The camshaft position sensor (phase sensor) on the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is an element of the electronic engine control system (ECM).
Purpose of the phase sensor
The phase sensor is designed to determine the top dead center (TDC) of the piston of the first cylinder during the compression stroke according to the position of the camshaft by the ECU controller. This makes it possible to achieve precise phased fuel injection into the engine cylinders (specifically for each injector), improved mixture formation, greater fuel efficiency, and throttle response.
Phase sensor device
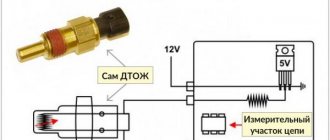
The phase sensor is a semiconductor device. It consists of a housing, copper winding, steel core and magnet. The sensor connection block has three outputs. A rubber O-ring is installed on the body.
Location on the engine
DPRV, on the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars, is located on the end cap of the cylinder head (on a carburetor engine this is the camshaft installation location).
Operating principle of the camshaft position sensor
The operating principle of the sensor is based on the Hall effect (see “Notes and Additions”). The control unit constantly supplies the sensor with a voltage 2-3 V lower than the voltage in the on-board network, which creates a certain magnetic field near it. A metal pin is installed at the end of the camshaft, which, when it rotates, passes by the DPRV in its magnetic field. This happens once every two revolutions of the crankshaft, just on the compression stroke. As a result, the voltage at the output of the phase sensor changes from constant (2-3 V lower than the voltage in the on-board network) to close to zero (when a metal pin passes through the sensor field).
The control unit receives a signal that the piston has passed the first cylinder TDC on the compression stroke and sends a command to inject fuel into it.
Phase sensor malfunctions
If the phase sensor fails, the controller switches the system from phased fuel injection to pair-parallel. The so-called reserve mode. In this case, the injection timing is calculated based on data on the position of the crankshaft obtained from the crankshaft position sensor. Injection is performed once per revolution of the crankshaft. This affects the fuel efficiency and power characteristics of the car engine. The error is recorded in the memory of the control unit, and the “Check Engine” lamp lights up on the instrument panel.
Applicability of the phase sensor on engines of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
The phase sensor is installed on injection 8-valve engines of VAZ cars with a system compliant with EURO-3 toxicity standards (neutralizer, two oxygen sensors). ECM with control unit BOSH MP7.0H - phase sensor 2111-3706040.
Notes and additions
The Hall effect is the appearance of a voltage across a semiconductor when an electric current is passed through it and placed in a magnetic field. The change in this voltage when a metal pin passes through the magnetic field of the sensor underlies the operation of the DPRV.
What happens when the camshaft position sensor wears out.
This can happen at any time without warning. Imagine, dear motorists, the following: you are driving along a highway and driving a car at high speed, and then, unexpectedly for you, the car’s engine simply turns off.(?) After you experience unpleasant moments in this situation, which will be associated with turning off the power steering control and deterioration in the effectiveness of the braking system, you will immediately park your car on the side of the road, and then you will wonder what happened. A common cause of this unexpected engine shutdown while driving on the road is a faulty camshaft sensor (camshaft position sensor).
Sometimes this camshaft sensor (CMP) can fail without warning, causing the engine to stall. In certain and some cases, the driver may not even be aware of problems with the sensor; this will happen until the car engine simply starts.
In this article, dear readers, we will look at the main symptoms of a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor, and also tell you what needs to be done to eliminate this malfunction. But first, friends, let's find out together what this sensor does in a car.
Lada 21099 › Logbook › Phase sensor
The phase sensor (PF) is one of the many sensors that ensure engine operation.
The phase sensor is also called the “camshaft position sensor (CPR)”. This sensor is not installed in a carburetor engine, or even in the first models of VAZ injectors. The sensor is present in all 16-valve AvtoVAZ engines; On 8 valves with Euro-3 toxicity standards and with phased, sequentially distributed fuel injection; It is worth noting that in the period from 2004 to 2005, the mass introduction of phase sensors began on such engines as 2111, 2112,21114, 21124 with Bosch M7.9.7 and January 7.2 engine control units.
Why do you need a phase sensor?
The phase sensor is designed to determine the engine operating cycle and generate a pulse signal. Phase sensor with an integral sensor, i.e. includes a sensitive element and a secondary signal-to-pulse converter. The sensor's sensitive element operates according to the Hall principle, responding to changes in the magnetic field. The secondary element of the sensor contains a bridge circuit, an operational amplifier, and an output stage. The output stage is designed as an open collector. The operation of the phase sensor represents the choice of stroke for the first cylinder: the camshaft determines which valve is open and which valve timing. Carburetor engines do not have this sensor. The fact is that a carburetor engine supplies a spark plug at the moment of compression and at the end of the exhaust gases, and for this principle of operation the readings of the crankshaft position sensor (CPS) are sufficient. This type of engine operation is called the “ignition system”. On injection engines, when the phase sensor (DF) dies, the check light comes on and the engine switches from phased injection to the ignition system, that is, relying only on the DPKV readings.
What is the advantage of phased injection?
The phased injection system is designed as follows: the phase sensor transmits an impulse to the ECM, which controls the fuel supply and the injector injects gasoline into the cylinder just before the intake valve opens. When the valve opens, air is drawn into the intake valve and the fuel is actively mixed with the air.
Where is the phase sensor located?
What is a Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor?
The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
In the cylinder head of a car engine there are one or two camshafts, which are equipped with special lobes that are designed to operate the intake and exhaust valves. The crankshaft is located in the cylinder block itself, which, when receiving torque from the movement of the pistons in the block, transmits it (torque) using gears, a timing chain (or timing belt) to the camshaft.
Camshaft
To determine which engine cylinder is on stroke, your vehicle's computer monitors the rotation position of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft position using the camshaft sensor (CMS). The information received from the CMR sensor is necessary to adjust the timing of the spark supply to the combustion chamber and for the operation of the fuel injectors. Thus, the camshaft sensor directly affects the fuel consumption of the car and the amount of emissions in the exhaust.
The most common camshaft sensors are: -magnetic, based on the Hall effect. Both types of sensors transmit a voltage signal to the electronic engine control unit or to the vehicle's on-board computer.
The magnetic type of camshaft sensor produces its own alternating current (sine wave). Typically this sensor has two wires. A Hall effect sensor uses an external power supply to generate a digital signal and typically has three wires.
Camshaft position sensor.
Depending on the make and type of your vehicle, your engine may have one or more camshaft sensors. There are also two types of CMP sensors that may be used in your vehicle.
Replacement
Alas, a visual inspection does not always provide an answer to the question about a non-working phase sensor. Therefore, you have to carry out dismantling work, inspect and, if necessary, replace the device.
Dismantled DF
You can begin dismantling the DF only if the battery is turned off. Otherwise, not only the sensor, but also all the wiring and the entire car may burn out.
Let's get to work. The procedure for replacing the DF on 8-valve and 16-valve engines is somewhat different, so we will consider both situations separately.
Replacing the DF on an 8-valve engine
- First of all, we determine where our sensor is located. And it is located at the top of the engine, on the right near the air filter.
- The device is fixed using one bolt. A regular 10mm wrench will help you unscrew it.
- After unscrewing the fastener, remove the camshaft sensor.
- Be sure to close the slot where the device is inserted. This will prevent debris and foreign objects from entering. This way you guarantee the correct operation of your new device.
- Having picked up the device, visually examine its current state according to the instructions given above.
- If dirt or dust has accumulated on the surface, remove it using an ordinary dry cotton rag. Wipe the device to remove moisture and dirt, and then try to put it back in place.
- If the above errors appear again on the screen of your on-board computer, you will have to remove the device and put a new one in its place.
- In some very rare situations, even replacing the meter does not solve the problem. This is due to the shift of the pressed control gear. It happens rarely, but who knows, maybe a similar situation is your case. Such a breakdown can only be corrected with the help of specialized equipment. It is impossible to solve the problem with your own hands, even if you want to.
- Somewhat more often, DF errors occur due to the fact that the timing belt was incorrectly installed during the replacement process, or it became too stretched as a result of installation or long-term operation.
Making our way to the device
Replacing the DF on a 16-valve engine
If you are dealing with a 16-valve power unit, then the procedure for removing and replacing a damaged camshaft sensor will look slightly different.
- The desired device is located on the front part under the air manifold. Look for the device in the immediate vicinity of the first camshaft pulley.
- Now that the location of the device has been determined, dismantling work can begin.
- Remove the radiator grille.
- Using an extension with a 10 mm socket, unscrew the two fasteners.
- Visually examine the condition of the measuring device, make sure the contacts are clean and the wiring is intact.
- If defects are found on the old sensor, replace it with a new one.
- During the replacement process, do not under any circumstances use additional sealants or sealing agents, since the sensor is constantly located in a very aggressive environment where the temperature changes regularly. Excessive compounds can cause breakdown of the oil system and even the entire engine.
Functionality check
So, you managed to replace the DF. The work is not difficult, but it has its nuances. The hardest part is getting to the device you are looking for. Everything else is a matter of a couple of movements.
But installing a new DF is not enough. You also need to make sure that the device works and sends the necessary information to your electronic control unit.
To check you need:
- Return the negative terminal to the battery;
- Start the engine;
- Using a scanner or controller, check the machine for errors;
- Listen to the operation of the power unit, which should function stably without signs of malfunction;
- Check the instrument panel to ensure that the Check light is not on;
- Be happy if the replacement is carried out correctly.
Practice shows that in the case of a 16-valve engine, work takes slightly longer compared to 8-valve power units. In any case, it should take you no more than an hour to check and replace.
Symptoms of a faulty camshaft sensor.
Just like any part or component of your car, this CMP sensor will eventually simply stop working due to wear and tear. This happens in any case as soon as its maximum service life has expired. This usually occurs due to wear on the internal wire wrap or associated component.
Typically, in this case, the engine begins to run erratically, and the symptoms of the malfunction may vary depending on the type of wear on the sensor. For example, the same connector in the sensor may wear out, the same internal circuit of the sensor may fail, or a component associated with the sensor may fail.
–
On some types of cars, if the camshaft position sensor is faulty, the transmission may be blocked in one of the gears, and will be blocked until you turn off the engine and start it back.
This can be repeated with a certain cyclicity. – If the camshaft sensor begins to work incorrectly while the car is moving , then you can immediately feel that your car has begun to move jerkily and lose speed.
– If the camshaft sensor is faulty, you may experience a noticeable loss of power from the engine itself. For example, your car will not be able to simply accelerate over 60 km/h.
– The engine may stall intermittently, and all this is due to a malfunction of the CMR sensor.
– If the sensor fails, you will notice poor engine performance, it will have a loss of dynamism, misfires when turning on the ignition, jolts during acceleration, popping noises in the exhaust system, etc. irregularities in work.
– On some car models, if the camshaft sensor is faulty, the ignition spark may completely disappear, which will ultimately lead to failure and the engine being unable to start.
Once your car's computer detects a faulty camshaft position sensor, which will (usually) cause the Check Engine light to appear (light up) on the dashboard. After detecting such poor performance of the CMR sensor, the computer will automatically record the sensor’s “error code” in its memory. In order to accurately determine the cause of the malfunction of this camshaft sensor, it is necessary to conduct computer diagnostics of the car, i.e. by connecting special equipment to the diagnostic connector of the machine. Then, using a special computer program, you can read the “error code”. Below, dear motorists, we present to you a table of diagnostic “error codes” that are directly related to wear on the camshaft sensor.
Camshaft position sensor VAZ 2108
If computer diagnostics determine that the VAZ 2108 camshaft position sensor is broken, then you need to buy a new one. Let's tell you a little about this sensor. The VAZ 2108 camshaft position sensor is mainly of two types. The first is induction, which is a coil of copper wire with a magnetic core, hermetically sealed in a polymer plastic housing. The second is a camshaft position sensor based on the Hall effect. In the first case, there are 2 wires coming from the sensor, in the second - 1. The sensor has 2 connectors.
One car can have one or several VAZ 2108 camshaft position sensors. Moreover, they can be installed on one engine of the same type or of different ones. The camshaft position sensor sends information to the car's on-board computer. It shows the angle of rotation of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft. This information allows you to adjust the ignition and synchronize the fuel supply to the injectors.
Cost of the VAZ 2108 camshaft position sensor:
| Options | Price |
| Camshaft position sensor | from 1200 rub. |
| Camshaft position sensor with wiring | from 1500 rub. |
Buy camshaft position sensor VAZ 2108
:
Phone: 8 (812) 409-46-75
Write to us on Whatsapp
Free delivery throughout St. Petersburg. Delivery to regions from 2 days.
The cost of the sensor depends on whether it is new or used, the manufacturer, as well as on availability in our warehouse or delivery time to our store.
The location of the VAZ 2108 camshaft sensor can be different, mainly in the area of the cylinder head or under the hood. You can find out the installation location in the vehicle's operating manual. If the sensor fails, it is necessary to check whether the connectors and electrical wires are intact; the contact parts wear out first. We recommend using special equipment at a service station for accurate diagnostics. We recommend selecting a VAZ 2108 camshaft position sensor based on the VIN number of your car.
Recommended crankshaft position sensor manufacturers: original, HELLA, BEHR, VDO, BOSCH, NGK.
When to buy a camshaft position sensor:
— The engine stalls while driving; — The ignition does not turn on on the first try, acceleration occurs with jolts, and there are popping noises in the exhaust system; — Loss of engine power; — The message CHECK ENGINE appears on the instrument panel; — The computer displays error codes P 0340 – 0344 CMP.
Location of the camshaft sensor in the car.
As you can probably guess, the exact location of the camshaft position sensor varies depending on the make and model of the vehicle. In most cars, this sensor can be found somewhere around the cylinder head itself. Look for the sensor around the top of the timing belt location or in protected parts of the electrical wiring at the front of the engine.
The sensor can also be located in the rear of the cylinder head.
Some car models may have a special compartment under the hood for this purpose, in which the camshaft sensor is installed (for example, in certain car models produced by).
In addition, in some cars (car models), the camshaft sensor may be located directly inside the cylinder head.
If necessary, you can look at the owner's manual for your vehicle to find out more precisely where the CMP sensor is located. If you do not have a manual for the repair and maintenance of your car, then you can find it on the Internet or purchase it at a car store, which has a large selection of such auto literature.
We, dear friends, strongly recommend that all car owners purchase a similar book (repair and maintenance manual) specifically for your modification and model of car. This manual for operating and repairing a car will certainly help each of you in the event of any breakdown or malfunction. It will become your valuable reference for performing routine maintenance on your vehicle and making minor repairs.
Phase sensor VAZ 21099 injector
The camshaft position sensor (phase sensor) on the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is an element of the electronic engine control system (ECM).
Purpose of the phase sensor
The phase sensor is designed to determine the top dead center (TDC) of the piston of the first cylinder during the compression stroke according to the position of the camshaft by the ECU controller. This makes it possible to achieve precise phased fuel injection into the engine cylinders (specifically for each injector), improved mixture formation, greater fuel efficiency, and throttle response.
Phase sensor device
The phase sensor is a semiconductor device. It consists of a housing, copper winding, steel core and magnet. The sensor connection block has three outputs. A rubber O-ring is installed on the body.
Location on the engine
DPRV, on the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars, is located on the end cap of the cylinder head (on a carburetor engine this is the camshaft installation location).
Operating principle of the camshaft position sensor
The operating principle of the sensor is based on the Hall effect (see “Notes and Additions”). The control unit constantly supplies the sensor with a voltage 2-3 V lower than the voltage in the on-board network, which creates a certain magnetic field near it. A metal pin is installed at the end of the camshaft, which, when it rotates, passes by the DPRV in its magnetic field. This happens once every two revolutions of the crankshaft, just on the compression stroke. As a result, the voltage at the output of the phase sensor changes from constant (2-3 V lower than the voltage in the on-board network) to close to zero (when a metal pin passes through the sensor field).
The control unit receives a signal that the piston has passed the first cylinder TDC on the compression stroke and sends a command to inject fuel into it.
Phase sensor malfunctions
If the phase sensor fails, the controller switches the system from phased fuel injection to pair-parallel. The so-called reserve mode. In this case, the injection timing is calculated based on data on the position of the crankshaft obtained from the crankshaft position sensor. Injection is performed once per revolution of the crankshaft. This affects the fuel efficiency and power characteristics of the car engine. The error is recorded in the memory of the control unit, and the “Check Engine” lamp lights up on the instrument panel.
Applicability of the phase sensor on engines of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
The phase sensor is installed on injection 8-valve engines of VAZ cars with a system compliant with EURO-3 toxicity standards (neutralizer, two oxygen sensors). ECM with control unit BOSH MP7.0H - phase sensor 2111-3706040.
Notes and additions
Troubleshooting the camshaft sensor (CMP).
If your car’s computer has detected a sensor error and turned on the “Check Engine” icon on the dashboard, then you can easily find out the “error code” yourself, which led to the appearance of the light indication on the dashboard. To do this, we advise each driver to purchase an inexpensive set of diagnostic equipment specifically for computer diagnostics. If you cannot afford to purchase this diagnostic scanner for your car, then contact any inexpensive car service center to diagnose your car, where they will read the “error code” from your car’s computer.
Once you know from the "error code" that your car has a faulty camshaft sensor or related components, you should do a few simple tests. Please remember, friends, that a fault “code” indicating a potential failure of the camshaft position sensor will not necessarily mean that the CMP sensor itself has failed on the car. After all, it is possible that the cause of the malfunction is not in the sensor itself, but in the sensor connector, or there is damage to the wires connected to it, or perhaps the components directly connected to it have failed.
The truth is, friends, you need to remember that in order to more accurately establish whether the camshaft sensor is functioning normally, for this you will need to carry out (maybe) quite a lot of diagnostics. It is especially necessary to take into account the following: in order to check the effectiveness of the SMR sensor signal, in some cases special equipment may be needed, without which it will be difficult to determine the cause of the malfunction.
However, you can do a few simple tests yourself using a digital multimeter (DMM):
–
First, check the electrical connector at the camshaft sensor and the condition of the wires. Disconnect the connector and check for signs of rust or dirt.
For example, the same fuel. All this can interfere with good contact for the transmission of electricity. Next, check for damage to the wires, namely, whether there are any broken wires or signs of melting of these wires from nearby hot surfaces.
Above all, please make sure that the camshaft sensor wires do not touch the spark plugs or ignition coils, which could cause interference and prevent the sensor from transmitting the correct signal.
– After the above checks, use a digital multimeter that can test alternating current (AC) voltage or direct current (DC) - depending on the specific type of camshaft sensor used in your vehicle..
Also, before testing, you need to set the correct electrical parameters on the multimeter for a specific type of CPM sensor. Typically, such information is indicated in the vehicle repair and maintenance manual.
– Some camshaft sensors allow you to create a splitter for the electrical circuit of the CMR sensor; this is done in order to read the signal directly from the sensor itself while it is operating in the car.
If the type of sensor you have does not allow you to connect multimeter wires to it, then you can simply disconnect the connector from the sensor and attach copper wire to it by inserting it into each connector of the sensor.
You can then connect the connector back to the sensor, being careful not to short the wires themselves during testing. If you use (apply) this method, do not forget to insulate the wires with electrical tape.
Testing a two-wire camshaft sensor.
– If the camshaft sensor in your car has two wires, then this means that the automaker installed a magnetic type of CMP sensor on the car. In this case, you need to set the multimeter to “variable voltage”.