Why is there low voltage in the network?
The reasons why there is low voltage in the network are the following:
- High equipment wear and insufficient wire cross-section.
Despite the fact that for many years now there has been an active modernization of networks throughout the country, many towns and villages are still powered by lines built back in Soviet times. And the load on the network (especially in the private sector) has increased many times over. For this reason, the lines are overloaded and, accordingly, the voltage entering your home will be already low.
- Overload of power transformers at urban substations due to severe phase imbalance.
- Unreliable contacts at tap points.
These are the main reasons that you cannot influence in any way or can only indirectly (complain to the company). And now I will tell you about the main reasons for low voltage in your home.
Possible consequences of low voltage on-board network
Before starting to analyze the possible causes of low voltage on the on-board network, we suggest briefly considering the consequences that you may encounter. This should help you understand that you should not drive a car for a long time with such a malfunction, as it will lead to other unpleasant problems.
Firstly , if the car’s on-board voltage is systematically below 14.4V, the battery will never be fully charged from the generator . That is, for example, if the voltmeter shows a maximum of 14.00V in different modes, under the best circumstances the battery can only be charged by 60-70 percent. There is nothing to say at all about voltages such as 13.5V or lower. The battery on such a machine will not be charged even to half.
Secondly , when the on-board voltage is low, the battery takes longer to restore its charge. This means that during short trips, the battery may not have time to recover the energy given the day before for the next engine start, as well as that lost during parking due to current leaks and self-discharge. Accordingly, after several such cycles of incomplete recovery, the battery will sooner or later drain too much, and one day the engine will not be able to start.
Thirdly , due to the low voltage of the on-board network and systematic undercharging, battery degradation accelerates . That is, the battery life is significantly reduced. This happens, first of all, due to sulfation, which affects absolutely any type of lead-acid battery that does not regularly receive a full charge. Although there are other reasons related to this same point.
Fourthly , low voltage of the on-board network means a guaranteed lack of power for powerful consumers . For example, if it is a fairly powerful acoustic system, it will sound distorted or even fail. Yes, the same headlights shine differently at 14.0V and at 13.2V. If you use an inverter that converts direct 12 volts into 220 alternating voltages, in such situations it will also not be able to produce full power.
Fifthly , if the on-board network voltage is too low or fluctuates greatly, unstable engine operation is possible . For example, idle speed may fluctuate, the power and dynamics of the car may decrease, and so on. But, in fairness, it is worth noting that such serious problems arise when the situation is extremely advanced and the tension has dropped below the baseboard. That is, the on-board system is powered only by an almost dead battery (nothing or critically little comes from the generator).
In addition , low voltage on the car's on-board network may indicate more serious problems . For example, about a break in “vital” circuits, or even about short circuits, the consequences of which can be very sad. In general, low voltage is a serious malfunction, and you simply cannot ignore it. It is necessary to look for the cause as early as possible and eliminate it before the situation leads to large losses.
What is the normal voltage value according to GOST
So, in order to understand low voltage in the network or whether it corresponds to the standard, you should refer to regulatory documents, namely GOST 29322-2014 (IEC 60038:2009). So, in Table 1 of this document it is indicated that the voltage in three-phase four-wire systems, which also include single-phase electrical networks, the voltage is 230 Volts.
Moreover, under normal operating conditions, the voltage deviation should not deviate by more than +/- 10%.
Based on this, the normal voltage in the network is considered to be a voltage from 207 to 253 Volts inclusive.
Topic: Voltage drop at start-up
Theme Options
Search by topic
Golf Registration 07/27/2010 Address Kemerovo region 42RUS Age 37 Messages 571
| Thank you: |
| Received: 1 Sent: 0 |
Lupo Registration 03/27/2010 Address Belarus, Vitebsk Age 36 Messages 100 Diary entries 1
| Thank you: |
| Received: 0 Sent: 0 |
Posted by Passat42
Yes, it cannot be that there is a maintenance-free generator. At least I've never seen anything like this in real life.
— Added a little later —
Posted by Passat42
Pointer Registration 08/28/2009 Address Russia, Moscow region Age 60 Messages 66
| Thank you: |
| Received: 2 Sent: 2 |
Posted by Passat42
Why is there low voltage in the house?
In order to understand whether the cause of the low voltage is in your home or is it a problem on the line, you should carry out the following manipulations:
- Take your multimeter and set it to measure voltage.
- Turn off your opening machine.
- Measure the voltage on the upper jaws of the disconnected machine.
- If you see that the voltage is equal to or more than 207 Volts, then the problem clearly lies in your home.
- Voltage below 207 Volts means you are not the problem.
So, you have determined that the voltage is leaking in your home.
In fact, there are not so many reasons:
- Insufficient wire cross-section
As in the case of main networks, the main reason for the low cross-section is old wiring (in the vast majority of cases aluminum), which is no longer sufficient to provide energy to the connected electrical appliances.
Such a lack of cross-section will lead to excessive heating of the conductors, which can lead to melting of the insulation and even a fire.
But this is far from the only reason for low voltage.
- Poor contact on breakers, sockets and junction boxes
You should also carefully inspect the distribution panel. Perhaps the connection has become loose and there is loose contact between the wire and the jaws of the machine. So, in this situation, there will be a high transition resistance in this place, which will lead to a voltage drop in the network, and in the heating area to melting and even a fire.
These are the main reasons why there may be low voltage in your home.
Possible causes of on-board voltage drop and their elimination
Unfortunately, there is no single reason for the on-board voltage drop. There are quite a lot of them. Therefore, searching for the problem and eliminating it should be done step by step - checking all potential culprits one by one. Let's look at the main places where on-board voltage is wasted.
Wires
A car's electrical wiring is almost always the first suspect for voltage sags. To understand how this happens, let’s not rush to get under the hood, but first consider the following simple and visual diagrams.
In this diagram we see a 12-volt power source and a light bulb of the same rating. Let's imagine that the power source in the figure is your car's battery. The light bulb will conditionally indicate any load. This can be not only lighting, but also a starter, stove, car radio, amplifier, and so on.
What to do with low voltage in the network
So, if the problem with low voltage lies in your home, then you can eliminate it by checking all the connections of the wires and eliminating all weak contacts.
If the problem is in thin wires, then only completely replacing the old wiring with a new one will help (yes, it’s expensive, but safety is more expensive).
If the problem is in the distribution networks, then you should submit a request to your sales organization (management company). They will consider your appeal and, if technically possible, raise the tension.
But from personal experience I will say that in most cases the answer will be that it is not possible to increase the voltage, since the networks are worn out and the installation of a new transformer, etc. is required. Therefore, in this case, the only solution would be to install either several voltage stabilizers or one powerful for the whole house.
If you liked the material, then give it a thumbs up and subscribe. Thank you for your attention!
Source
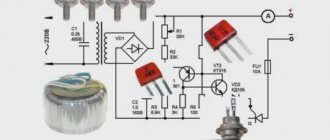
Reason #6. Burnt out diode bridge
The task of the diode bridge is to rectify the alternating voltage produced by the car's generator. It consists of at least six diodes connected in a bridge circuit. If at least one of the bridge diodes burns out (breaks through), the on-board network voltage drops. A very simple check of the diode bridge allows you to identify the problem. The solution is to replace burnt out (broken) diodes or the entire “horseshoe” at once.
Insufficient voltage in the house - possible causes
Low voltage in the network is an unpleasant phenomenon, but many people deal with it. Poor lighting, when the light bulb only indicates its presence, is not the biggest problem. It’s worse when it’s impossible to do laundry, boil water, cook food on an electric stove, or the refrigerator works intermittently. This happens when the voltage drops to a critical value, but 180 Volts, when everything seems to be working, is also not very encouraging. Devices consume the same current as at normal voltage, and motors consume even more current, but perform their functions over a longer period of time.
Reason #2. Battery is very discharged
A fairly common reason for low on-board voltage is the current battery charge level. If it is low, then the on-board network voltage may also be slightly underestimated. This happens because the discharged battery, after starting the engine, begins to charge intensively, consuming a large current. That is, it is a serious load on the generator.
To broaden your horizons on the topic of batteries, read the articles “Checking the battery with a load fork” and “Car battery voltage” on the Auto without service station website.
Life story . One good friend of the author once decided to overcome the low voltage of the on-board network using a well-known homemade method. We are talking about a diode that is soldered into the gap between the battery and the relay regulator. This solution allows you to “deceive” the relay regulator. The diode drops about 0.5-0.7 V, the regulator “detects” this and “demands” more from the generator.
Before installing the diode, the voltage in the car’s on-board network was 13.7 V. After - 14.3 V. Almost standard. But the author’s friend did not take into account one point, namely the current battery charge level. Since the on-board voltage was too low, the battery was constantly undercharged. The situation was further aggravated by the fact that the car was used for short trips.
The installation of the diode coincided with a case when it was necessary to drive a car over a fairly long distance. During this trip, the battery was charged normally, and the on-board voltage went up. It crept up to 14.8 V. And this is the voltage at which the battery boils (not every battery). As a result, as this experience showed, a diode was not suitable as a solution to the low voltage problem in this particular case.
But replacing the relay regulator helped.
The main reasons for the decrease in network voltage
Is it always 220 in our network? The question, of course, is rhetorical; very often the voltage in the network does not meet the standards and is either too low or too high. Here is a list of the main causes of low voltage:
- low voltage in the power line
- insufficient power of the transformer installed at the substation
- voltage imbalance across phases on the line from the transformer to the house
- problems in the switchboard, small cross-section of wires in the wiring.
Voltage and load: Physics
The network voltage is maintained constant.
This would be the case for an ideal source; a real one has internal resistance. That is, it depends on. Do I understand correctly that this is the voltage under load? And the magnitude of the load is essentially determined by the value? Then it turns out strange - the voltage increases as a function of the load. You understand absolutely correctly, but you have not yet established the connection between energy consumption and load resistance.
Let's imagine that . In this case, the value compared to can be neglected, and the voltage across the load turns out to be the maximum possible, equal to
In your example, when the electric heater turns on, the resistance of the entire load connected to the network decreases. At the same time, the voltage across the load decreases. Now imagine that before turning on the heater, a table lamp was connected to the same outlet. When the heater is connected, the resistance of the lamp does not change, but the voltage on the lamp, as we found out, decreases. Naturally, the brightness of the lamp decreases.
I note that voltage as a function of load and load magnitude are widely used, but fraught with the danger of misinterpretation of the expression. Very often, when they talk about increasing the electrical load, they mean an increase in current consumption or, equivalently, a decrease in load resistance. If we forget about this and by increasing the load we mean increasing the load resistance, it is easy to come to the wrong conclusions.
— Fri Nov 13, 2009 21:54:02 —
Mains voltage is maintained constant
The value (EMF) is maintained as constant as possible. And the voltage at the load - whatever happens. It is desirable to ensure that internal resistance is as close to zero as possible - for example, increase the cross-section of the wires of the power transmission line (local, not high-voltage) and the transformer at the substation.
Causes of voltage sag
There are certain requirements for the electrical network, they are given in GOST 13109 97. It states that long-term voltage deviations from the nominal voltage are possible within 10% (-5% and +5%). In addition, short-term voltage surges of up to 20% of the nominal value (from -10% to +10%) are allowed. That is, at a norm of 220 volts, a long-term “sag” to 209.0 V will not be critical, as will a short-term drop to 198.0 V. A voltage drop beyond the specified limits (for example, to 180 Volts) indicates that the network parameters are not meet established standards.
190 V is already a reduced voltage
It is important to establish the nature of voltage sags, otherwise eliminating the consequences will be ineffective. Problems with the electrical network may be due to the following reasons:
- Wear of power line wires , a large number of connectors, main lines do not correspond to the increased load, etc.
- The power of the transformers is insufficient for the current load . Most transformer substations were installed more than 30-40 years ago; naturally, over the past time the number of electricity consumers has increased significantly. As a result, the actual power exceeds the calculated one, which leads to overloading of transformers and, as a result, unstable network voltage.
- Power imbalance . As a rule, single-phase power is supplied to an apartment or house, but each phase is a separate arm of a three-line circuit. Accordingly, if the load is unevenly distributed, a decrease or increase in voltage will be observed. This effect is called “phase imbalance”.
- The supply is made with a cable with insufficient wire cross-section to connect the load. For example, with a design power of 11 kW, the load connection is carried out with conductors with a cross-section of 6.0 mm2, with a norm of 10.0 mm2. Table of correspondence between the cross-sectional area of the input cable and the connected load
- Poor quality branch from the overhead line.
- Poor contact on the input circuit breaker.
In the first three cases, it is not possible to eliminate the cause on your own, but you can file a complaint with the energy supply company against the electricity supplier (this will be discussed in detail in another section). Paragraphs 4-6 indicate malfunctions in home electrical networks, so such problems are solved by electricity consumers on their own or by hiring specialists for this purpose.
When starting the engine, the voltage drops: causes and diagnostics
Voltage drop when starting the engine is a fairly common problem, regardless of the type of power unit, as well as the make, model or class of the car.
The voltage drop often manifests itself in such a way that at the moment the starter begins to rotate, the headlights sharply dim or go out, the dashboard lights lose their brightness, the radio turns off and restarts, etc. A voltage drop can occur both when trying to start a cold internal combustion engine, and when starting an already warmed-up unit. As for the start itself, in some cases the starter actively turns for the first couple of seconds, then a certain “stutter” occurs. At this moment, the voltage drops, while the crankshaft continues to turn, but with great difficulty, but a serviceable engine usually starts.
There can be several reasons for such a malfunction, both obvious and easily removable, and hidden. In this article we will talk about why the voltage drops when starting the engine, as well as how to detect and fix the problem.
Ways to solve the problem
It is necessary to start by identifying the reason that led to the “subsidence” of electrical energy. Let us describe in detail the algorithm of actions:
- You can start by asking your neighbors to determine if they have a similar problem. If they are faced with a similar situation, then there is a high probability that there is an external factor (weak transformer at the substation, problems with overhead lines or power imbalance). But before writing a collective statement to Energosbyt, you should check the internal network, so regardless of the survey results, we move on to the next point.
- Disconnect the input circuit breaker and measure the voltage at the input terminals, then repeat the measurement with the connected load. The input circuit breaker is marked with a green oval
If the voltage is within normal limits without load, but after connecting the internal network it sags, then we can state that the problem is local in nature and will have to be solved on its own. First of all, it is necessary to check the input circuit breaker, since a weak contact at its input or output can cause a voltage “sag”.
Problems with the electrical contact in the circuit breaker (CB)
As a rule, in cases with poor electrical contact, a lot of heat is generated in the problem area, which leads to deformation of the AB housing. In such cases, it is necessary to replace the protective device. Since there is a high voltage at the input of the device, such work must be performed by a specialist with the 3rd clearance group; replacing it yourself is dangerous to life.
- If everything is in order with the AV and no defects are found, you should check the compliance of the cross-section of the input cable. For this purpose, you can use the table shown in Figure 2. If necessary, replace the wire.
- In the event that checking the cable and AV does not produce results (the circuit breaker is normal and the cable corresponds to the load), the outlet should be checked. A melted body or sparking when connecting a load indicates unreliable contact, therefore, it is necessary to reconnect.
Low voltage when starting the engine: how to find the cause
Let's start with the fact that the battery is not always the culprit of all troubles, although quite often reduced voltage occurs as a result of problems with the battery. In any case, before you start diagnosing a car regarding electrical parts, you must have a special auto tester (multimeter).
It is important that the device accurately measures certain parameters. As a rule, the functionality of the device should allow you to measure voltage, resistance, and current. At the same time, when troubleshooting voltage-related problems, you also need to take into account the crankshaft speed.
Checking the car battery
So, when diagnosing, you need to start by checking the battery, as well as the car generator. The condition of the battery is assessed by connecting the tester to the battery terminals. Normally, the voltage on the battery, taking into account the absence of load (all consumers are turned off), should be at least 12.6 V. A decrease in this indicator means that there is a partial undercharge or problems have arisen with the battery itself (sulfation of the plates, boiling off of the electrolyte, etc.).
One way or another, a discharged battery will not be able to quickly turn the starter and at the same time maintain the required voltage in the on-board network. As a result, the starter will turn slowly and the engine will be difficult to start. The battery capacity can also be assessed using a load fork. This plug makes it possible to implement resistance when connecting to the battery terminals.
You can also measure the voltage with a voltmeter, turning on the side lights and high beam headlights for the load. Typically, the discharge current under such a load (taking into account the installed halogen incandescent lamps) is about 5–6 A, and the voltage is about 11.5 V. If this is the case, then the battery is working and the problem needs to be looked for further.
Quick starter diagnostics
If we talk about the voltage directly at the moment of starting (when the starter turns), the voltage at the battery terminals should not fall below 9.5 V. In cases where this happens on a working and charged battery, it can be argued that a starter malfunction has occurred. In other words, the starter requires too much electrical energy when operating, which should not normally be the case.
Why does voltage drop occur?
The quality of power supply is prescribed in GOST R 54149-2010 “Standards for the quality of electrical energy in general purpose power supply systems”, which states that the voltage change can be within ± 10% of the nominal (or according to contractual terms) during 100% of the time of the measurement interval in one week. In real life, this standard is often violated. The voltage entering a house or apartment can be reduced by up to 50%. This is mainly observed depending on the season, but in some areas it can be a constant phenomenon.
Low voltage when starting the engine: how to find the cause
Let's start with the fact that the battery is not always the culprit of all troubles, although quite often reduced voltage occurs as a result of problems with the battery. In any case, before you start diagnosing a car regarding electrical parts, you must have a special auto tester (multimeter).
It is important that the device accurately measures certain parameters. As a rule, the functionality of the device should allow you to measure voltage, resistance, and current. At the same time, when troubleshooting voltage-related problems, you also need to take into account the crankshaft speed.
Checking the car battery
So, when diagnosing, you need to start by checking the battery, as well as the car generator. The condition of the battery is assessed by connecting the tester to the battery terminals. Normally, the voltage on the battery, taking into account the absence of load (all consumers are turned off), should be at least 12.6 V. A decrease in this indicator means that there is a partial undercharge or problems have arisen with the battery itself (sulfation of the plates, boiling off of the electrolyte, etc.).
You can also measure the voltage with a voltmeter, turning on the side lights and high beam headlights for the load. Typically, the discharge current under such a load (taking into account the installed halogen incandescent lamps) is about 5–6 A, and the voltage is about 11.5 V. If this is the case, then the battery is working and the problem needs to be looked for further.
Quick starter diagnostics
If we talk about the voltage directly at the moment of starting (when the starter turns), the voltage at the battery terminals should not fall below 9.5 V. In cases where this happens on a working and charged battery, it can be argued that a starter malfunction has occurred. In other words, the starter requires too much electrical energy when operating, which should not normally be the case.
Let us add that to measure the current you need an ammeter, which is connected to the gap. At the same time, it is highly not recommended to break the circuit in a car; also, not all ammeters are able to work correctly and record high readings that occur when the internal combustion engine is started.
For this reason, it is better to have a special motor tester for such tasks. The main advantage of the device is that the measurement accuracy is quite high, and there is no need to connect the tester to the break, since the device has separate sensors. These sensors are overhead and work even through wire insulation. These elements are capable of effectively recording changes in magnetic field strength when a current of one or another magnitude passes through the wires in the circuit.
Assessing the performance of a car generator
In cases where the battery has been previously checked and charged from the charger, and everything is in order with the starter, but the problem continues to appear, the generator needs diagnostics. The fact is that the generator recharges the battery after the engine starts. If the necessary recharging does not occur, then the battery quickly runs out, rapidly losing charge after just a couple of starts.
Then you can raise the engine speed, after which the charging voltage is also measured. For example, when the engine speed increases to 2 thousand rpm. The normal charge voltage ranges from almost 14 to 14.5 V. Next, the operation of the generator should be assessed under load. To do this, you will need to turn on the headlights again.
The voltage is normal after turning on the lights and dimensions should not be lower than 13.8. If the indicator drops to 13 or lower, then you need to start checking with the generator drive belt. If the alternator belt is loose or slipping, then the cause is obvious. If the belt is well tensioned, problems have arisen in the generator itself or its relay regulator.
As a rule, the relay regulator is one of the most common problematic elements on different cars. You can check the relay regulator in the following way:
- it is necessary to measure the voltage on a running engine;
- after the indicator reaches 14.5 V, the charge should stop;
- if the voltage continues to increase, the relay regulator requires replacement (adjustment is allowed on some cars);
Let us also add that the charging current after the engine has been started ranges from 6 to 10A. Subsequently, when the internal combustion engine is running, the charge normally drops to 0 (provided that additional electricity consumers are turned off).
What does low voltage in the network lead to?
- — significant deterioration in starting conditions for all types of engines and engine-based devices;
- — when starting the electric motor, the starting current increases;
- — overheating of the wires up to the melting of the insulation and the possibility of fire from a short circuit;
- - reducing the brightness of the lamps or their constant blinking, which leads to discomfort in living in the house;
- — reduction in the service life of household electrical appliances;
- — unstable operation of power-sensitive devices;
- — significant deterioration in the performance of electrical appliances.
All this together causes significant damage to all household appliances in the house. Televisions, computers, lamps, air conditioners, vacuum cleaners, refrigerators and other consumers of electricity receive great damage not only during startup, but also during normal operation. Devices with a switching power supply suffer a little less, but they also experience incorrect operation and deviations in modes. Ultimately, all this affects a person: heating devices take more time to heat up, electrical appliances with a motor operate with more noise, the refrigerator compressor may not start (i.e. food will defrost), lighting becomes dimmer, which can affect mental health. and the physiological state of a person or, at a minimum, worsen the comfort of living indoors.
Where to call and complain about the power supply?
Calls cannot solve the current problem; it is necessary to file a claim for inadequate quality of services provided. That is, write a statement to the company providing electricity supplies (if the contract is concluded directly) or file a complaint with the management company. The application must be registered or sent by registered mail (mailing address is indicated in the contract).
If the above measures do not help, you can contact the prosecutor's office, Rospotrebnadzor, the district administration, the public chamber, as well as the district court.
Please note that collective complaints are more effective, so if neighbors or other residents of a house (district, village, etc.) are faced with a low voltage problem, then it is better to involve them in the process.
If, due to voltage deviations from established standards (due to the fault of the service provider), household appliances fail, you can demand compensation for the damage. To do this, you must follow the following algorithm:
- You should contact the service provider so that its representatives record that the accident occurred and draw up a corresponding report.
- A conclusion is taken from the service center, which indicates the reason for the failure of the household appliance.
- A claim is filed with the service provider seeking compensation for damages.
- If refused, the issue must be resolved in court.
What can cause the voltage to drop:
- - transformer substation.
Transformer substations have been installed throughout Russia, the vast majority of them were installed back in the days of the USSR, while the calculation of the load on them was carried out based on completely different electrical appliances and their number. The age of operating transformers also plays an important role, which adversely affects the quality of the power supply. But it is worth noting that the engineers of that time laid down a significant margin of safety, both in terms of power and mechanical strength. - - power lines.
The situation is similar with transformer substations. The diameter of the cores and the cable material (aluminum) often cannot withstand increased electricity consumption, and numerous twists of steel over time bring its own losses in quality. At the moment, the aluminum cable is being replaced with copper cable, which is more suitable for loads. - - difference in power consumption between phases.
As you know, there are three phases in the power supply system. Mostly, one of the phases is connected to an apartment or private house. If there is a significant excess load on one phase relative to the other two, then a phenomenon called phase imbalance occurs, which provokes an increase or decrease in voltage.
Everything written above can be present either separately or in combination. Even if you repair or replace one of the components, the situation can only partially improve. There is one more nuance in power supply networks: at the end of the line from the transformer substation, electrical consumers work in more difficult conditions than consumers located closer to the transformer substation (They can consume more power and at the same time the quality of the power supply will be better.
Voltage drops at startup. Help!!
Sat, 28 Nov 2009, 23:11
Good evening! Help! I recently purchased an Octavia 1.8T 2000, I don’t really want to invest in it, but another problem arose: yesterday they installed an alarm system and it turned out that the on-board voltage drops when the car is started, to 8.8 V. which can lead to the alarm not working properly. Not to mention that two days ago I left from the officials, who said, after diagnostics, that I just needed to change the battery, but the result was the same. The guys who installed the alarm checked the mass, everything is normal, they didn’t check the plus yet, there wasn’t enough time, but the voltage drops during startup and a lot! Help as much as you can. PS this is my first time on the site, so don’t blame me if something goes wrong!!
Ways to deal with low-quality voltage
- 1. Complaint to the energy supply organization. Before filing a claim with the energy supply organization, it is necessary to collect evidence of the supply of low-quality energy. This is done by installing a special device that records all the characteristics and parameters of the power supply network. A prerequisite for this device is the presence of an appropriate certificate. This device is installed directly at the power input to a house or apartment. The recording takes place on a memory card, then the recorded data can be transferred to a computer and printed for presentation to the electricity supplier. It is also very important to draft a letter of claim correctly; if you do not have the necessary knowledge, it is better to seek advice from a lawyer. If your letter was rejected, you have every right to file a claim with a judicial authority. If poor-quality electricity supply is observed not only in your home, but also in your neighbors, then you can file a collective claim, which will significantly speed up the resolution of the problem with electricity.
- 2. . This method is the fastest and less time-consuming. Therefore, it is most popular among the population. The problem of power supply quality is solved immediately after installing a voltage stabilizer at the input. The voltage stabilizer will not only “bring” the supply voltage to the standard 220 Volts, but will also reliably protect household electrical appliances from sudden voltage changes (surges) and from various types of emergency situations in the network. Energy voltage stabilizers have all the necessary properties for use not only in everyday life, but also in production.
- 3. (uninterruptible power supply). The solution is more expensive than installing a voltage stabilizer, but in this case there is one big advantage. The inverter not only stabilizes low-quality voltage, but also provides backup power from batteries in the event of a complete absence of supply voltage. Depending on the model, battery capacity and connected load, it can reserve power from 15 minutes to 2 days. The inverter is installed either at the entrance to the house, or individually on important electrical equipment, for example, a heating boiler, refrigerator, fire or security alarm system. Energy inverters have an ideal sine wave output, which is very important for modern sensitive equipment.
- 4. Installation of alternative energy devices. They are installed mainly in private houses and cottages. In this case we are talking about solar panels and wind generators. The main advantage of this method is that solar and wind energy is free, financial expenses occur only for the purchase and installation of installed equipment. Production technologies make it possible to achieve a service life of these systems of at least 30 years. The main disadvantage of alternative energy systems is their high cost, calculated depending on the volume of energy generated, tens or even hundreds of thousands of rubles. But taking into account the fact that the cost of electricity increases every year, the payback of such systems is no more than 10 years.
- 5. Own transformer substation. Of all the listed methods for solving electrical problems, this method is the most expensive. The cost of replacing the substation and transmission lines runs into the millions. And not everywhere it is possible to install it.
It is better to entrust the answer to the question why the voltage in your home drops and the decision on the need to install a voltage stabilizer to a professional electrician. You can view prices for ETK Energy products at
Source