Brake system VAZ 2101
Any car is equipped with a braking system, and the VAZ “kopek” is no exception. Its main purpose is to slow down or completely stop the vehicle at the right time. Since brakes can fail for various reasons, their performance and the condition of their components must be periodically monitored. Therefore, it is worth dwelling in more detail on the design of the braking system, problems and their elimination.
Brake system design
The Zhiguli brakes of the first model are made of working and parking systems. The first of them consists of the following elements:
- master brake cylinder (GTC);
- brake wheel cylinders (RTC);
- hydraulic drive reservoir;
- hoses and tubes;
- pressure regulator;
- brake pedal;
- brake mechanisms (pads, drums, brake disc).
Diagram of the VAZ 2101 brake system: 1 - front brake protective casing; 2, 18 — pipelines connecting two cylinders of the front brake caliper; 3 - caliper; 4 — hydraulic drive reservoir; 5 — brake light switch; 6 — parking brake lever; 7 — adjusting eccentrics of the right rear brake; 8 — fitting for bleeding the hydraulic drive of the rear brakes; 9 — pressure regulator; 10 - brake light; 11 — rear brake wheel cylinder; 12 — lever for manual drive of the pads and expansion bar; 13 — adjusting eccentric of the left rear brake; 14 — brake pad; 15 — rear cable guide; 16 — guide roller; 17 — brake pedal; 19 — fitting for bleeding the hydraulic drive of the front brakes; 20 — brake disc; 21 - main cylinder
The parking brake (handbrake) is a mechanical system that acts on the rear pads. The handbrake is used when parking a car on a slope or on a descent, and also sometimes when starting off on a hill. In extreme situations, when the main braking system has stopped functioning, the handbrake will help stop the car.
Operating principle
The principle of operation of the VAZ 2101 brake system comes down to the following actions:
- When the brake pedal is applied, the pistons in the turbocharger move, which creates fluid pressure.
- The fluid rushes to the RTC located near the wheels.
- Under the influence of liquid pressure, the RTC pistons are set in motion, the pads of the front and rear mechanisms begin to move, as a result of which the discs and drums slow down.
- Slowing down the wheels leads to overall braking of the car.
- Braking stops after the pedal is released and the working fluid returns to the GTZ. This leads to a decrease in system pressure and loss of contact between the brake mechanisms.
The principle of operation of hydraulic brakes on the VAZ 2101
Brake system malfunctions
The VAZ 2101 is far from a new car and owners have to deal with malfunctions of certain systems and troubleshoot problems. The braking system is no exception.
Low brake efficiency
A decrease in the effectiveness of the braking system can be caused by the following reasons:
- violation of the tightness of the front or rear RTCs. In this case, it is necessary to inspect the hydraulic cylinders and replace worn-out parts, clean the brake elements from dirt, and bleed the brakes;
- presence of air in the system. The problem is solved by bleeding the hydraulic drive system;
- The lip seals in the GTZ have become unusable. Requires disassembly of the master cylinder and replacement of rubber rings with subsequent bleeding of the system;
If the sealing elements of the GTZ have become unusable, the cylinder will have to be completely disassembled for repair. - damage to flexible pipes. It is necessary to find the damaged element and replace it.
The wheels do not release the brakes completely
Brake pads may not fully release from the drums or rotors for a number of reasons:
- The compensation hole in the gas turbine engine is clogged. To eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to clean the hole and bleed the system;
- The lip seals in the GTZ are swollen due to oil or fuel getting into the liquid. In this case, it will be necessary to flush the brake system with brake fluid and replace damaged elements, followed by bleeding the brakes;
- the piston element jams in the GTZ. You should check the functionality of the cylinder and, if necessary, replace it, and then bleed the brakes.
Braking of one of the wheel mechanisms when the brake pedal is depressed
Sometimes a malfunction occurs when one of the car’s wheels spontaneously brakes. The reasons for this phenomenon may be the following:
- The tension spring of the rear brake pads has failed. Inspection of the mechanism and elastic element is necessary;
- RTC malfunction due to piston sticking. This is possible when corrosion forms inside the cylinder, which requires disassembling the mechanism, cleaning and replacing worn-out parts. In case of significant damage, it is better to replace the cylinder completely;
- an increase in the size of lip seals due to fuel or lubricant entering the working environment. It is necessary to replace the cuffs and flush the system;
- There is no gap between the brake pads and the drum. The handbrake needs adjustment.
The car skidding or pulling to the side while pressing the brake pedal
If the car skids when you press the brake pedal, this indicates the following malfunctions:
- leakage of one of the RTCs. Replacement of cuffs and bleeding of the system is required;
Fluid leaks on the inside of the wheel indicate a leak in the brake system. - jamming of the piston element in the working cylinder. It is necessary to check the performance of the cylinder, eliminate malfunctions or replace the assembly part;
- a dent in the brake pipe, which led to blockage of the incoming fluid. The tube needs inspection and subsequent repair or replacement;
- The front wheel angles are not set correctly. Angle adjustment required.
Brakes squeal
There are times when the brakes squeak or make a squealing sound when you press the brake pedal. This may occur for the following reasons:
- The brake disc has uneven wear or excessive runout. The disc needs to be sanded, and if the thickness is less than 9 mm, it needs to be replaced;
- oil or liquid getting on the friction elements of the brake pads. It is necessary to clean the pads from dirt and eliminate the cause of leakage of lubricant or liquid;
- Excessive wear of brake pads. Elements that have become unusable need to be replaced.
General structure of the working vehicle
The schematic diagram of the vehicle includes the following elements:
- brake mechanism;
- brake drive.
The brake mechanism implements the function of braking - achieving the torque that is necessary to reduce the speed of movement or stop.
The VAZ-2107 is equipped with a classic version of friction mechanisms based on friction force.
Their design can be represented by the following two options:
- disk (compression mechanism);
- drum (unclamping mechanism).
In the VAZ-2107, a disc mechanism is used on the front wheels, and a drum mechanism on the rear.
A brake actuator is needed to control the braking mechanisms. There are mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, electric and combined operating principles of drives. The VAZ-2107 uses the most common hydraulic principle, based on the action of brake fluid (a special oily substance).
The hydraulic drive circuit includes:
- brake pedal (to control the hydraulic drive);
- vacuum booster (to create additional force when pressing the pedal);
- master brake cylinder with an expansion tank (to ensure an increase or decrease in fluid pressure in the dual-circuit system, as well as to replenish fluid);
- wheel (or working) cylinders (to bring the control functions of the pedal to the brake mechanism);
- rear brake pressure regulator (to adjust the braking force as the vehicle weight increases);
- pipelines and hoses (for placing and moving brake fluid throughout the system).
The implementation of braking functions in the VAZ-2107 (as well as in related models - sedans 2101, 2103, 2105, 2106 and station wagons 2102, 2104) involves the use of two parallel independent hydraulic drive circuits. In the event of a malfunction of one circuit, the braking functions are redistributed to the second.
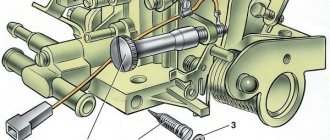
Master brake cylinder
The GTZ of the VAZ “kopek” is a hydraulic type mechanism, consisting of two sections and designed to operate a system with two circuits.
The master cylinder creates fluid pressure throughout the entire brake system.
If problems arise with one of the circuits, the second, although not as effective, will ensure that the car stops. The GTZ is mounted to the pedal assembly bracket.
Design of the GTZ VAZ 2101: 1 - plug; 2 — cylinder body; 3 — rear brake drive piston; 4 — washer; 5 — front brake drive piston; 6 - sealing ring; 7 — locking screws; 8 — piston return springs; 9 — spring plate; 10 — pressure spring of the sealing ring; 11 — spacer ring; 12 — inlet; A - compensation hole (gaps between sealing ring 6, spacer ring 11 and piston 5)
Pistons 3 and 5 are responsible for the performance of different circuits. The initial position of the piston elements is ensured by springs 8, by means of which the pistons are pressed into screws 7. The hydraulic cylinder is sealed with the corresponding cuffs 6. In the front part of the housing is plugged with a plug 1.
The main problems with the GTZ are wear of the lip seals, the piston or the cylinder itself. If rubber products can be replaced with new ones from the repair kit, then if the cylinder or piston is damaged, the device will have to be completely replaced. Since the product is located under the hood near the clutch master cylinder, replacing it does not cause any difficulties.
Video: replacing the GTZ with a “classic”
Relative vehicle malfunctions
This list of faults does not apply to absolute (or categorical) faults. Their presence is associated with the convenience (or inconvenience) of driving.
Increased hydraulic pedal travel (as an option - a “soft” pedal)
The reasons for the “sinking” of the pedal are determined by the presence of air in the system; extreme wear of brake pads; failure of the main or wheel cylinders. The action plan for eliminating technical problems includes checking and repairing all components and assemblies of the system; and, if necessary, replacing failed ones and bleeding the system.
Shift towards the vehicle's trajectory when braking
The malfunction is due to either a failure of the working (wheel) cylinder or wear of the pads. Replacing them (or repairing them) will solve the problem.
Increased background noise, friction (grinding) in the brake mechanism
Deficiencies are localized mainly in the rear mechanisms and are determined by contamination of the mechanism, critical wear of the pads, breakage of spring elements, uneven wear of discs or drums. Fault repair involves washing and replacing mechanism parts.
Vibration when braking
This is a fairly common malfunction that is associated solely with critical or uneven wear of the discs or drums, and the repair will consist of replacing them.
Tubes and hoses
Brake pipes and hoses of the braking system of the VAZ “kopek” are used both front and rear. Their purpose is to connect the GTZ and RTC to each other and supply brake fluid to them. Sometimes connecting elements become unusable, especially hoses, due to aging rubber.
Damage to the hose leads to fluid leakage and depressurization of the brake system.
The parts in question are attached using a threaded connection. There are no difficulties in replacing them. You just need to unscrew the fasteners on both sides, remove the worn element and install a new one in its place.
Video: replacing brake pipes and hoses on a “classic”
Absolute vehicle malfunctions
During operation, the braking functions of the system deteriorate. This is due to wear and tear of components, assemblies and parts that require repair. Some vehicle malfunctions are included in a special “List...”, and driving with them is prohibited.
Inefficiency of the working vehicle
The most common malfunction of the brake system (including the VAZ-2107) is inefficiency, which is diagnosed by two main parameters (when carrying out a specialized instrumental study):
- increasing braking distance;
- increase in steady deceleration during braking.
Such faults can be determined by eye. After driving a passenger car on a dry road at a speed of 40 km/h, when braking, the car travels a distance exceeding 12.2 m. In this case, according to paragraph 2.3.1 of the traffic rules, the use of the vehicle is prohibited (even to the parking or repair site) .
This malfunction may be due to:
- presence of air in the system;
- fluid leakage from the system;
- worn out pads;
- failure of the main or wheel cylinders.
Article on the topic: Penalty for hitting or crossing the stop line
In other words, almost the entire vehicle should be subject to monitoring. Repair (replacement) of components and assemblies will require bleeding the system to remove air from it.
Leakage of the working vehicle
During vehicle operation, components, assemblies and parts are subject to wear, which leads to depressurization of the system and leakage of brake fluid. This most often occurs in brake hoses or wheel cylinders. Fault repair is carried out by monitoring leaks and replacing damaged elements.
Leakage of the system also excludes the possibility of operating the car (according to paragraph 2.3.1 of the traffic rules).
Ineffective parking vehicle
This defect is the most common when the car moves involuntarily even with the handbrake locked. This is due to wear on the pads, discs or drums, as well as stretching of the cable elements.
According to the requirements of the “List...”, a parked vehicle must ensure that the passenger car is stationary:
- on a slope of up to 16% at full load;
- on a 23% slope when equipped.
In the event that these requirements are not met, the vehicle can only be driven to a parking or repair site. Repair of the malfunction is ensured by adjusting the cable tension with a special nut or replacing worn parts.
Brake pedal
The main control element of the VAZ 2101 braking system is the brake pedal, located in the cabin under the steering column between the clutch and accelerator pedals. The pedal transmits the muscular force from the driver's legs to the GTZ. If the brake pedal is adjusted correctly, the free play will be 4–6 cm. When you press it and travel the specified distance, the vehicle begins to smoothly slow down.
Free play of the brake pedal: 1 — master cylinder; 2 - pusher; 3 — brake pedal; 4 — brake light switch buffer; 5 — switch nut; 6 — brake light switch; 7 — pedal release spring