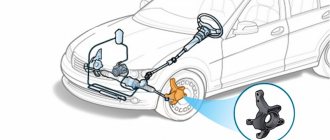
The differential is rightly called one of the most important elements of a car transmission. It is he who can ensure the rotation of wheels at different angular speeds. The energy for rotation, as you might guess, is taken from the engine. Previously, in the “Useful Tips” section, Avto.pro already published material on the rear axle gearbox. So, in this material the differential was mentioned only in passing, but it was said that this device is very complex and requires a comprehensive analysis in a separate article. Well, you are reading this very article. We suggest you familiarize yourself with the structure of the differential, the principle of its operation, as well as the main malfunctions.
Differential purpose
An automobile differential is designed to distribute the torque received from the driveshaft between the wheels of the front or rear axle. The latter depends on the type of drive . This ensures that the wheels rotate without slipping - this is a very important point, although we will touch on it later. It may seem that a regular gearbox will do the job just fine. In fact, it turns out that the gearbox turns out to be completely ineffective in cases where unequal load is applied to each of the drive wheels. For example, one wheel hits an obstacle, while the second one moves on a flat surface. It follows from this that the transmission needs a special unit that redistributes torque based on road conditions. This is the differential.
As with gearboxes, differentials can be located in different locations. Depending on the vehicle drive, the following differential layouts are distinguished:
- Front-wheel drive - the differential is mounted in the gearbox housing;
- Rear-wheel drive - the mechanism is part of the drive axle (often this element is simply called a gearbox);
- All-wheel drive - there are two options: location in the housing of one of the axles or in the transfer case.
In the absence of a differential or its complete failure, the car sharply loses maneuverability .
Motor transport at the beginning of the last century especially suffered from this - the first models of trucks and production cars had difficulty overcoming obstacles or went into an uncontrolled skid. The first differentials began to be installed on Volkswagen cars. They differed favorably from American, English, French and Italian cars in that in their transmission the torque was distributed relatively evenly between the wheels.
More about the device
Spare parts for Mazda 2
Steering rack/mechanism oil seal (see standard sizes)
1.25 FUJA
Spare parts for volkswagen sharan
Hydraulic compensator (hydraulic pusher), valve pusher 2.0 TDI CFFA
The structural basis of the differential is a planetary gearbox. We remind you that the gearbox is essentially a pair of interlocking gears - small and large diameters with different numbers of teeth. When a rapidly rotating small gear is meshed with a larger one, the latter rotates at a noticeably lower speed. For example, if the first gear has 50 teeth , and the second has 100 teeth , then the second gear rotates twice as slow as the first. When rotating, the larger gear makes one revolution when the first one makes two revolutions .
A planetary gearbox, otherwise called a differential gearbox, performs only one task - converting and transmitting torque. Unlike the more familiar “gear-gear” scheme, in planetary gearboxes the transmission is based on the interaction of three main and several more auxiliary elements. The uniqueness of planetary gearboxes is that they allow you to choose between several gear ratios and have two degrees of freedom. This “variability” of planetary gears made it possible to use them in automobile gearboxes .
So, we figured out what a planetary gearbox is. The differential uses the advantages of such a mechanism to the fullest. The main elements of a car differential are:
- Semi-axial (sun) gear;
- Cup;
- Driven gear and main gear drive gear;
- Satellites.
It is more correct to call the car differential cup a housing. Torque from the power unit through intermediate components (including through the main gear) is received by the housing. Next, the torque is transmitted to the semi-axial gears through satellites. It is the satellites that play the role of planetary gears - they transmit torque and ensure normal connection of the housing with the semi-axial gears. Usually there are two satellites (passenger vehicles) or four (trucks, off-road vehicles, etc.). As you may have guessed, side gears are responsible for transmitting torque to the drive wheels through the axle shafts.
Many car enthusiasts wonder: what is the difference between a gearbox and a differential. To put it simply, a gearbox is just a gear pair that changes (reduces) torque. The differential is a whole set of gears that, roughly speaking, divide the torque in a certain ratio between two consumers. At the same time, the concept of “rear axle gearbox” covers both the gearbox and the differential - both of these mechanisms can be located in the same housing, but they perform their specific tasks.
Differential operating modes
It is impossible not to tell us about the operating modes of the differential. Let us immediately note that differentials are divided into symmetrical and asymmetrical. A symmetrical mechanism is capable of transmitting torque to the axes in equal proportions. Their work does not depend on the angular speeds of the drive wheels . An asymmetrical mechanism can “share” the torque, as a result of which it can be installed between the drive axles of the vehicle. The symmetrical cross-axle differential operates in one of three modes:
- Rectilinear movement;
- Entering a car into a turn;
- Driving on atypical surfaces, somehow slippery.
In the first mode, both car wheels overcome the same road resistance. From the main gear, torque is transmitted to the differential housing (cup). The satellites shift without engaging with the semi-axial gears and transmit torque to the drive wheels. There is no difference in the torque perceived by the wheels. In the second mode, the following is observed: the outer wheel, i.e. distant from the center of rotation, encounters much less resistance than internal. internal semi-axial gear of the differential slows down, which leads to rotation of the satellites against its axis. As a result, the rotation speed of the outer side gear will become higher. Note that the sum of the side gear speeds is always twice the speed at which the final drive gear rotates.
The third operating mode of the differential is especially interesting. When driving on a slippery surface, one of the car's usual wheels encounters a lot of resistance, and the second one even begins to slip. In this case, the differential will increase the rotation speed of the slipping wheel, and reduce the speed of the second one. This leads to a stalemate: one wheel has no traction and its torque is increased by the differential, and the second wheel, which has traction, receives no torque at all. Because of this, a car caught, for example, in a swamp, will not move - only the suspended wheel . The problem can be solved by locking the differential.
Signs of problems with the machine
Of course, to accurately diagnose automatic transmission problems, you will have to contact a professional service center. However, there are visible signs of automatic transmission malfunction or structural failure. Let's look at some warning signs and obvious malfunctions:
- The automatic transmission does not change gears. This is definitely a noticeable problem with the box. In this case, the speed may not turn on at all and remain neutral. But most often the car switches to first gear in position D. In most cases, it is accompanied by characteristic sounds and the car shaking;
- automatic transmission slipping. If the transmission slips, it is immediately noticeable: the car has difficulty picking up speed when the speed increases, and makes a characteristic sound when the gear is reset. If you notice this, contact the service;
- if there is a malfunction in the valve body, the car begins to move with characteristic jerky jerks;
- overheating of the transmission, a small amount of special fluid in the box, insignificant pressure of internal lubrication - these are direct signs of a failure. However, they are available on machines with appropriate sensors or instruments.
It is worth saying that in general, any unpleasant and uncharacteristic sound is a reason to contact a specialist . This also applies to all kinds of disturbances in the operation of the machine. Fortunately, today an initial cursory inspection of a car is not so expensive.
Even if you don’t see any obvious reasons for calling for repairs, have your car serviced and inspected regularly. It is not recommended to increase maintenance intervals or neglect them altogether. Yes, you will save money at first, but in the future, problems with the box in particular will cost you a pretty penny.
More about differential lock
A situation was described above in which the movement of the car becomes impossible - one wheel rotates as if idling, and the second perceives too little torque. This is a serious problem with any center differentials. Don't think that it's only about symmetrical differentials. Useful in all other cases, such mechanisms turn out to be harmful when trying to remove a car from deep snow, mud or when driving on ice. by blocking them , which becomes possible if:
- The differential cup is connected to one of the two axle shafts;
- The rotation of the satellites is limited.
The blocking can be complete or partial. When fully locked, the differential elements are rigidly connected, which ensures full transmission of torque to the wheel with the best grip. With partial blocking, only part of the torque is transferred to such a wheel, while the slipping wheel continues to rotate. The difference between the torques is determined by the locking coefficient. In a symmetrical differential, under normal conditions, the locking coefficient is equal to one, since the torques on each wheel will always be equal. But when it is blocked, the coefficient will vary between 3 and 5.
The differential lock can be either manual or automatic. Electronic locking differentials have proven themselves to be excellent. It works in tandem with the vehicle's stability control system. Its sensors monitor the vehicle's movement parameters and, if necessary, the control unit gives a signal to lock the differential . This allows you to effectively control the car both when turning and on slippery surfaces.
tips
- After inspection, you will have to replace the cap, close the system and fill with differential fluid. NEVER attempt to drive a vehicle without differential fluid. Get more information about maintaining your differential with my eHow articles How to Drain a Rear Differential and How to Fill a Rear Differential.
- Learn about the design of differentials and how each component and assembly mechanism works in Automotive Manual Transmissions and Powertrains, a textbook by William H. Crouse and Donald L. Anglin, published by McGraw-Hill.
Differential faults
Since any differential is a collection of axles and gears, there is nothing surprising in the relatively frequent failure of this unit. It is operated under very harsh conditions, so failure can occur at the most unexpected moment. However, some things will indicate to the car owner the need for maintenance . In particular:
- Increased noise;
- The appearance of knocks and impacts;
- Lubricant leak.
The most serious malfunction is a jammed bridge. This only happens in cases where the car owner ignored the problem of increased differential noise, regular knocking and lubricant leakage. Often the latter indicates the need for inspection by a specialist in a car service. We recommend measuring the temperature of those transmission components that include the differential. For example, the crankcase - its temperature should be between 50-60°C . It is also recommended to check the condition of the lubricant and add oil if necessary.
Oil leakage can cause differential failure. Usually it flows through oil seals and special gaskets, which require urgent replacement . If there is a shortage or severe contamination of oil, the mechanisms begin to make noise and wear out at a high rate. It is extremely important for a car enthusiast to avoid dry friction - it will cause damage to satellites, bearings, and wear of gear teeth. Often, a differential malfunction can be identified even before a visit to the service station. For this you will need a partner. Here's what to do:
- Put the car in neutral gear;
- Raise the drive axle on a jack;
- Spin the wheel first in one direction and then in the other direction;
- Ask your partner to do the same with the other wheel;
- If the wheels rotate in both directions without noise, the differential is working.
Even after such a check, the car owner should contact a specialist for further diagnostics. However, some problems can be solved with independent repairs. So, for example, the unit can be disassembled, washed in gasoline, and then replaced with worn bearings, satellites and seals - most often fail . But if the cup, spline joints and gears are damaged, it is often necessary to replace the entire assembly and adjacent parts.
Table of signs and causes of automatic transmission malfunction
The table of typical automatic transmission faults , which is located at the bottom of the article, presents the most common automatic transmission faults .
| Signs | Cause |
| The car is not moving forward. It's slipping. Reverse speed operates in operating mode. |
1. Worn friction discs, forward clutches.
2. Worn or broken clutch piston cuffs.
3. Clutch rings are worn
4. One of the valve body valves is stuck.
Finding a New Differential
We hasten to assure you: finding a differential is very easy. But there is also a sad fact: a new differential costs a lot of money. The price can range between $300 and $1,000. If only for this reason, it is categorically not recommended to ignore a differential malfunction - it is cheaper to repair . However, even with some differential elements, such as satellites, you can cost a pretty penny. An assembled unit or its individual components are searched by:
- The parameters of your car (taking into account the year of manufacture and engine parameters);
- VIN code;
- Unit and parts code.
Typically, car enthusiasts do not know the code of the required spare part until the actual installation of the unit or its individual elements. For this reason, we recommend starting your search by vehicle parameters. Despite the fact that automobile differentials are created according to approximately the same schemes, their interchangeability is a big question. The same rear axle gearbox can have several versions for the same car model, and a car enthusiast can even install a gearbox with a “non-native” gear ratio. True, the result will probably not please him. But it’s not worth the risk of buying a differential for another car. It is also not recommended to buy a used differential, since its key elements may be severely worn out.
What's the result?
As you can see, when selecting a used car with an automatic transmission, it is important that the automatic transmission works flawlessly. Normally, the automatic transmission operates softly and smoothly, without slipping. The thrust from the engine should be transmitted to the wheels predictably, without obvious losses, the car should not significantly overuse fuel (provided there are no other problems with the engine, power system, etc.).
Finally, we note that even if at first glance the operation of the gearbox does not cause suspicion or criticism, it is optimal to visit a service station before purchasing a car for professional diagnostics of the automatic transmission and the entire car. This approach makes it possible to detect hidden defects and breakdowns of the machine, engine and other components and assemblies, subject to their availability, at a relatively low cost.
Why the automatic transmission kicks, the automatic transmission jerks when changing gears, jerks, jerks and impacts occur in the automatic transmission: the main reasons.
Automatic transmission slipping when changing gears: the main reasons why an automatic transmission slips. Box diagnostics, troubleshooting.
When switching to mode D or R, the automatic transmission jerks, a shock occurs in the automatic transmission: causes of failures and malfunctions. What to look for when diagnosing.
High oil level in the automatic transmission: consequences of oil overflow into the automatic transmission. Why pouring oil into an automatic transmission is dangerous for the unit, recommendations.
What can a low oil level in an automatic transmission lead to: the consequences of a low oil level in an automatic transmission. What to pay attention to.
A jolt in the automatic transmission, the appearance of jerks when shifting gears of the automatic transmission, jolts of the automatic transmission in place: the main reasons for such malfunctions of the automatic transmission.
Conclusion
The differential is an important component of a car transmission. If the gearbox receives, converts, and then transmits torque to the car wheels, then a unit such as a differential ensures the normal transmission of this torque and is responsible for the driving performance of the vehicle. For example, it provides maneuvering on and off the highway. Without a differential, it is impossible to create either a truck or a passenger car. And if you try, its operation will become very dangerous. At least from the very moment the car reaches high speed or begins to turn.
Troubleshooting methods
We looked at the causes and signs of machine malfunctions. Now it’s worth saying a few words about repairs. Let’s say right away that there are two methods for solving transmission problems:
- Self-repair or prevention.
- Contacting specialists.
Needless to say, the first option is cheaper and preferable for every car enthusiast. However, in reality, not all operational problems can be solved with your own hands. For example, if the automatic transmission does not change gears or slips, then only a qualified specialist will assist the car.
Let's select specific examples for both situations.
Independent solution
We present a number of correctable errors in the appropriate form: general cause – possible problems – ways to eliminate them.
1. Misalignment or malfunction of the gear shift component:
- the car moves in gearbox mode P;
- The speed letter on the panel does not match the set one.
Remedy: Diagnosis and replacement of the faulty part; you can repair it yourself according to the instructions provided.
2. Oil leakage from the automatic transmission. Common problem with the box:
- the fastenings of the mechanisms inside the transmission come off on their own;
- destruction or unsuitability of oil seals and gaskets.
DIY repair methods:
- tightening bolts, purchasing and installing new seal rings;
- lowering the oil level in the automatic transmission.
3. Noise or uncharacteristic sounds when the box is operating:
- the car changes gears itself;
- switching positions occurs with great difficulty;
- The car does not respond to switching and does not move.
Remedy: Measure the oil level and add the required amount.
Only the main cases of minor breakdowns inside the automatic transmission are given. If your situation fits at least one of the points, read the instructions for the car. Inside you will find step-by-step steps to solve the problem. In the future, it is recommended to turn to professionals.
Repair in service
We will describe the problems that require contacting a qualified workshop.
1. The car remains in place during any action with the gearbox mechanism. There is no reaction or the slightest movement.
- little oil in the system;
- valves or rings are clogged;
- hydraulic system malfunction;
- filter failure;
- Main gear malfunction or wear.
2. Shocks and impacts when changing gears.
- coupling wear;
- hydraulic unit valve malfunction;
- Valve spring damage.
3. Unhealthy noise in the differential area of the car
- bearing or gear wear;
- some mechanisms jam or become loose.
Many problems are more often identified at the stage of disassembling the transmission. Thus, a trip to the service center is a priority for a working car.