no ignition in at least one engine cylinder, then the engine begins to “triple”, and the control unit records the omission of one of the mandatory cycles of the power unit. Ignition is the process of igniting the air-fuel mixture, and if the mixture does not ignite, then the cylinder has no power stroke. That is, one of the engine cylinders accelerates much more slowly than the others, which disrupts the entire ignition order as a whole.
In this regard, when the ECU detects such a failure, it immediately sends a signal to the dashboard in the form of error p0300: the yellow “Check Engine” light comes on.
It should be noted that immediately after skipping one of the cylinder operation cycles, the level of toxin concentration in the exhaust gas system increases. And the superheated exhaust gases in the pipe quickly heat up the catalyst unit, which can cause it to undergo deformation (the honeycombs melt at temperatures above 800 degrees Celsius).
Driving a car with multiple misfires is comparable only to walking on one leg. Sooner or later the motor will no longer cope with the load and will fail. Therefore, car owners are strongly recommended to immediately take the necessary measures when an error is displayed.
How to replace a spark plug?
Replacing the spark plug is a simple task and you can do it at home. Before changing spark plugs, make sure the engine temperature is low.
Step 1: Open the hood and locate the spark plug
Open the hood and you will see several wires running in the engine compartment. The spark plugs are located in the engine at the end of these wires.
Step 2: Pull the wire
Pull the wire and you will see the spark plug installed.
Step 3: Remove the candle
Insert the spark plug wrench and turn to loosen the spark plug. Remove the old spark plug and note its condition.
Step 4. Install a new spark plug
Using the same spark plug wrench, install the new spark plug and tighten it correctly. Then connect the wire as it was before. All is ready.
Error codes VAZ 2112 8 and 16 valves on the instrument panel: decoding
In modern Lada models, a Euro shield is installed. There is an enlarged display here, where the main and secondary fault codes are displayed. On models 8 and 16 cells, the BC failure codes during self-diagnosis are identical, and the procedure for decoding them requires instructions. There are 9 direct ciphers in total. Codes can stack if there are two or more problems at the same time. If the tidy shows 21, this may mean there are problems No. 6, 7 and 8 at the same time.
If we talk about computer diagnostics, fault codes are deciphered according to a standard scheme that is relevant for all OBD2 variants.
Error 1 1
Says that a critical failure has been detected in the microprocessor system. Open the ECU module and perform a thorough diagnosis using special equipment. Simply cleaning or replacing damaged terminals often helps.
Error 2 on VAZ 2112
The actual on-board voltage differs from the set voltage. The problem may be a short circuit in the main wiring line or a critical discharge of the battery. Study the wiring and basic power components of the car.
Error 3
The fuel level sensor is damaged or not working properly. Check the condition of the float. The cause is a breakdown of the control wiring.
VAZ 2112: error 4
The code indicates that the DTOZH is out of order or is not functioning correctly. The problem should be resolved in the same way.
Error 5
The outdoor thermometer has failed. Check the sensor and its wiring.
Error 6
The code indicates overheating of the power plant. You need to stop immediately and wait for the engine to cool down.
Error 8 2112: 8 valves
Brake system malfunction. Troubleshooting begins with checking the brake fluid level and pad wear.
Error 9
The battery has gone into a deep discharge. Replace the module with a new one or charge the worn element.
Error 10: decryption
In the most common case, the code is a combination of problems 6 and 4. We are talking about a failure of the DTO and overheating of the motor. Problems should be resolved in parallel.
Error 12
Indicates a problem in the electrical circuit of the indicator on the device. Check the appropriate fuse and bulb.
Error 14
Increased signal from the DTOZh controller. There is a short circuit in the controller circuit.
2112 displays fault 18
It is a combination of errors 2, 9 and 7. Problems are resolved in the same way as individually.
Lada 2112 shows breakdown 26
A software glitch that combines three or more problems at the same time. To troubleshoot the problem, perform detailed network diagnostics.
Error 45
Similar solution to problems as in the above paragraph.
Error 34
Mass air flow sensor – low output signal level. The circuit may be damaged or the sensor may be faulty.
Code 78
A simple combination that the machine can use to represent problems 7 and 8 at the same time.
Error 89
Similar meaning and principle of education.
Error 210
Communication with the immobilizer is lost. Perform diagnostics of the wiring and contact groups of the module.
Malfunction P0102
A controller error indicates a low signal from the mass air flow sensor. There is an open circuit or the sensitive area of the sensor is dirty.
P0123 - breakdown
Short circuit on TPS. The circuit is producing too high a signal. There is a short circuit in the circuit. Check the line carefully for damage.
P0131 - error
Lambda probe No. 1 – line damage.
Error 132
Same for DK2.
Breakdown 0134
DK1 wires are broken. Code P0134 indicates a complete loss of communication with the sensor.
Error P0171
The malfunction can be displayed as the number 171. The coding indicates the problem of the fuel mixture being too lean. Check the line for cracks, leaks and damage - air is being sucked into the system.
Lada 2112: error 0172
A similar problem P0172 indicates the opposite effect. Here the fuel mixture is too rich. At 172, you need to check the air filter and mass air flow sensor for functionality.
Error P0300
When code 0300 lights up on the diagnostic scanner, check the ignition system. The error indicates multiple misfires in the cylinders.
P0301 - breakdown
A similar problem with more precise location indication. A misfire was detected in the first cylinder. The repair sequence is identical to point 0300.
Code 0328
Excessively high signal level from the knock sensor. The reason was the filling of low-quality fuel or a physical malfunction in the ignition unit.
Code 0325
There are problems with the knock sensor. Inspect the sensor for damage and replace it with a new device if necessary.
0335 - error
Displayed as 335. There is a problem with the DPKV wiring. The lines are examined for oxides or mechanical damage.
Fault 0340
Likewise for DPRV. For code P0340, the repair steps are identical.
Code 0343
Phase sensor – excessively high signal.
0443 - code
The canister purge valve is faulty, check the unit for damage or mechanical failure.
Error 0505
Short circuit on the speed sensor. Check the entire line.
Fault 0507
Idle speed too high. Check the mixture formation and mixture supply control module.
Code 456
The evaporative emission control module is not functioning properly. Check systems for damage.
Error 603
The ECM is damaged or there is a software glitch. Take the car to an electronics technician. Self-repair will not be effective.
P1135 - error
Incorrect mixture formation in partial load mode. Run system diagnostics.
Error 1426
Code P0426 indicates a problem in the wiring of the canister purge valve.
Error P1513
The idle speed regulator is damaged - a break with a short to ground. The wires need to be insulated or replaced.
1514 - malfunction
The idle speed control is damaged or there is a short circuit.
Error 1602: 2112 16 valves
Indicates that the powertrain control controller is losing voltage. The car does not start well when cold and crashes while driving.
Error 3456
The system requires checking the fuel level sensor. The module is damaged or its wiring is broken.
RAM error 2112
Indicates that there is a problem with the external thermometer. The sensor cannot be repaired; it must be replaced with a known good one.
KB 2112 sensor synchronization error
Indicates that there is damage in the sensor line or a malfunction of the sensor. The wiring and element are fully checked.
Error: lean mixture
If this code lights up on the dashboard, the control unit has nothing to do with it. If the mixture is lean, perform diagnostics on the fuel lines. The trouble is caused by air leaks at the joints or pipes.
Error: Mixture too rich
A similar problem caused by an air line obstruction. Here the filter may become clogged, the mass air flow sensor may break, or air may be sucked into the system after the sensor.
Phase sensor error
Check the sensor for problems. Repair consists of replacing the entire module.
Knock sensor error
The cause of the breakdown and the corrective actions are completely similar to the point indicated above.
Oxygen sensor malfunction
The controller may fail due to filling with low-grade fuel or problems with the mixture formation system.
Camshaft sensor malfunction
The DPRV may malfunction after passing a puddle or too active washing. To fix the problem, just dry the device well.
Crankshaft sensor malfunction
Worn gear on the working part of the sensor. The sensor can only be replaced entirely with a fully functional one.
Speed sensor malfunction
The DS on a car is reliable, but a problem can happen after driving along a broken road or crossing a ford - the sensor simply floods with water. If the diagnostics determines that there is a problem, the entire sensor must be replaced.
ECU malfunction
The module is diagnosed using special equipment. Experienced electronics engineers can resolder or repair the part, but in most cases, the unit is simply replaced with a new one.
Diagnosis of error P0300
What can we do with our own hands and without leaving home, so to speak? The first thing you need to think about is when did this error appear? Maybe it appeared after falling into a “good” hole or appears exclusively in wet weather? Or after refueling? After visiting a tire shop? After an oil change? Etc. All these little things can really help in choosing the direction of your search.
A visual inspection can also bring positive results. Cracked insulation on electrical wiring wires, the presence of moisture in connectors, oil or coolant getting on electrical equipment elements and other troubles can be easily detected by the human eye. It is also worth looking at the explosive wires and ignition coils in complete darkness with the engine running. After all, checking explosive wires and coils for resistance with a multimeter gives only a small picture of what is happening. Most often, these elements of the ignition system fail not due to a break or short circuit in the electrical part, but due to an insulation breakdown. And in the dark you can see a neon glow in the places where the ignition coils are attached or on the explosive wire near the valve cover mounting bolts. The check should be carried out not only at idle, but also in revving mode, because when the throttle valve is opened sharply, the breakdown voltage on the spark plug increases quite noticeably due to the increased pressure in the cylinder.
Cracks and dark marks on the ignition coil housing may also indicate a breakdown of the coil. Although when checked with a multimeter it may seem absolutely fine.
Oil in spark plug wells due to an ever leaking valve cover gasket is also a fertile area for misfires, which can be detected by the same visual inspection
In general, attention and a meticulous visual inspection can quickly identify the culprit of a misfire.
Next, you need to unscrew the spark plugs and compare them with each other. As a rule, this is the most informative process. The difference between one spark plug and the rest clearly indicates problems in a particular cylinder, which will significantly narrow the search range. Next, let's get creative. We move the problematic spark plug to another cylinder and drive for a while. We are re-inspecting. If the same candle is different again, then it’s the problem. And if the spark plug from the same cylinder is different again, it means either the high voltage wire or the injector of this cylinder. Or maybe the iron of this cylinder.