Modern cars with internal combustion engines use a closed liquid cooling system. In most cases, antifreeze circulates inside the system. Although some stubbornly continue to pour ordinary water into it, which is a gross violation of the operating rules.
A constant excess pressure is created inside this system while the engine is running. Not everyone understands why this is necessary, since the main task is to ensure efficient circulation of the cooling fluid in small and large circles.
In fact, pressure plays a big role in the operation of the internal combustion engine. It allowed us to get rid of a common and very pressing problem with old cars.
Why is internal pressure created?
Having dealt with the pressure in the engine cooling system, much will become clear and obvious.
There is an example of old cars. In them, the liquid continuously circulated in the motor, heated up, taking away excess heat, and then cooled in the radiator due to the counter flow of air and air from a forced fan.
Then ordinary water was poured into the radiator, and the car drove smoothly. But it often happened that the driver was forced to stop in the middle of the road, because thick white steam began to pour out from under the hood. The engine simply began to boil, and the water began to boil and actively evaporate. This is what provoked the appearance of thick white smoke (steam).
To continue the journey, I had to cool the internal combustion engine, fill in new cold water and drive off. At that time, the concept of engine boiling was familiar to almost every car owner.
You will soon understand why the cooling system of a modern engine requires pressure. The reason for boiling of old internal combustion engines is extremely simple. Water under normal conditions at normal atmospheric pressure boils when the temperature reaches 100 degrees Celsius. Circulating in a circle, with a heavy load on the motor, the water does not have time to cool down, and therefore boils.
In modern antifreezes poured into cars, the boiling point has increased to 105-115 degrees Celsius.
Now remember your school physics course, and it will immediately become clear why you really need to create pressure in the cooling system. As the pressure increases, the boiling point of the corresponding liquid also increases.
As the pressure inside the system increases, the antifreeze will boil at a correspondingly higher temperature.
This significantly protects the motors from the boiling effect. Most engines under normal conditions heat up to a temperature of 90-95 degrees Celsius during operation. Using ordinary water and without pressure inside the system, literally with a slight overload the motor would boil. And since antifreeze is poured in, plus the boiling point has increased due to the pressure created, the boiling threshold is pushed back to about 110-120 degrees Celsius. This allows you to eliminate the occurrence of problems even under heavy loads on the internal combustion engine.
And in order to create the required level of pressure in the system itself, there was no need to develop any special technologies. For this purpose, closed cooling systems are used. The liquid in them gradually heats up as the engine operates, steam is formed, and it creates the same pressure.
Pressure cannot increase indefinitely, but it also cannot fall below a certain level. To control these parameters, valve covers are used on the radiator and expansion tank.
The cap allows you to release or build up pressure as needed. This is a compact, but very useful and important device that works for the benefit of the cooling system and the entire engine.
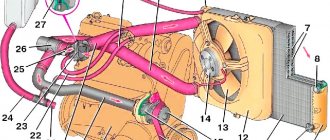
The design of the VAZ 2101 cooling system
The VAZ 2101 cooling system includes the following elements:
- cooling jacket;
- liquid pump (pump);
- main radiator;
- cooling fan;
- heating module radiator with tap;
- thermostat;
- expansion tank (tank);
- temperature sensor with pointer;
- communication pipes and hoses.
Let us consider in detail the purpose, design and main malfunctions of each of the listed elements.
The cooling system of the VAZ 2101 has a sealed liquid-type design
Cooling jacket
The cooling jacket is a set of specially designed holes and channels inside the cylinder head and the block itself. Forced circulation of coolant occurs through these channels, resulting in cooling of the heating elements. You can see the channels and holes if you remove the head from the cylinder block.
The cooling jacket is a system of channels inside the engine for circulating coolant
Cooling jacket malfunctions
The shirt can only have two faults:
- clogged channels;
- surface damage due to corrosion.
In the first case, the throughput of the channels is reduced due to the entry of debris, water, wear products and oxidation into the system. All this leads to a slowdown in coolant circulation and possible engine overheating. Corrosion is a consequence of using low-quality coolant or water as a refrigerant, which gradually destroys and expands the walls of the channels. As a result, the pressure in the system drops or depressurization occurs.
Corrosion is most often caused by using low-quality coolant or water as a coolant.
Using antifreeze recommended by the manufacturer, timely replacement and periodic flushing of the cooling system will help to avoid such problems. In the most advanced cases, only replacing the cylinder block or head will help.
Water pump (pump)
The coolant pump is considered the central element of the cooling system. It is the pump that is responsible for circulating the refrigerant and maintaining the required pressure in the system. The pump itself is installed on the front wall of the engine cylinder block and is driven by a V-belt from the crankshaft pulley.
The pump ensures forced coolant circulation, maintaining operating pressure in the cooling system
Design and principle of operation of the pump
The water pump consists of:
- housings;
- rotor with impeller, bearing and drive pulley;
- covers;
- oil seal.
The operating principle of the pump is similar to that of a conventional mechanically driven centrifugal pump. Rotating, the crankshaft drives the pump rotor on which the impeller is located. The latter forces the refrigerant to move inside the system in one direction. To reduce friction and ensure uniform rotation, a bearing is provided on the rotor, and to prevent coolant leakage from the cylinder block, a seal is installed at the location of the pump.
Common pump faults
The average service life of a VAZ 2101 water pump is 50 thousand kilometers. It is usually changed together with the drive belt. But sometimes the pump fails much earlier. The reasons for this may be:
- manufacturing defects;
- incorrect tension of the drive belt;
- use of low-quality coolant;
- use of coolant whose properties do not meet the manufacturer’s requirements;
- the presence of water, dirt, and corrosion products in the cooling system.
The listed factors can have both a single and complex effect on the condition of the water pump. The result may be:
- premature failure of the bearing with possible subsequent jamming of the pump;
- pump seal wear;
- corrosion of the pump casing, cover and impeller.
The most dangerous of these situations is a jammed pump. This usually occurs when the rotor is misaligned due to improper belt tension. As a result, the load on the bearing increases sharply and at a certain moment it stops rotating. For the same reason, rapid wear and breakage of the belt often occurs. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically check its tension.
Checking the tension of the VAZ 2101 water pump drive belt
The belt that drives the pump also rotates the generator pulley. At a car service center, its tension is checked with a special device, with which the belt is pulled inside the triangle it forms with a force of 10 kgf. In this case, its deflection between the pump and crankshaft pulleys should be 12–17 mm, and between the generator and pump pulleys – 10–15 mm. In garage conditions, you can use a regular steelyard for these purposes. With its help, the belt is pulled inward and the amount of deflection is measured with a ruler. The belt tension is adjusted by loosening the generator mounting nuts and moving it to the left of the crankshaft.
The pump drive belt must have the correct tension.
Video: types of water pumps of classic VAZ models
Cooling system radiator
At its core, a radiator is a conventional heat exchanger. Due to the features of its design, it reduces the temperature of the antifreeze passing through it. The radiator is installed in the front part of the engine compartment and is attached to the front part of the body with four bolts.
The design and principle of operation of the radiator
The radiator consists of two plastic or metal horizontally located tanks and tubes connecting them. The upper tank is equipped with a neck connected by a hose to the expansion tank, and a fitting for the underwater pipe, through which heated coolant enters the radiator. There is an outlet pipe on the lower tank through which cooled antifreeze flows back into the engine.
The radiator consists of two tanks and tubes with lamellas
On the radiator tubes, made of brass, there are thin metal plates (lamellas), which accelerate the heat transfer process by increasing the area of the cooled surface. The air circulating between the lamellas reduces the coolant temperature in the radiator.
Basic malfunctions of the radiator of the cooling system
There are two reasons for radiator failure:
- depressurization;
- reduction in tube capacity as a result of clogging.
The main sign of radiator depressurization is leakage of antifreeze from it. You can restore its functionality by soldering, but this is not always advisable. Often, after soldering, the radiator begins to leak in another place. It is much easier and cheaper to replace it with a new one.
You can restore the functionality of the radiator using soldering
Clogged tubes can be eliminated by flushing the radiator with special chemicals, widely available in car dealerships.
You can remove clogged radiator tubes using special chemicals.
In this case, the radiator is removed from the car, filled with flushing fluid and left for some time. Then it is washed with running water.
Video: replacing the radiator of the VAZ 2101 cooling system
Radiator cooling fan
Under increased engine loads, especially in the summer, the radiator may not cope with its tasks. This may cause the power unit to overheat. For such situations, forced cooling of the radiator using a fan is provided.
Design and principle of operation of the fan
On later VAZ models, the cooling system fan is turned on by a signal from the temperature sensor when the coolant temperature increases critically. In the VAZ 2101 it has a mechanical drive and works constantly. Structurally, it consists of a plastic four-bladed impeller, pressed onto the hub of the water pump pulley, and is driven by the generator and pump drive belt.
In the VAZ 2101, the cooling system fan is permanently driven by the crankshaft pulley
Basic fan malfunctions
Considering the simplicity of the design and fan drive, there are few breakdowns. These include:
- belt break;
- belt loosening;
- mechanical damage to the impeller.
All these faults are diagnosed during the inspection of the fan and checking the belt tension. As necessary, the belt tension is adjusted or replaced. The latter is also necessary in case of mechanical damage to the impeller.
The fan impeller of the VAZ 2101 cooling system is mounted on the pump pulley
Heating system radiator
The heating radiator is the main unit of the stove and is used to heat the air entering the car interior. The function of the coolant here is also performed by the heated coolant. The radiator is installed in the central part of the stove. The temperature and direction of the air flowing into the cabin is regulated by dampers and a tap.
The heater radiator has the same design as the cooling radiator
The design and principle of operation of the stove radiator
The heating radiator is designed in exactly the same way as the cooling radiator. It consists of two tanks and tubes with lamellas. The differences are that the dimensions of the stove radiator are noticeably smaller, and the tanks do not have necks. The radiator inlet pipe is equipped with a valve that allows you to shut off the flow of hot coolant and turn off the interior heating during the warm season.
When the valve is in the open position, hot coolant passes through the radiator tubes and heats the air. The latter enters the cabin either naturally or is forced by the stove fan.
Main malfunctions of the stove radiator
The heater radiator may fail for the following reasons:
- clogging of the device tubes (complete or partial obstruction);
- depressurization of the radiator caused by corrosion;
- faucet malfunction (souring or leaking).
One of the main reasons for the failure of the stove radiator is clogging
Diagnosing a faulty heater radiator is not difficult. To check for clogging of the tubes, just touch the inlet and outlet pipes with your hand when the engine is warm. If they are both hot, coolant circulates normally inside the device. If the inlet pipe is hot and the outlet pipe is warm or cold, the radiator is clogged. This problem can be solved in two ways:
- replacing the stove radiator with a new one;
- flushing the radiator using chemically active substances.
Video: flushing the radiator of the VAZ 2101 stove
Radiator depressurization manifests itself in the form of traces of coolant on the carpet under the dashboard or fumes that condense in the form of a white oily coating on the inside of the windshield. Faucet leaks have similar symptoms. To completely eliminate faults, the failed part is replaced with a new one.
Video: replacing the heater radiator on a VAZ 2101
There are often faucet breakdowns associated with its souring. This usually happens when the faucet is not used for a long time. As a result, the parts of the locking mechanism stick to each other and stop moving. In this case, you should also replace the tap with a new one.
Thermostat
Thermostat is a device designed to regulate the coolant temperature in different operating modes of the power unit. It speeds up the warm-up of a cold engine and ensures optimal temperature during its further operation, forcing the coolant to move in a small or large circle.
The thermostat speeds up engine warm-up and maintains its optimal temperature
The thermostat is located on the right front part of the power unit. It is connected by pipes to the engine cooling jacket, the water pump and the lower tank of the main radiator.
The device and principle of operation of the thermostat
The thermostat consists of:
- housings;
- temperature sensitive element;
- main and bypass valves.
The main unit of this design is a thermoelement, consisting of a metal cylinder containing technical paraffin, which can expand in volume when heated, and a rod.
When the engine is cold, the main thermostat valve is closed and coolant circulates from the jacket through the bypass valve to the pump, bypassing the main radiator. When the refrigerant heats up to 80–85°C, the thermoelement is activated, partially opening the main valve, and coolant begins to flow into the heat exchanger. When the refrigerant temperature reaches 95°C, the thermoelement rod extends all the way, fully opening the main valve and closing the bypass valve. In this case, antifreeze is directed from the engine to the main radiator, and then returns to the cooling jacket through the water pump.
The thermostat causes the coolant to move in a small or large circle
Basic thermostat malfunctions
If the thermostat is faulty, the engine may or may not overheat to operating temperature in the proper time. To check the functionality of the device, you need to determine the direction of movement of the coolant on a cold and warm engine. To do this, you need to start the engine, wait two or three minutes and touch the pipe going from the thermostat to the upper radiator tank with your hand. It should be cold. If it is warm, the main valve is constantly open. As a result, the engine heats up for longer than the set time.
The higher the refrigerant temperature, the more the main valve is open
Another thermostat malfunction is the main valve sticking in the closed position. In this case, the coolant constantly moves in a small circle, bypassing the main radiator, and the engine may overheat. This situation can be diagnosed by the temperature of the upper pipe. When the indicator on the instrument panel shows that the coolant temperature has reached 95°C, the hose should be hot. If it is cold, the thermostat is faulty. It is impossible to repair the thermostat, so if a malfunction is detected, it is replaced with a new one.
Video: replacing the thermostat VAZ 2101
Expansion tank
Antifreeze, like any other liquid, expands in volume when heated. Since the cooling system is sealed, its design must have a separate container into which the refrigerant and its vapors can flow when heated. This function is performed by the expansion tank located in the engine compartment. It has a translucent plastic body and a hose connecting it to the radiator.
The expansion tank is used to collect excess antifreeze and its vapors when heated
Design and principle of operation of the expansion tank
The tank is made of plastic and has a lid with a valve that maintains pressure at 1.3–1.5 atm. If it exceeds these values, the valve opens slightly and releases refrigerant vapor from the system. At the bottom of the tank there is a fitting to which a hose is attached that connects the tank and the main radiator. It is through it that coolant vapors enter the device.
Main malfunctions of the expansion tank
More often than not, the tank cap valve fails. At the same time, the pressure in the system begins to sharply increase or decrease. In the first case, this threatens the depressurization of the system with possible rupture of pipes and leakage of coolant; in the second, the risk of antifreeze boiling increases.
You can check the serviceability of the valve using a car compressor or a pump with a pressure gauge. This is done as follows.
- The coolant is drained from the reservoir.
- A compressor or pump hose is connected to the tank fitting using a larger diameter hose and clamps.
- Air is pumped into the tank and the pressure gauge readings are monitored. The lid must be closed.
- If the valve operates before 1.3 atm or after 1.5 atm, the tank cap must be replaced.
The expansion tank cap acts as a valve
Tank malfunctions also include mechanical damage, which can be caused by excess pressure in the system. As a result, the tank body may become deformed or rupture. In addition, there are frequent cases of damage to the thread of the neck of the tank, due to which the lid cannot ensure the tightness of the system. In all these cases, the tank needs to be replaced.
Coolant temperature sensor and indicator
The temperature sensor is used to determine the coolant temperature inside the engine and transmit this information to the dashboard. The sensor itself is located on the front of the cylinder head next to the spark plug of the fourth cylinder.
The working element of the sensor changes resistance depending on the coolant temperature
To protect against dirt and technical liquids, it is covered with a rubber cap. The coolant temperature gauge is located on the right side of the instrument panel. Its scale is divided into two sectors: white and red.
The coolant temperature sensor is located next to the spark plugs of the fourth cylinder
Design and principle of operation of the coolant temperature sensor
The operation of a temperature sensor is based on changes in the resistance of the working element when heating or cooling. A voltage of 12 V approaches one of its terminals along the wire. From the other terminal of the sensor, the conductor goes to an indicator, which reacts to a decrease (increase) in voltage by deflecting the arrow in one direction or another. If the arrow is in the white sector, the engine is operating at normal temperature. If it goes into the red zone, the power unit overheats.
Basic malfunctions of the coolant temperature sensor and indicator
The temperature sensor itself rarely fails. More often than not, problems are related to wiring and contacts. When diagnosing, you should first check the wiring with a tester. If it works, move on to the sensor. It is checked as follows:
- The sensor is unscrewed from its seat.
- The probes of a multimeter turned on in ohmmeter mode are connected to its terminals.
- The entire structure is lowered into a container of water.
- The container heats up.
- The resistance of the sensor is recorded at different temperatures.
The resistance of a working sensor depending on the temperature should change as follows:
- 20°C - 3.0–3.5 kOhm;
- 40°C - 2.0–2.5 kOhm;
- 60°C - 0.65–0.5 kOhm;
- 90°C - 0.3–0.25 kOhm.
If the measurement results do not correspond to the specified data, the sensor must be replaced.
Video: replacing the coolant temperature sensor in a VAZ 2101
As for the temperature indicator, it is practically eternal. Of course, troubles happen to him too, but very rarely. Diagnosing it at home is quite problematic. It is much easier, after making sure that the sensor and its wiring are in good condition, to buy a new device.
The pointer scale is divided into two sectors - white and red
Cooling system pipes and hoses
All elements of the cooling system are connected using pipes and hoses. All of them are made of reinforced rubber, but have different diameters and configurations.
Cooling system pipes have different sizes and configurations
Each pipe and hose of the VAZ 2101 cooling system has its own purpose and name.
Table: pipes and hoses of the VAZ 2101 cooling system
| Name | Connecting nodes |
| Pipes | |
| Underwater (long) | Cylinder head and upper radiator reservoir |
| Underwater (short) | Water pump and thermostat |
| Bypass | Cylinder head and thermostat |
| Branch | Lower radiator reservoir and thermostat |
| Hoses | |
| Underwater heater | Cylinder head and heater |
| Heater outlet | Heater and fluid pump |
| Connective | Radiator neck and expansion tank |
Malfunctions of pipes (hoses) and their elimination
Pipes and hoses are subject to constant temperature loads. Because of this, over time, the rubber loses its elasticity, becomes rough and rigid, which can lead to coolant leakage at the joints. In addition, the pipes fail when the pressure in the system increases. They swell, become deformed and even rupture. The pipes and hoses cannot be repaired, so they are immediately replaced with new ones.
Over time, the pipes lose elasticity and become rougher
Replacing pipes and hoses is quite simple. All of them are attached to the fittings using spiral or worm clamps. To replace it, you need to drain the coolant from the system, loosen the clamp, remove the faulty pipe or hose, install a new one in its place and secure it with a clamp.
Video: replacing the cooling system pipes of a VAZ 2101
Normal parameters
It is difficult to say unambiguously what pressure should be in the cooling system of each car. Even on the same model with different installed internal combustion engines, the parameters may differ.
If we talk about average values, then this range is from 1.2 to 2 atmospheres. Although it is extremely rare that the indicators reach 2 atmospheres. But in the automotive industry there is an example when a pressure of 2.2 is considered the norm.
When calculating fluid pressure, the unit of measurement is usually Bars. But they are analogous to atmospheres. That is, 1 atm = 1 bar.
The internal pressure in an automobile cooling system depends on a number of factors. And not the least important role is played by what kind of coolant is poured into the radiator, what design the car’s engine has, its tightness and other nuances.
You can find out accurate information regarding the pressure level specifically in your engine from the manual and operating recommendations from the car manufacturer.
Flushing the VAZ 2101 cooling system
Whatever fluid is used, there will always be dirt, water and corrosion products in the cooling system. To reduce the risk of clogging of the jacket channels and radiators, it is recommended to periodically flush the system. This should be done at least every two to three years. Flushing the cooling system is carried out in the following order:
- The coolant is completely drained from the system.
- The cooling system is filled with a special flushing fluid.
- The engine starts and runs for 15–20 minutes at idle speed.
- The engine stops. The flushing liquid is drained.
- The cooling system is filled with new refrigerant.
As a washing liquid, you can use special compounds that are widely available on sale, or distilled water. It is strictly not recommended to use Coca-Cola, citric acid and household chemicals, as they can cause serious harm to the engine.
It is recommended to flush the system only with special products or distilled water.
How is blood pressure checked?
Quite often, motorists are interested in how to check the current pressure in the cooling system in a garage. This is not so easy to do.
For such tasks, special stands are usually used in a car service center, and complex diagnostics are carried out in different operating modes. Approximate indicators can be determined by connecting a pressure gauge to a sealed system. But such manipulations should not be carried out in a garage and without specialized equipment.
Typically, a self-check involves diagnosing the valve cover of the expansion tank. It needs to be checked for integrity, make sure there are no cracks or damage, examine the condition of the seals, etc.
There is also an alternative verification option. To do this, you will need a pressure gauge, pump or compressor. The upper pipe is removed from the expansion tank, and a hose connected to the pump is connected in its place. Pressure is created. When the peak value is reached (usually about 1.4-1.5 atm), the valve should operate.
Engine cooling system VAZ 2101
The manufacturer installed two types of gasoline engines on VAZ 2101 cars - 2101 and 21011. Both units had a sealed liquid cooling system with forced circulation of the refrigerant.
Purpose of the cooling system
The engine cooling system (ECS) is designed not so much to reduce the temperature of the power unit during operation, but to maintain its normal thermal conditions. The fact is that it is possible to achieve stable functionality and optimal power performance from a motor only if it operates within certain temperature limits. In other words, the engine should be hot, but not overheat. For the VAZ 2101 power plant, the optimal temperature is considered to be 95–115°C. In addition, the cooling system is used to heat the car interior in the cold season and heat the carburetor throttle assembly.
Video: how the engine cooling system works
Main parameters of the VAZ 2101 cooling system
Any engine cooling system has four main individual parameters, deviation of which from standard values can lead to system failure. These parameters are as follows:
- optimal coolant temperature;
- time for the engine to warm up to operating temperature;
- optimal coolant pressure;
- volume of coolant in the system.
Coolant temperature
The optimal temperature conditions for engine operation are determined by:
- type of fuel consumed;
- cylinder volume;
- design power.
For VAZ 2101, the operating temperature is considered to be from 95 to 115 ° C. The discrepancy between the actual indicators and the recommended values is a sign of a violation of the temperature regime. In this case, it is not recommended to continue driving the car.
Engine warm-up time
The manufacturer-regulated time for warming up the VAZ 2101 engine to operating temperature is 4–7 minutes, depending on the time of year. During this time, the coolant should heat up to at least 95°C. Depending on the degree of wear of engine parts, the type and composition of the coolant and the characteristics of the thermostat, a slight deviation of this parameter (1–3 min) towards an increase is possible.
Operating coolant pressure
The magnitude of coolant pressure is the most important indicator of the performance of the SOD. It not only promotes forced circulation of the refrigerant, but also prevents it from boiling. From a physics course we know that the boiling point of liquids can be increased by increasing the pressure in a closed system. Under normal conditions, coolant boils at 120°C. In a working VAZ 2101 cooling system under a pressure of 1.3–1.5 atm, antifreeze will boil only at 140–145°C. A decrease in coolant pressure to atmospheric pressure can lead to a deterioration or cessation of fluid circulation and its premature boiling. As a result of communication, the cooling systems may fail and lead to engine overheating.
Coolant volume
Not every owner of a “penny” knows how much refrigerant fits into the engine of his car. When replacing fluid, as a rule, they buy a four- or five-liter coolant canister, and this is usually enough. In fact, the VAZ 2101 engine holds 9.85 liters of refrigerant, and when replaced, it is not completely drained. Therefore, when replacing coolant, you need to drain it not only from the main radiator, but also from the cylinder block, and you should immediately buy a ten-liter canister.
The role of the valve cover
Not everyone understands how important a role is played by a seemingly ordinary cap that closes the expansion tank for filling the coolant.
In fact, it is a complex device. Modern lids are equipped with two valves at once. These are exhaust (steam) and inlet. They are also called bypass and atmospheric, respectively.
In fact, this is a special valve that is responsible for the pressure inside the system in question. As the internal temperature rises as the engine heats up, the pressure also rises. If at some point the excess is not dumped, then the seal will be at risk. Elements can simply tear apart from the inside. Usually it all starts with damage to the most vulnerable elements in the form of seals and seals. A rupture of the expansion tank itself, hoses and pipes cannot be ruled out.
The valve cover directly on the expansion tank helps to remove excess pressure and pump it in as needed.
Each valve has a certain response threshold. Its mechanism is designed in such a way that when a certain value is reached, it opens or closes. This relieves excess pressure or sucks in atmospheric air.
When parked for a long time, the engine cools down, the liquid cools, which causes a rarefied atmosphere to form inside. This indicates insufficient pressure inside. To compensate, the valve cover opens and air is sucked in. Thus, the pressure is normalized.
What should normal blood pressure be?
The pressure in a car's engine cooling system cannot be increased indefinitely, since too high will eventually lead to rupture of its weakest elements. Normally it should be 1.2–1.4 atm. As the antifreeze heats up and reaches its boiling point, the pressure reaches a critical value. At this moment it must be reset in order to avoid failure of the cooling system first, and then jamming of the pistons in the cylinders, and as a result, breakdown of the latter.
To maintain pressure within acceptable limits, an air valve is installed in the cap of the expansion tank (for VAZ-2110) or radiator.
It has a simple device:
- inside the case, which has identical holes at the top and bottom, there is a ball slightly larger than the holes.
- The weight of the ball is selected in such a way that when a pressure reaches 1.5 atm, it rises, opening the lower hole and releasing air from the cooling system into the atmosphere.
- At the same time, while the coolant is not heated, the ball closes the lower hole, and the upper one remains open, providing an influx of atmospheric air and ensuring faster heating of the antifreeze.
Nowadays, the most common version of the lid is one that has two valves (inlet and outlet). As the pressure rises, the release valve opens and the excess is discharged from the system. When it falls below atmospheric pressure, the intake begins to work.
Often, due to malfunction of the valves, the system ceases to function correctly. Moreover, even a new cover does not guarantee that everything will work as expected. Car owners often complain that the expansion tank bursts. This can be caused either by improper operation of the lid valves or by a defect in the tank itself (thin walls).
The actuation moment of the valves directly depends on the stiffness of the springs, so craftsmen regulate the actuation time by cutting off excess turns from it.
What causes excess pressure
The problem of excess pressure in engine cooling systems has not completely disappeared, despite the introduction of new technologies. That is, the engine can still boil.
It is too much pressure and forced pressure on the internal walls that provoke all sorts of problems, including boiling. To prevent a malfunction in your engine cooling system, you need to quickly solve the problem.
You won’t have to look long for the reasons why there is excessively high pressure in the cooling system of a modern engine. You need to look for it in the steam-air valve mounted on the cover of the expansion tank used to fill the cooling liquid.
Sometimes the reasons lie in the expansion tank itself, which becomes jammed or clogged. But mostly the culprit is obvious. It is because of its loss of performance that too much pressure arises inside the engine, and this can greatly harm the cooling system.
The most correct solution in such a situation would be to replace the cover. There is simply no alternative. But since the valve cover is inexpensive, the car owner will definitely not go broke buying and replacing it.
Some people try to restore the valve when it is stuck due to contamination. For flushing, use liquid to clean carburetors. If this does not help and the increased pressure continues to persist in the cooling system, it will be better for your engine to purchase a new similar cap. Otherwise, don’t be surprised later why the engine boiled, the tank ruptured and serious and expensive repairs were required.
To maintain optimal operating condition of the cooling system, it is recommended to replace the valve cover every 2 years.
Excessive blood pressure is considered a more dangerous phenomenon than its deficiency. But even in this case there are some threats.
Let's sum it up
So we figured out why there is pressure in the engine cooling system, why it can be excessively high or, conversely, low. There is often nothing complicated about checking it yourself, although a lot depends on the car. For example, it happens that the coolant temperature sensor fails. It can provide incorrect data to control devices, thereby misleading the driver. It can show both a high temperature of the power unit and, conversely, a low one. But this will not mean that the system is not working correctly.
If there are any breakdowns in the cooling system, they must be repaired as soon as possible. It is advisable not to operate a vehicle with a stuck cover or thermostat. After all, for some engines overheating is fatal, and major repairs are not cheap at all. In general, it is worth regularly checking the coolant level in the system to ensure that there are no leaks or other defects. It is also recommended to periodically clean the radiators from dirt, as this can cause increased engine temperature.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Source
Reasons for lack of pressure
It even happens that there is no pressure in the cooling system, which can also cause certain troubles.
There are probable reasons for this situation. They consist in violating the tightness of the system. This will require special equipment to find the problem area. Although sometimes in garage conditions ordinary folk methods are used. By visually searching for the breakdown location, it is sometimes possible to find the area where the depressurization occurred.
First, the condition of the air valve is checked. If it hangs in the open position, the pressure in the system will not increase. Hence the boiling of the engine and its overheating.
If the valve is working normally, then there is a leak in the system. It needs to be found and eliminated. Sometimes antifreeze comes out through damaged pipes and hoses. A worn-out cooling radiator or heater core could also be the cause. The most unpleasant moment is when antifreeze enters the engine. The culprit is a broken cylinder head gasket.
You can also check the system for leaks in a garage. To do this, you need to remove the upper pipe from the expansion tank, and in its place connect a hose with a pump and a pressure gauge. The pump can be replaced with a compressor. Next, begin to build up pressure and watch where the antifreeze will flow from.
System leakage
An even more popular problem among motorists is lack of pressure. This may happen due to:
- stuck air valve;
- presence of leaks in the cooling system.
Accordingly, identifying the problem will not be difficult. The first thing you can do is look at the antifreeze level on a cold engine. If it does not change from trip to trip, then there are no leaks in the system. The second step is to replace the air valve with a new one. After this, the pressure should normalize and the antifreeze will not overheat. Very often, increased pressure in the engine cooling system causes it to then drop. This is partly due to the wedging valve. Sometimes it works, sometimes it doesn't. As a result, pressure builds up, which can cause a leak to form in a weak spot, and then the seal disappears.