What are the differences between spark plugs?
Spark plugs provide the current discharge necessary to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber of the cylinders. The better the quality of the spark coming from them, the more powerful the operation of the “engine” and the lower the risk of incomplete combustion of the mixture, and therefore engine wear. The types of spark plugs depend on the design features of the engine: requirements for thermal data, the pitch of the connecting thread, and the number of electrodes. When choosing this part, you need to be aware of what spark plugs are available in order to choose the best option for your car.
What are the Best Spark Plugs in 2021 ()
Which spark plugs are best for your car ? Surely every car owner has asked this question at least once. After all, the choice is influenced by several factors - the size of the spark plug, the heat rating, its type, the size and type of engine (carburetor/injector), the fuel used (gas/gasoline) and so on. You should also take into account the car manufacturer's recommendations.
How they work
The general structure and operating principle are the same:
Depending on the material of the electrodes. Since high electrical conductivity must be present, the following metals are used:
Silver, gold, and platinum coatings that enhance electrical conductivity are allowed, but these materials are used less frequently due to their high cost.
Depending on the heat number. Taking into account thermal parameters, there are “hot” and “cold” spark plugs:
Depending on the engine type. When choosing a part, it is equally important to understand the difference between spark plugs for a carburetor and an injector:
In both cases, spark plugs are used, but in the case of an injector, variations are possible. One of the important parameters for classification is the number of valves in the power unit. What is the difference between 8-cl and 16-cl spark plugs? First of all, the electrode material: for 16-cell, platinum or iridium is used. 8-cl. has a larger thread diameter. There is also a difference in the heat rating: for 16-cl it is higher, so they are more suitable for an injector.
Is it possible to install spark plugs from an injector on a carburetor engine?
What are you doing? Do you do engine repairs? Damn, I asked so many questions.
There are no such spark plugs for this or that, the spark plugs are marked and put them accordingly, they receive power from coils that produce voltage from 18 to 23 thousand volts, so select one for the coil that you have differently or there will be a weak spark or they will often come out building, and the engine runs poorly, on “hot” and “cold” spark plugs
They are not divided into engineers. and carb. There is a marking, we put it according to it.
in principle, you can only reduce the gap on the injector 1-1.1 and on the carburetor 0.7-0.8
How to choose candles
When determining the required types, you should be guided by the following characteristics, which depend on the characteristics of the motor:
It is important to pay attention to the quality of the fuel used. Is it worth taking iridium spark plugs, which supposedly can withstand a mileage of 60 thousand km? There is no definite answer, because it is unknown how they will behave in a particular motor. Therefore, in the absence of proper experience, it is better to carry out diagnostics from specialists.
The differences in spark plugs are associated with the rapid evolution of the automotive industry: new, more powerful models are created with new requirements for parts.
The car market is filled with a lot of manufacturer brands. The biggest difficulty is not only to choose the right ones according to the characteristics, but also to choose a manufacturer of high-quality spark plugs.
Source
What are the dangers of choosing the wrong candles?
There is a wide range of spark plugs on the automotive spare parts market, which causes some inconvenience for car owners when selecting the appropriate model. The main difficulties are related to the fact that each engine is designed for a specific modification of spark plugs. When installing incompatible options, the following problems may occur:
Other types of malfunctions that negatively affect the operating comfort of the vehicle cannot be excluded.
How to choose the right spark plugs
An error in choosing spark plugs can “kill” the engine. Spark plugs can affect fuel consumption. There are “incompatible” spark plugs and high-voltage wires. In this article, we'll look at what you really need to know and consider if you service your car yourself. After all, this small device, which looks so simple, is in fact a complex and high-tech product with strictly adjusted dimensions, made from materials specially designed for candles.
Spark plug device
Device
The candle is assembled in a metal case, which has a threaded part (thread diameter from 8 to 18 mm) and a hexagon (from 13 to 25.4 mm). A ceramic insulator is installed in the housing, with an electrode running through the center. The lower part of the insulator forms a thermal cone, which is placed on a heat sink for better heat removal. Depending on the design, a resistor or glass sealant is placed between the central electrode and the contact rod. The assembled insulator is rolled into the housing. In the lower part, one or more side electrodes are welded to the end of the housing.
“Hot” and “cold” or what is the heat rating
The part of the spark plug that is inside the combustion chamber must have a strictly defined temperature when the engine is running at full power - from 500 to 600 degrees Celsius. Engines with different degrees of boost have different thermal load, based on which the size of the thermal cone and the contact area between it and the housing are selected.
If the temperature is lower, the candle will not “self-clean” and will become covered with soot. After some time, the electrodes will close and the spark plug will stop working. This happens when the installed spark plugs are too “cold” - they have too high a heat rating: for example, if instead of A17 you install A23, the engine “doesn’t like” such spark plugs, it will begin to have difficulty starting, often “triple”, and shake at idle. The engine loses power and gasoline consumption increases. This is, of course, bad.
It is much worse when spark plugs that are too “hot” are installed in the engine, that is, those with a lower heat rating. Due to the high temperature of the electrodes and the thermal cone of the insulator, the combustible mixture, entering the cylinder, is ignited not by a spark, but by the hot parts of the spark plug. This happens “spontaneously” - sometimes earlier, sometimes later, the engine suddenly loses power, runs after the ignition is turned off, and the valves and piston may “burn out.”
Highly accelerated, high-speed engines are usually equipped with “cold” spark plugs. They feel great under heavy loads, but long periods of idling or light loads will lead to the formation of a layer of carbon deposits.
Engines with an average degree of boost, for example VAZ engines, require spark plugs with an average heat value.
Low-speed, unboosted engines are equipped with spark plugs with low heat ratings – “hot”.
What you need to know about the marking of spark plugs and which ones to put on the VAZ-2107
According to domestic GOSTs, this is A17DVRM , where 17 is the heat number (candles are produced from 10 to 23 units). The remaining letters indicate design and dimensional features. Today we need the letter “P” to indicate that a noise suppression resistor is built into the spark plug.
Here is an example of NGK markings: BPR6ES11 . Here the number 6 is the heat number (on a scale from 2 to 13 units), the letter R indicates the presence of a resistor. Expensive brands of candles have the letter “Z” instead of “R” - this is an inductive resistor, it does not lead to loss of spark energy. The number “11” at the end of the mark indicates a gap of 1.1 mm. These spark plugs are suitable for injection “seven”.
NGK spark plugs for “classics” (VAZ 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107)
We will select NGK spark plugs (Japan-France) for carburetor and injection engines of “classic” VAZ cars (2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107) with contact and non-contact ignition systems.
The list below is far from complete, but includes the most common and most frequently used NGK spark plugs on “classics”.
General requirements for spark plugs for carburetor and injection engines VAZ 2101-2107
— Heat number — 17
— Length of the threaded part — 19 mm
— The heat cone protrudes beyond the spark plug insulator
— The gap between the electrodes is 0.7-0.8 mm (contact and non-contact ignition systems, carburetor engine), 0.9-1.1 mm (injection engine)
— Availability of an interference suppression resistor for spark plugs for engines with non-contact ignition systems and injection engines
— Hexagon (nut) — 21 mm
Selection of NGK spark plugs for “classics”
Contact ignition system
BP6ES code 7811 (standard)
BP6ES V-LINE No. 4 code 5637 (with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
BPR6EIX code 6637 (with resistor and iridium center electrode)
BUR6ET V-LINE No. 1 code 2876 (with resistor, three-electrode, with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
Contactless ignition system
BPR6ES code 7822 (standard with resistor)
BPR6ES V-LINE No. 2 code 2268 (with resistor and v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
BPR6EIX code 6637 (with resistor and iridium center electrode)
BUR6ET V-LINE No. 1 code 2876 (with resistor, three-electrode, with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
Injection (injection) engines
BPR6ES-11 code 4824 (standard with resistor)
BPR6ES-11 V-LINE No. 13 code 5339 (with resistor and v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
BPR6EIX-11 code 3903 (with resistor and iridium central electrode)
BUR6ET V-LINE No. 1 code 2876 (with resistor, three-electrode, with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
Notes and additions
— Spark plugs for a contact ignition system, with some exceptions, are not recommended for installation on engines with a contactless system or fuel injection, but vice versa is possible.
— The “classic” injection engines discussed in the article are 2104 and 21067.
Source
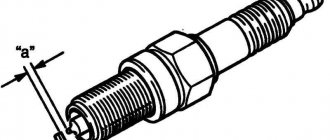
Spark plug gap - what should it be?
The situation when spark plugs were purchased from a trusted seller, but the engine does not function correctly, is familiar to many. When the car starts to move jerkily, almost everyone starts diagnosing the ignition system, thinking that the problem cannot be hidden in the new spark plugs. But the optimal gap on a car’s spark plugs is sometimes violated even with new products. This is not considered a manufacturing defect, because this problem can be fixed on your own. But before this, you need to decide what gap should be on the spark plugs and why it does not correspond to the factory settings.
What is the correct spark plug gap?
The design of such products provides a central electrode, to which a high-voltage voltage is supplied, in order to generate a spark together with the side electrode. The gap is the distance between them. If the spark plug gap size deviates from the factory settings, the car will twitch when driving or detonation will occur, leading to the power unit tripping. Thus, this simple technical nuance can negatively affect the working processes of the motor, and due to inexperience, many do not find it right away.
The engine operates by compressing the combustible mixture by lifting the piston to its highest point. This is the main condition for pressure to build up in the combustion chamber. At this moment, voltage from a high-voltage coil comes to the spark plug, and a discharge occurs between the electrodes, which is enough to ignite the combustible mixture.
Let's look at why this doesn't happen if the spark plug gaps deviate from the factory settings. This minor situation can happen to anyone. Even expensive products from well-known brands can have electrodes placed at the wrong distance. There is no point in talking about low-quality products, because little-known manufacturers do not provide proper technical supervision over their products. Therefore, you should know what the correct spark plug gap is in order to be able to regulate the operating processes of the motor.
Big gap
If the spark plug gap is large, the electrical discharge will be weak or may not occur at all, causing unburned fuel to escape through the exhaust manifold. The problem arises not only with new spark plugs, in which the electrodes were installed at the wrong distance during production, but also when they have already completed some mileage.
Gradually, the contact surface of both electrodes, between which an electric arc is generated, burns out, and the distance between them accordingly increases, which is a problem. How does spark plug gap affect engine performance when this happens? This is difficult not to notice, because its power decreases, tripping begins and operation occurs intermittently.
For the insulator that protects the lower contact from breakdown, the gap of the spark plugs also matters. This is due to the fact that with an increased distance, the spark is forced to look for a path as short as possible to reach the other electrode, and therefore can break through the insulation. And in winter, a long distance negatively affects engine starting, especially in cold weather. There is a high probability that it will not start at all.
You should also know what gap to set on the spark plugs, because as it increases, the likelihood of carbon deposits appearing on the contact surfaces increases, which completely eliminates the possibility of a spark. To prevent sudden failure of these parts, the spark plugs should be serviced or changed after the car has traveled 15-20 thousand kilometers.
Replacement of these products or adjustment of the distance is carried out if the engine spark plug gap is more than 1.3 mm.
Small gap
If the design shows a decrease in the spark plug gap with the naked eye, the spark will be strong, but not so strong that the combustible mixture will ignite. Therefore, as in the previous case, there will also be gaps, which leads to the above problems. In addition, if fuel injection into the engine is carried out via a carburetor, you can expect regular filling of the spark plugs, which will completely paralyze their work.
During operation, only an increase is possible, and therefore insufficient distance is observed exclusively in new products. This is how the spark plug gap affects engine performance if it is too small. Therefore, when choosing such products, it is necessary to measure them. The minimum distance should not exceed 0.4 mm.
If it is less than this value, it is definitely a small gap on the spark plugs, and it is better to choose others or increase it yourself using special tools.
Which spark plug gap is best?
Let's consider what is the optimal spark plug gap between the above values, because the difference is 0.9 mm. For each car, this figure may differ depending on how the ignition is implemented:
see also
“Peter - AT” INN 780703320484 OGRNIP 313784720500453
Spark plugs are used to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber of carburetor or injection gasoline engines. For each type of gasoline engine, “native” spark plugs are produced, recommended by the manufacturer, fully meeting its thermal and power characteristics. spark plug markings are applied to them.
.
Spark plug markings
Each spark plug has a special marking that allows you to determine its type, design and purpose. Plugs are also divided into spark plugs for carburetor engines and spark plugs for injectors. Today there is no uniform marking of candles and for the same candle with similar parameters, each manufacturer uses its own designation for it.
Russian spark plugs
In Russia, there is a unified labeling of candles for all manufacturers that meets the requirements of the state standard - OST 37.003.081. The marking of Russian candles includes letters and numbers, for example, A11, A17, A23, A26DV, etc., where:
• The first letter is the spark plug thread size. In most cases, this is a standard thread size - M14x1.25, designated “A”. When the first letter is “M”, it will be a thread – M18x1.5 (similar candles were used before); • The number after the first letter indicates the heat value. The lower the number, the higher the temperature the spark occurs; Russian manufacturers produce candles with a heat value from 8 to 26. The most popular ones are candles with numbers - 11, 14, 17 and 23. Depending on the number, candles can be “cold” and “hot”.
Cold and hot candles
Cold spark plugs are designed for highly accelerated engines. For example, a spark plug for VAZ engines is A 17 DV: standard thread, heat rating -17, D - thread length 9 mm (the letter is missing when the thread is shorter), B - protruding cone of the spark plug insulator. The spark plug may also have the following marking – A17DVR, where the letter “P” indicates the presence of an interference suppression resistor in the central electrode. If there is an “M” at the end of the marking, then the shell of the central electrode is made of heat-resistant copper material. The spark plug is AU17DVRM, where “U” denotes the increased size of the hexagon for a spark plug wrench -16mm (usually 14mm), when the hexagon size is 19mm, then instead of “U” there will be the letter “M”, for example – AM17B.
Carburetor or injector. Which is better and what is the difference between them?
It seems to me that this topic has long been “worn out” and, with the development of new environmental standards, has long been removed from the agenda. BUT IT TURNS OUT NOT! Many people write - what is really better, a carburetor or an injector? And “newcomers” to cars also ask the following question: what’s the difference between them? Everything is already obvious to me (I closed this question a long time ago), but if there is such interest, then I will write an article and shoot a video, and there will be a video below. So read and watch, it will be interesting...
I have almost 20 years of driving experience. During this time, I had a lot of fun with the carburetor (there were several VAZs, such as 2101, 2103, 2105, etc.), and already had a lot of fun with injection modifications of cars (not only ours, but also imported ones). Therefore, I really have the opportunity to evaluate both units, although I think this is not correct, it’s like comparing a tube TV and a modern LCD panel.
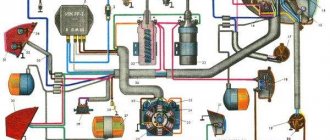
What are both systems responsible for?
This point is specifically for beginners - but what are both of these systems really responsible for? Friends, it's very simple. In fact, they are needed to “power” our engines, namely to create an air-fuel mixture that burns in our engine cylinders .
The only difference is that one system is mechanical (there are practically no electronics), but the second, on the contrary, is electronic (sensors, electronic pumps, etc. are responsible for everything)
The mechanical system is also known as a carburetor.
Electronic – also known as an injector.
Well, now in more detail.
CARBURETOR
It was invented first, its exaggerated modifications were still at the dawn of internal combustion engines, so it can be called the grandfather of modern engine power systems.
A device in the power supply system of carburetor internal combustion engines, designed for mixing (carburetion, from the French - carburation) gasoline and air, creating a combustible mixture and regulating its flow.
What did such a system consist of (for example, I’ll take the VAZ 2101):
The system, by modern standards, is VERY SIMPLE and unpretentious. In fact, there was nothing to break, but inside the carburetor there were several jets, a needle, a float, and a throttle valve (flaps), which could affect the performance of this unit. It should be noted that the dampers opened by pressing the gas pedal, and the drive was mechanical (ordinary cable).
PROS:
MINUSES:
No matter how simple and easy to maintain carburetor systems may seem, there was more hassle with them. Over a year of operation, you would definitely adjust it at least 3 – 4 times, and maybe more. In winter, in severe frosts, the engine was not started once; the chance that it would start at all (without calcining the spark plugs) decreased significantly. It was necessary to play with the choke after starting (modern drivers now don’t even know what it is).
And to be honest, I DO NOT REGRET AT ALL THAT CARBURETORS ARE A thing of the past. They completed their task, and essentially reached their limit.
INJECTOR
Electronic air-fuel mixture supply system. It appeared much later and has now been modernized several times. All mechanical parts have been replaced with electronic ones, there is also a control system (ECU), which is based on various sensors
Injector from the word INGECTION, translation - fuel injection or injection
There are now three main types of systems:
I already had an article - about MPI and GDI .
What does this system consist of:
Of course, to make the injection version work, you need a large number of sensors that control the supply of fuel, air, vehicle speed, crankshaft rotation, throttle position, coolant temperature, detonation.
The system may seem complicated, but it is not. One of the main sensors is the CPPS (crankshaft position sensor). Based on its readings, the cylinder, fuel supply and spark timing are determined.
Bosch YR7MPP33 (0 242 135 509) with platinum electrode
Very expensive new generation spark plugs with platinum electrodes. The thread is M12, its length is 26.5 mm, pitch is 1.25 mm. A wrench of 16 is used for tightening. The heat rating is 7. The model is used for Mercedes-Benz cars, but they are installed on any gasoline cars, including VAZ.
Recommended for the engine of modern cars, the main thing is that it is used on the injector and not on the carburetor. The model is 8-valve; it is not worth using it for a 16-valve engine, although it is possible. Very high quality, German candles. The product weighs 47 g. It costs 480–500 rubles per piece.
What is the difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine?
Let's summarize and formulate a list of differences between the two fuel systems:
The difference between an injector and a carburetor is obvious. Fuel economy and compliance with environmental standards are forcing car manufacturers to use injection engines.
Every car enthusiast who is interested in the design of his car knows that modern gasoline engines are equipped with a carburetor or fuel injector. However, if you take the first driver you meet and ask him a question about how these systems differ, you most likely will not get a clear answer. General erudition, as a rule, is limited to the fact that the systems perform the same function - they form a combustible mixture for supply to the engine.
So, what is the difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine? How do they function? Our note is devoted to these issues.
The main difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine is the technology for supplying air and fuel to the engine. from In the carburetor
an air-fuel mixture is created and its flow rate is regulated; the combustible fuel-air mixture is sucked into the engine due to the difference in pressure between the atmosphere and the intake manifold.
is a modern electronic fuel supply system. In it, the composition of the air-fuel mixture is regulated by an electronic system. Fuel is injected into the air stream using special nozzles. The combustible mixture is injected into the combustion chamber and enters the engine cylinders. Most modern cars are equipped with injectors due to the advantages described below.
What is the difference between an injector and a carburetor and which is better?
You go outside on an autumn, spring or winter morning, get into your car, start the engine and calmly warm it up along with the interior of the car. And next to your car stands an unfortunate neighbor, bent over, searching for something under the hood of his car. You approach him to find out what is the reason for his gymnastic exercises, and at first glance you immediately understand everything, feeling the source and the problem with your nose. Of course, he has a carburetor under the hood, which has filled the spark plugs with gasoline and therefore there is a persistent smell of fuel in the frosty air. A familiar picture, isn't it? So what should supply the engine with fuel - a carburetor or an injector?
? What is best for starting the engine in winter? What advantages and disadvantages do both have?
This “monstrous” question is asked by many drivers and everyone has strong arguments both in favor of one and in favor of the second. Moreover, everyone is partly right when they present their own evidence. Let's try to figure it out in detail and thoroughly, without regard to anyone's conjectures, but only based on objective facts. Everyone understands perfectly well that there is no perfection in this world. In relation to this investigation, we can say that the injector and carburetor have their own obvious advantages and disadvantages. We’ll talk about them, as well as about their purpose and some nuances. At the end of the article, we will try to draw a subjective conclusion whether it will suit someone or not - the main thing is that we will draw a conclusion based on real application.
Comparison, purpose and features
A carburetor is a kind of air-fuel device that forces fuel with a large amount of air into the engine. Moreover, this rut always occurs in the same volume, without reference to the engine speed. An injector is an electronic device for precise distribution of fuel injection, responding to commands from the on-board computer, which sends them to the microcontroller. The use of an injector leads to a very accurate and economical dosage of fuel, depending on the number of revolutions.
Thus, the difference in using an injector and a carburetor lies in the consumption and distribution of fuel at a particular point in time and effort. In other words, they simply have completely different efficiencies. Although, you can simply indicate all the differences in a specific list for greater clarity.
- The carburetor sucks the fuel mixture into the engine, and the injector itself injects certain doses.
- The carburetor injection is very unstable, while the injection injection is precise and accurate.
- In the cold season, the injector works with the same success as in the warm season, and the carburetor can easily freeze.
- Due to fuel economy and careful distribution, the injector emits much less harmful substances into the atmosphere, while the carburetor craps mercilessly, which in the light of CO2 emission laws is a very serious argument when undergoing maintenance.
- The carburetor does not always maintain speed precisely and accurately (there are many reasons for this), but the injector is much more stable in operation.
- Fuel savings on injection engines can reach 30-40%, which cannot be achieved on the most well-regulated carburetor.
- Although the injector is much more expensive than a carburetor, it still fails less often, being a closed type unit.
Obvious pros and cons
The only “grand” difference between an injector and a carburetor is that in the first case, fuel is supplied electronically and by the “brains” of the machine, while in the second, purely mechanical mixing occurs. However, both units have an equal number of advantages and disadvantages. The old mechanical method has the following advantages:
- A relatively simple repair that any driver can perform if desired.
- Simple and cheap device components.
- Reduced demands on fuel quality (literally, as long as it still smells like gasoline).
- Lack of essential diagnostics.
But this antiquity also has its disadvantages:
- Very high unreliability.
- Sensitivity to temperature changes, when in winter it doesn’t start, and in summer everything overheats.
- High and stupid fuel consumption.
- Quite a frequent failure.
The injector is also not ideal. As stated above, nothing is perfect or eternal. Electronics also have their positive and negative sides. The positive ones include:
- Relatively high operational reliability.
- Extremely rare failure.
- Modest and correct fuel consumption.
- Indifference to temperature changes.
- Very little CO2 emissions into the environment.
- Clear control over the unit from the car’s on-board computer.
However, the negative aspects cannot be ignored:
- A very complex repair that cannot be handled without special tools and knowledge.
- High cost of all injector parts.
- Only complete replacement of any broken part.
- Demanding requirements for fuel in terms of its quality characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of carburetor engines
The main advantages of carburetor systems are simplicity of design, ease of maintenance, and reliability. Adjustments and repairs can be carried out without resorting to the services of professional workshops. Just read the instruction manual. A properly adjusted carburetor can operate for a long time without additional maintenance. During operation, it does not require precise diagnostic equipment; a simple set of keys and screwdrivers is sufficient.
Unlike injectors, a carburetor is unpretentious to the quality of gasoline and is capable of operating on fuel with a high content of impurities. Clogged jets can be removed by purging and cleaning. A distinctive feature is the engine response, good traction at low speeds.
The disadvantages, unfortunately, outweigh its advantages. These include:
The technology is currently outdated.
Video “Checking the gap on new SZ”
A specialist in the video (author - Nail Poroshin) will tell you more about what a modern VAZ owner needs to know about diagnosing the gap on the SZ.
By the way, number 13 without a V-shaped groove on the central electrode... but I liked it so much (((
What do you think about this? Which ones should I install?
Any acquaintance of a car enthusiast with a particular car system is learned mainly through a breakdown. The same applies to the ignition system when the engine malfunctions. Over time, the driver learns to solve this problem by simply replacing the spark plugs, but does not always make the right choice. Today you will find out which spark plugs are best to choose for your car.
Which spark plugs are better for VAZ 2110
AU17DVRM
The original spark plugs for all VAZs are AU17DVRM. These spark plugs from the domestic manufacturer are of excellent quality and have proven themselves well in the market. AU17DVRM are an excellent alternative for replacing spark plugs, as these spark plugs have good spark formation, reliability and durability, and are also not inferior to imported analogues.
NGK No. 11
NGK spark plugs have performed well on the market and are one of the most popular spark plugs for domestic cars. Most Lada owners prefer NGK No. 11 spark plugs. These spark plugs have a long service life and high reliability.
How to choose spark plugs
To choose the right candles, you need to be guided by only two important parameters:
A completely different matter is a large number, which allows the electrodes to withstand enormous thermal loads. These spark plugs are designed for use on sports cars that are designed for fast driving.
Before you go to the store to buy spark plugs, you need to read the technical documentation for the car. It will detail the parameters that also apply to devices designed to create spark discharges.
Best premium spark plugs DENSO 4712 IXEH22TT
- with iridium soldering;
- mileage - up to 120 thousand km;
- increase engine power and service life;
- save fuel.
Reliable spark plugs for cars with a central electrode made of iridium alloy. The latter is ultra-thin, its cross-section is 0.4 mm. The service life of the product is 120 thousand kilometers. The design provides significant fuel savings and more complete combustion of fuel. The thread is M12, its length is 26.5 mm. A 14 mm wrench is used. Heat number – 22, refers to cold ones, gap – 1 mm.
The part is intended for use on Japanese (Subaru, Mazda, Toyota, Infiniti, Lexus, Nissan) and European (Mercedes-Benz, Renault) cars. They are also installed on VAZ. In particular, you can use these spark plugs on Grant 8 valves with an injector. But this is not always justified - in order for the model to reach its service life, you need to use high-quality fuel.
Types of spark plugs
Of course, the manufacturer did not limit the buyer’s choice. Candles are divided into injection and carburetor. It must be borne in mind that the former are much more expensive, so you need to be as careful as possible in their selection. Otherwise, there is a risk of parting with a certain amount of money. Do not forget that the use of such products should be solely for their intended purpose, this means that carburetor devices cannot be installed on an injection engine.
The cheapest are single-electrode spark plugs, which are used on most domestic cars. However, the best performance is achieved by multi-electrode spark plugs, as well as spark plugs that have a capsule with a conductor made of precious metals.
The last thing that determines the quality of spark plugs is the price. If you purchased them for 200-300 rubles, then be prepared for the fact that the engine will quickly go into an unstable mode, and the spark plugs will soon become covered with soot.
So what should you choose?
The carburetor engine is ideal for remote areas or small towns. The carburetor is quite simple in design, so repairs or replacements can be done even with your own hands, if, of course, you can distinguish a screwdriver from a hammer. And it is less picky about the quality of fuel (for example, the carburetor for the VAZ-2107 works perfectly on both 92 and 95 gasoline), which is often of great importance.
The injector is better suited for residents of large cities, where there are many high-quality service stations and a selection of high-quality gasoline. In addition, in city driving mode, an injection engine has a reduced (compared to a carburetor) fuel consumption, which will allow significant savings.