Checking the ignition coil on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
If such malfunctions occur in the operation of the engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars such as the disappearance of a spark or a weak spark, unstable idling, inability to adjust idle speed, difficult starting or impossibility of starting the engine, failures and jerks when starting and in motion, etc., It makes sense to check the functionality of the ignition coil.
Required Tools
- 8 mm spanner or open-end wrench
— a tester (multimeter or similar device) with an ohmmeter mode (preferably also a megohmmeter)
Preparatory work
You can check the ignition coil on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars without removing it from the car.
- remove the negative terminal from the battery
- disconnect the high-voltage wire from the ignition coil
- disconnect the wires leading to the two terminals of the coil
To do this, use an 8 mm wrench to unscrew the nuts securing the wires to terminals “K” and “B”. We disconnect the wires, remembering their position, so as not to confuse them when installing them back.
Checking the ignition system coil of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Check the serviceability of the primary winding of the ignition coil
Checking the primary winding of the ignition coil of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099
To do this, connect one tester probe to terminal “B” and the second probe to terminal “K” - the terminal of the primary winding. We turn on the device in ohmmeter mode. The resistance of a serviceable primary winding of the ignition coil should be close to zero ( 0.4 - 0.5 Ohm ). If it is lower, then there is a short circuit, if higher, there is a “break” in the winding.
— Check the serviceability of the secondary (high-voltage) winding of the ignition coil
Checking the secondary winding of the ignition coil of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099
To do this, connect one tester probe to terminal “B” of the ignition coil, and the second probe to the terminal for the high-voltage wire. We measure resistance. For a working secondary winding it should be 4.5 - 5.5 kOhm .
— Check the insulation resistance to ground
For such a test, it is necessary that the multimeter has a megohmmeter mode (or a separate megohmmeter is needed) and can measure significant resistance.
To do this, we attach one tester probe to terminal “B” of the ignition coil, and press the second probe to its body. The insulation resistance must be very high - 50 mOhm or higher.
If at least one of the three checks shows a malfunction, the ignition coil should be replaced.
Notes and additions
— Ignition coils installed on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars can be of two types: dry with a closed magnetic circuit (3122.3705) and oil-filled with an open magnetic circuit (8352.12, 027.3705, 27.3705, 27.3707-01, ATE1721). The winding resistances for them are slightly different. Coil 3122.3705 – primary winding 0.43±0.04 Ohm, secondary 4.08±0.4 kOhm. Coils 8352.15, etc. – primary winding 0.42±0.05 Ohm, secondary 5±1 kOhm. Measurements were carried out at +25 degrees.
Twokarburators VK - More information on the topic in our VKontakte group, on Facebook Twokarburators FS , in Odnoklassniki - Twokarburators OK and in Yandex Zen - Twokarburators DZ
More articles on the ignition system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— The procedure for connecting high-voltage wires to the distributor cover on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Malfunctions of the distributor of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Checking high-voltage wires on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Setting the ignition timing on the engines of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Comparative test repair
— Checking the ignition coil of the ignition system of carburetor engines of VAZ 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107 cars
Contactless ignition, features of structure and operation
The entire ignition system on the VAZ 2108 includes several elements. Each of them performs its own function. Such elements include:
- ignition distributor sensor;
- switch;
- ignition coil;
- candles;
- egnition lock;
- high voltage wires.
The distribution sensor is also called a Hall sensor. This is a vacuum device that has a centrifugal advance regulator. A small electronic sensor is built inside it, with the help of which the pulses are regulated. The 4-spark unshielded distributor design is very easy to use.
The sensor contains an integrated circuit. It is capable of converting potential differences into voltage pulses of polarity with a “-” sign. This occurs due to the Hall effect: a transverse electric field is formed in the semiconductor plate. They are supplied to the ignition system when it is exposed to a magnetic field.
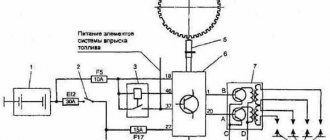
Diagram of a non-contact ignition system: 1 - non-contact sensor; 2 — ignition distributor sensor; 3 — spark plugs; 4 - switch; 5 - ignition coil; 6 — mounting block; 7 - ignition relay; 8 - ignition switch
The electronic ignition switch is capable of cutting off the current in the initial circuit of the ignition coil. VAZ 2108 cars use A-17DV-10 or FE65R spark plugs, which are produced in Slovenia. A built-in mechanism that suppresses interference can extend their service life.
The VAZ ignition switch is attached to the steering shaft bracket. It is located under the control panel and is equipped with a restart lock. It also has an anti-theft system built into it. In order to check the VAZ ignition switch, it is enough to gradually turn it on and test it in each operating mode, while monitoring for problems.
The ignition coil of the VAZ 2108 is sealed and filled with oil. It has an open magnetic circuit. The vacuum regulator can change the ignition parameters. This process directly depends on the load on the engine. When it is too large, ignition should occur later, and vice versa, when the load is small, it should happen earlier.
The operation of the vacuum regulator diaphragm depends on the vacuum, which is transmitted from the area located above the throttle valve of the first chamber of the carburetor. If the damper is slightly open, the diaphragm retracts and turns the support plate located on the sensor in the direction of rotation of the roller. In this case, the voltage advance increases.
Further opening of the damper with increasing load will cause the spring, pressing the diaphragm to its original position, to rotate the sensor support plate in the direction of rotation of the roller. This will cause the ignition timing to decrease.
Ignition coil device for VAZ 2108
Ignition coils for each individual car model have their own nuances. On VAZs it is placed in the engine compartment, right under the hood. Externally, it is a metal cylinder (also called a bobbin), inside of which a simple system is hidden: a transformer with a steel core inside, located between two windings. The bobbin itself is secured to the left side of the mudguard using long pins.
Note that the connection diagram on VAZs is one of the most complex when compared with other cars. But this, in many ways, guarantees the reliability and good performance of VAZs.
Features of the operation of different ignition systems
Ignition on the VAZ 2109 is necessary to ignite the air-fuel mixture when starting the engine. If the ignition does not work correctly, the engine will start and run intermittently, and its power during start-up and acceleration will noticeably decrease. In addition, fuel consumption will be noticeably increased. The conclusion from this is that the correct operation of the ignition system should be constantly monitored.
It’s worth mentioning right away the differences in the ignition design of “nines” with different types of fuel supply. Their SZ is similar, but they differ in the elements of electric charge distribution.
- In “nines” equipped with a carburetor, there is a coil and a distributor.
- For systems with an injector, an ignition distribution module consisting of several coils and an electronic controller is installed.
The second difference is how the system works. In cars with an injector it is not required, but in VAZs with a carburetor you have to do it manually.
In nines, two types of ignition systems are used:
- contact;
- contactless with transistors.
The first is installed in carburetor “nines”, and the second in injection ones. Thanks to the use of contactless ignition, the system has the following advantages:
- Working with a Hall sensor, which makes the system more stable and increases its overall efficiency.
- The absence of contact with the working parts and elements of the system increases the service life of the elements and makes maintenance of the circuit components easier.
- Excellent spark distribution between spark plugs.
- Generating a powerful spark, which prevents system failures.
- Fuel economy.
- Works even with low battery charge.
Over time, the contact type SZ has practically ceased to be used, so from now on we will focus on the contactless analogue.
VAZ 2109 ignition coil device
The photo shows a VAZ 2109 ignition coil, which is needed to obtain a high-quality spark on the spark plug electrodes.
Regardless of whether an injector or carburetor is installed on a one and a half liter Nine engine, the ignition system is made according to a prehistoric distributor type. On the one hand, this is good, it costs less, but on the other hand, it affects the service life of the parts. The more elements in the system, the higher the likelihood of failure of the entire ignition system.
An ignition coil, or module, is necessary to obtain a high-quality spark at the spark plug electrodes. It is capable of delivering high voltage pulses that will provide a discharge between the spark plug electrodes. Roughly, this is a small transformer that operates not in a constant, but in a pulsed mode, which allows you to convert car 12 volts into a huge 20-30 thousand volts at the output. To transmit a pulse of such enormous voltage, high-voltage wires are used, which can sometimes also slip a pig. The operating principle of this type of ignition system is simple - the distributor, or distributor, receives a low-voltage pulse from the on-board network, supplies it to the ignition coil, which transforms it into a high-voltage pulse. The distributor, at its own discretion, distributes a spark to the cylinders, according to the order of operation.
Structurally, a simple ignition coil is made of two windings - primary and secondary, wound on a magnetic circuit. The primary is wound from a thicker wire and with fewer turns, while the secondary winding has a thin wire and more turns. High voltage is generated as a result of electromagnetic induction and the accumulation of electromagnetic charge, and the transfer of high voltage charge occurs when the primary winding is turned off. In some powerful sports engines, to improve the reliability of spark formation, dual remote ignition systems were installed, which minimized the risk of detonation and made engine operation more stable. These ignition systems have two spark plugs per cylinder.
Video tutorial about why there is no spark in the VAZ 21099