Checking burnt elements
Motorists should understand how to check the fuses in their car.
An overload in the electrical network does not always lead to failure of the fuses themselves. They are the easiest to check, so diagnostics usually start from here. When an electrical appliance stops functioning, it is far from certain that the protective element is to blame. Here the most correct and rational solution would be to check the status of the device responsible for the faulty device in the car.
A fuse map will be a very useful tool in the diagnostic process. On all modern cars it is located directly on the cover of the safety block.
There are several main verification methods:
- visual,
- replacement method
- multimeter.
The simplest method is considered to be by replacement. You just need to install a new fuse in place of the potentially faulty device. But it is fair to consider this technique identical to visual inspection. After all, it is easier to determine by external aspects than to change each of the fuses located in the block in a row.
Visual inspection
Let's start with how to understand whether a fuse has blown in a car, based purely on the appearance of the element. This method is considered the most correct, since it is quite easy for many people to visually verify that a breakage of a low-melting component has occurred.
To check, you will need to remove the element, bring it to the light and look at it carefully. It will not be difficult for an experienced motorist to find out and understand whether the fuse in his car has blown or not. Beginners do not understand this right away, which raises several more questions regarding how to get an accurate answer.
A worn fuse is not difficult to identify. This manifests itself in the form of broken wire (low-melting alloy) or burnt marks. Symptoms such as these indicate that the electrical circuit has broken and the fuse needs to be replaced.
A similar testing method is relevant for those fuses that are made from glass or transparent plastic. Most of them are found in passenger cars.
But the method also has a significant drawback. The test is performed by a person, without the use of any instruments. In some cases, especially for beginners, a visual examination does not provide a 100% guarantee of a correct diagnosis. Therefore, it is much more correct and efficient to check fuses using multimeters.
Checking with a multimeter
This is a great way to identify a blown fuse in your car. Anyone can calculate using this method, since there is nothing particularly complicated in the procedure. The only condition is to have a multimeter. You can also check with a regular tester, but a multimeter can later solve a number of other issues. This is a more versatile device. Having a car multimeter in your hands, you should understand in more detail how to independently check a potentially blown fuse.
Using such a device, verification is performed using 2 methods:
- by voltage,
- by resistance.
Let's start with a technique that involves checking the condition by voltage. Here you need to perform the following procedures:
- turn on the measuring device in voltage test mode,
- turn on the electrical circuit of the machine where there are problems,
- check the voltage parameters on one terminal of the protective element, and then on the second,
- if there is no voltage at one of the terminals, the device has burned out and needs to be replaced.
The method is extremely simple, for which it is appreciated by motorists. Just a couple of minutes is enough to verify that the fuse is working or confirm that it has failed.
But in certain situations, checking by voltage is not very easy. This mainly concerns the fuses responsible for the operation of the horn and door lock. This is where an alternative method comes to the rescue.
If for some reason the voltage test is not suitable for you, use the resistance diagnostic method.
- The multimeter switches to Ohm measurement mode. These are units of resistance
- the terminals of the measuring device are connected to the terminals of the fuse,
- if the screen is zero, the element has failed and needs to be replaced.
And there is nothing complicated here, because even a novice motorist who has only recently started operating a vehicle independently can easily cope with the task.
In fact, to check you only need a little free time and a good multimeter with the appropriate measurement modes. It’s not difficult to buy a device, but its capabilities are enormous in terms of self-diagnosis of a car.
The article was written for those learning the basics of repair.
Is the input fuse in the power supply blown? Let's figure out the reasons and how to properly diagnose. We will also touch on a couple of related topics when analyzing this malfunction.
I think many have encountered this situation when we turn on the device but there is no reaction, and after a short diagnostic we identify a blown mains fuse. And it doesn’t matter whether it’s the computer’s power supply or the power supply board for a copier or fax machine. Naturally, many people immediately change it or, even worse, put a jumper and immediately turn on the device. And here, with a greater degree of probability, it will burn out again or knock out the machine guns in the shield. Let's take a closer look at what's going on and why you can't change the fuse without diagnostics.
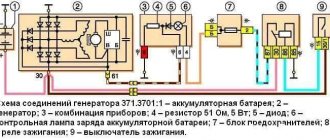
First, let's take a look at the typical input circuit in switching power supplies.
As you can see, fuse FU1 is the first in the circuit, and its main function is protective. But, this is not protecting the internal components of the circuit from overvoltage, but protecting the entire board from short circuiting these same components, and ultimately preventing ignition inside the device.
Therefore, when the mains fuse in the input circuit burns out, this does not mean that there was an excess of the supply voltage, but a short circuit in the circuit after the fuse. And as a rule, in 80% of cases, if you restore the circuit by inserting a new circuit breaker and measuring the resistance at the input of the block between contacts L and N, you will find a resistance equal to zero or slightly more.
A blown fuse is a consequence, so as soon as we discover that it is faulty, we begin diagnostics.
We start diagnostics from the input, the first on the list is varistor VR1, they look like this in general:
So they just perform the function of protecting the power supply from voltage surges. Their essence is that when a certain voltage threshold is exceeded, they begin to pass current through themselves, protecting the rest of the circuit. Several scenarios are possible:
1. The input voltage pulse was insignificant and the varistor, when triggered, absorbed it and dissipated it into heat, which is why the datasheets on them indicate how much power they can receive.
2. The input voltage pulse was stronger, and the varistor, having closed the circuit, led to the formation of an increased current flowing through the fuse, which burned out. In this case, the varistor was not broken and remained functioning. In this case, replacing the mains fuse will restore functionality.
3. Long-term overvoltage. In this situation, a thermal breakdown of the varistor occurs, leading to a short circuit. As a rule, this can be seen with the naked eye in the form of splitting, blackening, and so on.
But the defect can also be hidden, so if there is a short circuit in the circuit, then we unsolder it first and check it. If there is a defect in it, then we have a choice, not to solder it back at all, this will not affect the performance of the circuit, but next time something else will burn out, and replace it with an analogue one. I advise you to always install a new one.
Unfortunately, varistors are not available in all power supplies. It is also worth noting that it can be located in the diagram either before or after the chokes, and can be designated as you like.
Let's look further: Capacitors C1 and C4 are used to suppress low-frequency differential interference, with a capacitance of the order of hundreds of nanofarads and a voltage of 250 volts. In the diagram it can be designated as Cx, and have a rectangular appearance. It is a film type and almost never fails. But it's still worth checking.
Choke T1 - serves to suppress common-mode interference. Despite the fact that the windings may be located on the same magnetic circuit, the phase windings are spaced apart from each other at a distance, and there should be no short circuit. But winding breakage may occur. In this case, this clearly indicates a short circuit in the circuit further.
Capacitors C2 and C3 also act as a common mode filter. Breakdowns happen, but it looks a little different, since at a common point they are connected to the device housing, then in the absence of grounding, an electric shock will be felt when touching the metal parts of the housing. Thermistor T - performs the function of limiting the starting current when the device is connected to the network. The essence of the thermistor is that in a de-energized power supply and at normal temperature it has a high resistance; when voltage is applied, the thermistor heats up and its resistance decreases to zero. This ensures a smooth start of the power supply.
And so, we have looked at the main elements of the so-called input filter, but it is worth considering that this is only an approximate circuit; various manufacturers can modify it, for example, eliminating capacitors, replacing chokes with jumpers, eliminating varistors and thermistors. In some devices, on the contrary, a complication may be observed in the form of additional varistors between ground and phase. When checking elements for breakdown, be sure to unsolder them; checking for a short circuit in the circuit is pointless.
Now let's move on to the next component:
Diode bridge D1-D4. According to statistics, the cause of a short circuit in the input circuit holds the leading position. Moreover, it can be made either in the form of four separate diodes or in the form of an assembly.
It doesn’t make sense to check in the circuit, so we unsolder and look for a breakdown, we also check the voltage drop is normal from 400 to 600, but the exact information is in the datasheets on them. The main thing is that these values do not differ for each diode or junction in the assembly by more than a few units. The reasons for the failure of the diode bridge can be either a breakdown due to excess voltage or current, or degradation of the np junction over time.
In the circuit after the diode rectifier there is a network capacitor C5, with a voltage of usually 400 volts and a capacity of 40 to 200 microfarads. It can also cause a short circuit due to a breakdown between the plates. To check it, you also need to remove it from the circuit, and care should be taken, since a working capacitor can store a charge for a long time. To check, you already need a special LC meter device. Having previously discharged the capacitor, we check its capacity and leakage current. Although it is possible to visually determine the malfunction in the form of swelling, or, if you rub it, in the form of tapping inside, this method cannot show hidden defects.
And the last stage of the test will be to measure transistor Q1 for breakdown. In the above figure, the transistor control circuit is omitted, so depending on the layout, it would be a good idea to check its wiring. And by the way, if it is broken, then before changing it, you should understand in more detail the control circuit of the transistor and the transformer next to it for an interturn short circuit.
And we come to the conclusion:
Only after carrying out all these checks in the circuit and replacing faulty components can we install a fuse of the same rating and turn it on.
I hope the article was useful.
Fuse repair
Fuses and relays Mercedes w124
What to do if the fuse has become unusable
during the journey? There is no spare one. There is a way out in this situation if you have a thin copper wire
But here it is important to choose the right diameter of the thin wire depending on the nominal value. This piece of wire should be inserted into the tips of the fuse and pressed well with pliers
Please note that you do this at your own peril and risk!
Fuel pump - diagnostics and repair Headlights do not light - low beam does not work, diagnostics and repair Electric trunk lid - always convenient! Replacing the fuel pump with your own hands - video Heated rear window does not work - how to repair Repairing and replacing the cigarette lighter - video instructions
A blown fuse in a car is a sign of a short circuit. But it happens that they burn out for other reasons. Let's consider all cases.
The first thing to do when a fuse blows is to make sure there is no short circuit. If the check shows that there is no such phenomenon in the on-board network, then the following options are possible:
Too much load on the fuse
The cause of a blown fuse may be the connection of abnormal power equipment to the power line. For example, if you install 100-watt lamps in the headlights instead of the standard 55-watt ones, then with a high degree of probability you will have to change the fuse, since the “regular” one will constantly burn out. The same situation can occur if an abnormal load on the fuse occurs “independently”. For example, when electric drives move poorly and jam, the current in their electric line increases and the fuse may blow.
Incorrect fuse rating
The opposite situation, when the fuse is too strong, is much more dangerous. In this case, it can withstand increased current for which the wiring is not designed, which can lead to fire.
Poor quality fuse
If you buy fuses from an unknown dealer on the side of the highway, then anything can burn out, even your car. Unknown manufacturers, unknown brands, low-quality fuses, etc. are not for those who love their car. Buy fuses only from trusted auto stores!
Perhaps the most difficult situation is when a fuse burns out from a short circuit, but it is not stable, but occurs from time to time, for example, from accidental contact of a loose contact. In this case, long and very tedious work awaits.
Half of car electrical faults are related to fuses. Their number in the car can be more than a hundred.
The driver must know the types of car fuses, their purpose, methods of checking functionality, replacement methods and determining the rating.
How to find a blown fuse in a car
Automotive fuses are simple but quite reliable protectors of the car from electrical threats.
During short circuits in the wiring, they permanently fail, so the car owner must know where and how to look for a blown fuse. Most fuses are installed in so-called mounting blocks. There may be one such block on a car, or maybe several. In modern cars, mounting blocks, as a rule, are divided according to the “territory” of action: fuses responsible for protecting interior equipment are installed in the cabin, and those that protect external equipment (for example, headlights) are installed under the hood.
Fuse and relay block from Priora. On the right in a separate socket there is a red tweezer for flag fuses
In addition, there are single fuses that literally “shove” where you don’t expect them. So on the VAZ-2110 the central locking fuse is located behind the mounting block and provides a small thickening on the wire. Inside the thickening there is a fusible insert.
However, there are still standard locations for mounting blocks with fuses and relays. As a rule, they are installed on the left side of the dashboard, under the center console, behind the glove compartment, next to the battery or near one of the A-pillars under the hood. Where the fuses are located specifically on your vehicle should be found in the owner's manual or electrical diagram.
Once you have found the correct fuse box, open its cover and inspect it. Almost always, on the outside or inside of the cover there is a diagram of the location of the fuses with captions and icons indicating the devices that each fuse protects. This will allow you to find what you need even without an electrical diagram at hand.
There are two types of fuse blocks - with claws and for so-called “flag” fuses. You will encounter the former only on classics and early Samaras, while all modern cars use flag fuses.
Accordingly, the classic “column” with a metal insert placed on it can be inspected without pulling it out of the block’s legs. If the insert is torn, it means the fuse has blown. With flag ones it’s a little more complicated. To determine the functionality of such a fuse, it must be pulled out of the block socket. To do this, use special tweezers, which should be located in the same block, or thin pliers. You can also pry the fuse with a screwdriver.
Blade fuses can have a transparent or opaque body. If the case is transparent and the insert is visible in the light, then its rupture will also be visible. In the case where the housing is “blind”, the integrity of the insert can only be determined by “ringing” the fuse using a multimeter.
When there is no equipment at hand, you can put a suitable worker in place of the suspected fuse (read how to choose fuses for a car). It can be taken from any adjacent socket, but it is worth considering that if there is a short circuit in the wiring, the second fuse will immediately burn out and then you will already have two sets of non-working devices, so it is better to check flag fuses with a non-transparent body with a multimeter .
Posts 6
1 Topic by Mixail 2012-10-24 22:22:12
- mixail
- New member
- Inactive
- Registration: 2012-10-24
- Messages: 1 Thanks: 0
Topic: Resolved: Oversize fuse blows
Why does a car battery explode and how to prevent it?
hello, the VAZ2112 size fuse has blown, it’s pitch dark in the cabin
2 Reply from Admin 2012-10-25 06:13:09
- Admin
- Administrator
- Inactive
- Registration: 2012-02-20
- Messages: 3,257Thanks: 624
Re: Resolved: Dimensional fuse blows
Mixail, at what point does it burn out? Often the cause of this may be problems in the contacts of the rear license plate light.
3 Reply from Admin 2012-11-14 06:24:56
- Admin
- Administrator
- Inactive
- Registration: 2012-02-20
- Messages: 3,257Thanks: 624
Re: Resolved: Dimensional fuse blows
Mixail, is the problem solved?
- From: Arkhangelsk region. Velsk
- Registration: 2012-03-16
- Messages: 472Thanks: 229
- Car: VAZ 21124
Main reasons
Fuses for UAZ Hunter: description, diagram
Each fuse is responsible for the stable operation of certain electrical circuits. If the low-melting element melts, then some kind of malfunction has occurred. Sometimes such situations are isolated, that is, after replacing the fuse, the problem does not recur. But often it turns into a trend.
Experts identify several main reasons why protective fuses burn in a car. If you understand the reason and find the source of the trouble, you will be able to return the machine to normal operation.
- bad connection. It is possible that during installation or during operation on uneven roads, the quality of contact between the fuse and the block was impaired. Sometimes it’s all about the quality of the products themselves, which are not able to guarantee a tight connection. In this situation, the best solution would be to purchase higher quality security elements,
- wear. There is a fairly widespread opinion that the first time the load on the fuse is exceeded, it immediately fails. This is not entirely true. When the situation is critical and the load is really huge, the fuse element is immediately destroyed to break the circuit. But when the load is only slightly higher than normal, the fusible component gradually fails. The cross section decreases, and as a result, after several load sessions it finally burns out. Since fuses are consumables, they tend to fail without causing serious problems in the car itself,
- wrong choice at face value. Each fuse has its own rating. This is the current strength that he is able to pass through himself. If an element with an incorrect value is installed, it cannot withstand the load acting on it and quickly fails,
- sudden surges in voltage. If a sharp surge occurs in the electrical circuit for which the fuse is responsible, the element melts and fails,
- disturbances in the current path. Each fuse is designed for a specific load and is installed on the electrical circuit corresponding to its rating. If you shorten the length of the circuit, the resistance will decrease, and the fuse will pass a higher current through itself. On modern cars, electronics are not designed to withstand overloads. Therefore, special sensitive protective elements are installed in their electrical circuits. Under critical loads, they melt and break the circuit, thereby protecting the equipment from breakdowns.
When devices and components that depend on electricity fail in a car, it is recommended to first check the condition of the fuses before repairing or replacing them. They could simply burn out, causing the systems to stop working. A simple replacement of the element will restore functionality.
What to do if the fuse is blown
Since the price of fuses is more than affordable, many car enthusiasts carry with them a whole set of similar elements that can be installed in an electrical circuit if necessary. A blown fuse is a normal situation, since no electrical circuit is protected from surges in current and voltage. However, when a fuse blows regularly, you should not only think about diagnosing the electrical components of the car, but also carry it out as quickly as possible.
If a fuse blows almost immediately after it is installed in the circuit, it is necessary to determine which device is causing such problems. For this:
- Check the technical documentation of the car which devices are included in the circuit of this fuse;
Turn on all consumers that interact with this fuse;- Take a screwdriver with an insulated handle and touch the fuse mounting terminals with its metal end. If a spark jumps upon contact, it means that the fault is still in the circuit - turn off one of the devices in it, and then touch it again with a screwdriver. When, after turning off the next device, the spark stops jumping, you will identify the element of the car's electrical circuit that causes the fuses to constantly blow.
Once the faulty electrical circuit component has been identified, it must be repaired or replaced.
INDEPENDENT REPLACEMENT OF FUSES
Replacing a burnt-out device with your own hands is a matter of just a few minutes. Naturally, in order to avoid subsequent replacement of the entire fuse box, this simple manipulation should be taken with full responsibility. After accurately identifying the source of the problem, replacing the fusible protector should begin with selecting a new one that exactly matches the damaged one. For ease of “identification”, all devices have a different color - in accordance with their power.
It is best to purchase fuses in advance, without waiting until one of them fails. At the same time, you should be based not on your own preferences and cost, but on the recommendations of the manufacturer. If they are not available for sale, it makes sense to place an order and wait a little rather than put your car and yourself at risk. As a last resort, temporary use of fuses of suitable size and characteristics is allowed. A detailed algorithm of actions for correctly replacing a faulty fuse can be seen in the video:
Traditionally, increased attention must be paid if the cigarette lighter fuse has blown - as a rule, in a modern car it is subject to quite a serious load. Accordingly, not only should the cigarette lighter fuse be replaced promptly, but also an independent diagnosis of the causes of the incident should be carried out
At a minimum, you will need to evaluate the feasibility of using a cigarette lighter to charge several electronic devices at once.
CORRECT WIRING, OR HOW TO AVOID REPLACING A FUSE
The fact that occasionally a car's fuses will blow is not a cause for serious concern. A reason to think arises when such a situation repeats itself too often. In order to understand that the fuse has burned out and needs to be replaced, you do not need to be an expert - in this situation, those electrical appliances for which the damaged “protector” is “responsible” stop working.
For an experienced driver, the question “how to find out if a fuse has blown in a car” is not difficult, but to understand why it burns out, especially the same one, is a more difficult task. The first step is to check all the wiring in the engine compartment, or rather the integrity of its insulation.
You should be especially careful with the onset of frost - some types of automotive insulation simply cannot withstand, crack and cause a short circuit, which is the answer to the question of why fuses in a car burn out. Naturally, finding problem areas in the wiring requires a lot of work, since the breakdown can be masked by dirt, and it is not always possible to find it right away.
Why do fuses melt in a car?
Let's look at why fuses burn in a car - the most common typical reasons.
Cigarette lighter
The cigarette lighter fuse often fails. In most cases, it is not related to smoking. The cigarette lighter often contains power connectors for additional equipment (radar detectors, navigators, other auto gadgets), a compressor, chargers for mobile equipment, splitters and tees of dubious quality.
In some cases, simultaneous connection of several gadgets can lead to exceeding the maximum current in the power circuit of the cigarette lighter connector.
Such situations often arise when using an advertised additional electrical device.
Washer
The failure of this fuse is associated with possible freezing of water in the tank and washer system pipes at negative and slightly positive temperatures. The mobility of the electric pump drive is impaired, as a result of which the current increases and the fuse blows. To prevent such situations, it is necessary to promptly replace the water with non-freezing liquid and clean the entire system of water.
Dvornikov
It fails if the wipers freeze to the glass or the gearbox jams. Therefore, before starting to drive in the morning in the cold season, it is necessary to check the brushes for freezing to the glass.
Heated glass and mirrors
It may burn out due to a short circuit in the electrical wiring. The weakest wiring points are in the corrugated hoses of the front doors, the trunk door, and under the driver's sill trim.
Stoves
A fuse rated at 30 Amps is usually responsible for the stove. If the heater electric motor wears out, especially the bearings and bushings, the current in the electric drive circuit increases significantly. Timely maintenance of the stove fan helps to avoid such situations.
Lighting systems
They often burn out if the power is set, non-standard lamps are installed, especially xenon lamps with an ignition unit, the current consumption of which is much higher. When increasing the rating, you should simultaneously “strengthen” the electrical wiring of the lamps by laying wires of a larger cross-section.
Engine cooling systems
They fail when the radiator fan current consumption increases for the following reasons:
- foreign objects entering the area of rotation of the fan blades;
- wear of fan motors;
- production of engine lubrication.
Engine control unit
Their burnout leads to failure to start the engine. For this reason, the driver must know where the fuses serving the engine control unit are located. Almost half of all malfunctions associated with failure to start engines are determined by their burnout.
Electric power steering
Electric power steering systems are increasingly being used in automobiles. The electric drive of the electric amplifier consumes a large current; under increased loads, the fuses often fail.
Electric parking brakes
Electric parking brakes on some car models (for example, VW PASSAT B6) are a headache for many car owners. The electric parking brakes are located in an “uncomfortable” place near the wheels.
This contributes to mechanical destruction of the housing, moisture and dirt getting inside, as a result, jamming of the engine, and blown fuses along the power circuits.
ABS systems
As a result of pump wear, the current increases and the ABS fuse blows. This leads to the inoperability of the anti-lock brake system, which is especially necessary when the road surface is in poor condition.
Central locking, power windows
The central locking drives and power windows often jam, resulting in blown fuses. Also problematic is the short circuit of the wiring in the corrugated hose of the door wiring.
Methods for checking fuses in a car: visually, by voltage, by resistance
Electronics in a car are becoming more and more complex every year, and electrical circuits include more and more elements. Almost all of them are connected to each other in one way or another, and the failure of one of the elements can lead to the failure of others. To avoid this, fuses began to be installed in the car, the task of which is to protect electrical circuits from short circuits. When fuses break, they break the circuit, thereby cutting off the current and protecting the devices in it.
The fuse in the microwave has blown
A clear sign indicating such a breakdown is the complete absence of visual and noise effects (the display does not light up, nothing buzzes). This indicates a failure of the main fuse in the power supply.
There can be up to three of them in total.
The second is located in the high-voltage circuit and protects the supply transformer from overloads from the magnetron.
The third are equipped with furnaces with electronic control units, which are powered, as a rule, through a separate branch.
Why do fuses blow in a microwave?
There can be many reasons. Let's look at some of them.
Malfunction of individual parts
To prevent the device from being turned on with the door open, protection is provided.
Its role is played by microswitches.
The door has pushers that bring them to the desired position. If these parts do not work correctly, the fuse-link may burn out.
Contact disappeared
Malfunction of switches is often caused by deposited grease, burning or breaking of connecting contacts, and abrasion of the mechanical pusher.
Closure
Short circuit of the power transformer is another cause of the defect.
Burnout also causes a malfunction of the magnetron or capacitor of the high-voltage circuit.
What to do if the fuse is broken?
What to replace
Instead of a damaged part, you can only install an element that has the same data and capabilities.
You can buy it in radio parts or electrical goods stores. They are marked according to the maximum available load current.
If you are not sure that you will select the new part correctly, you can contact a specialist. It is guaranteed to return all functions to the kitchen appliance.
How to fix the problem yourself
You can try to repair the device yourself, saving time and money.
In this case, a minimum set of tools and basic knowledge of electrical engineering are required.
- If you decide to fix the problem yourself, then first of all you need to remove the back cover using a screwdriver.
- After removing the protective cover, remove the fuse. It is usually located at the base of the power wire.
- If obvious signs of burnout are visible, you will have to install another one.
- If there are no visual signs, test the continuity with a multimeter.
- After replacement, check the operation of the oven.
Other troubleshooting methods
If a repeated burnout occurs, you need to pay attention to the serviceability of the switches described above. First of all, make sure that they are pressed all the way by the pushers.
It happens that the base bends and the elements are not included. If necessary, adjust the location. It is worth making sure that the position of the push button instantly changes when opening the door. A slight delay caused by fat deposits melts the insert, which affects the performance of the device. The next possible reason is the contact burning and sticking inside. To eliminate the cause, cleaning or replacement with a new one is required. The parts are easy to understand, so it won’t be difficult to decide what to do. If the main fuse is intact and the microwave does not work, you need to check the insert in the high-voltage circuit. It is located in a closed plastic holder. We extract and call her. If a malfunction is detected, we replace it with the same one, taking into account the current strength. If the equipment still does not work, you need to check the insert in the control unit circuit or replace it with a known intact one. The lack of voltage here makes it impossible to start the microwave oven.
Read also: How to check how many amperes are in a battery with a multimeter
How to determine a quality fuse
Automotive fuses are priced hundreds of times lower than the cost of the equipment they protect. That is why it is not recommended to save when buying fuses, giving preference to dubious models. It is necessary to purchase only circuit protection elements whose parameters are perfectly met.
Since it is not possible to check each specific fuse from an unknown manufacturer, when purchasing such electrical circuit elements you should pay attention to the brands that produce them. Some of the more well-known companies that make quality fuses include Bosch, Hella, Vibe, Hollywood, CarPoint and SoundQuest.
When purchasing many fuses from an unknown manufacturer, do not be lazy to check them before installing them in the car. To do this, short-circuit the new fuse to the battery and pay attention to its behavior. If it blows instantly, it means the fuse is of high quality, and it will be able to break the circuit if a current exceeding its parameters flows through it. In the case when, during a short circuit to the battery, the fuse does not blow out, but begins to melt, you should be wary of installing it in a car - it will not be able to instantly break the circuit, and a destructive increased current will begin to flow to electrical devices.
( 398 votes, average: 4.51 out of 5)
Timing belt: when and how to change it, what to do if it breaks
EGR valve: why is it needed, how to turn it off
Related Posts
Safety precautions
Do not forget that repairs to a microwave oven can only be carried out if you have experience working with electrical engineering. In addition, you should adhere to all safety rules specified in the instructions for use.
List of basic rules when repairing a device:
- It is forbidden to start the device if the door does not fit tightly to the body.
- The stove should be repaired only after disconnecting from the power supply and completely discharging the capacitor.
- It is allowed to replace parts only with high-quality analogues.
- Never operate a stove with a faulty fan system.
- Before carrying out diagnostics, it is necessary to place a container of water inside in advance.
Basics
The basis for the operation of mechanisms of this type is the transformation of the so-called electromagnetic microwave field. Such fields are transformed into thermal energy and heat the products that are inside. The operating features of a microwave oven differ from other household appliances in which food is prepared: ovens (both gas- and electric-powered) and stoves.
The ability of a microwave oven to heat only the item inside. Because of this, food heats up very quickly. It is this ability that has gained popularity among buyers and has confidently taken one of the leading positions in the kitchen appliances market. Defrosting or heating food did not require the expenditure of excess energy, since in a matter of minutes electromagnetic waves raised the temperature to the desired level. Thus, the cooking and defrosting processes began to take much less time.
Read also: Equipment for the production of plastic dowels
Identifying a faulty fuse
Cars come with one block and two fuse blocks, usually one is located in the engine compartment, and the second is under the dashboard to the right of the driver.
The block located in the engine compartment is responsible for equipment related to the direct operation of the engine and everything that works together with it, as well as for external lighting.
As you might guess, the fuse box located in the cabin is responsible for all the equipment located in the cabin, including the instrument panel and lighting.
Often, on the covers of these blocks there is an explanation of which vehicle equipment a certain fuse belongs to. It is also possible to determine at random by examining each fuse for its malfunction; in this case, the main thing is to determine in which block it is located.
Automotive fuses and their classification
On a car, most fuses are located in blocks. Most often there are two or more fuse boxes on a car. One of them is located under the hood or in the luggage compartment area. It is called the main one and includes the largest number of fuses. The other unit is located under the front panel in the passenger compartment, but in different places for all cars. Also, fuses can be located separately throughout the machine - 1, 2 or 3 pieces.
Automotive fuses are classified according to two parameters - size and rated operating current.
When choosing a car fuse, you should pay attention to the size:
In addition to the size, when purchasing a fuse, you should know its current rating. Most often, elements are installed in cars that have a rated current of 5 to 30 A. The easiest way to determine the fuse current is by its color, and below is a table that shows how the color and rated current of the fuse are related.
Protected circuits and fuse numbers in the VAZ 2106
The headlight, heater fan, interior light and similar faults do not work, it is worth starting to repair them by checking the reliability of the contact on the fuse protecting this circuit.
Thanks for subscribing!
So, let's start, the photo below shows a standard VAZ 2106 fuse box, numbering, as you can see, starts on the left side, from the driver's door. In VAZ 2106 older years of production, as well as in VAZ 2103, VAZ 2101, there is no additional fuse block. It is available in new models that have additional consumers - heated glass, electric cooling fan, etc.
How to identify a blown fuse in a car?
For completely safe operation of all electrical systems in the car, special fuses are used that protect against overload and short circuits. These are the simplest, inexpensive protective elements that prevent damage to expensive units, which significantly reduces the car owner’s expenses for car repairs. Let's talk in more detail about how to identify a blown fuse in a car.
Main causes of burnout
Insurance companies collecting statistics have found that over 90% of all car fires are caused by faulty on-board wiring and the use of poor quality fuses or “bugs”.
Possible causes of burnout are:
- short circuit (short circuit) directly in the load (consumer);
- Short circuit in the wiring caused by insulation failure and short circuit to the housing;
- increasing the voltage of the on-board network;
- using the wrong denomination;
- poor connection with the contacts of the block;
- physical and chemical wear.
Short circuit in the electrical circuit
More often than other reasons, the fuse link burns out due to a short circuit. The resistance of the electrically conductive section decreases greatly, and the current increases tens or hundreds of times. This situation leads to:
- violations of wiring insulation due to strong heating;
- water entering unprotected live areas;
- mechanical damage to components;
- incorrect load connection.
Exceeding the permissible current limit
An increase in current strength above the permissible limit differs from a short circuit in the nature of the increase and the duration of the effect. This situation leads to:
- connecting a load exceeding the calculated value;
- consumer work in difficult conditions, for example, pulling out a car stuck in mud with an electric winch.
Poor connection to the block
Unreliable contact with the block leads to the formation of sparks in this place, excessive heating of the material and burnout of the fusible insert. Occurs when using parts of unsatisfactory quality, the thickness of the legs is less than normal or the contact group has lost its springy properties.
Wear
This process is primarily caused by oxidative processes and atmospheric influences. Over time, corrosion destroys the insert material, contacts are broken, which leads to interruption of power supply to consumers.
Violation of the current supply path in the circuit
The current strength in the circuit is calculated in advance and does not exceed the specified values if the equipment is in working order. However, mechanical damage to wires, contacts, and insulation failures for various reasons change the load value and affect the distribution of current in the circuit.
Disturbances in the flow path in most cases lead to an increase in current strength.
Wrong fuse selected
By mistake, a fuse with a lower rating may be installed instead of the standard one. Then, even with working equipment, the amount of current flowing will exceed the limit value of the part used, and the fuse-link will soon burn out.
VAZ 2106 fuses
Every car is equipped with various electrical appliances. The power circuit of each of them is protected by a special element - a fuse. Structurally, the part is made of a body and a fusible element. If the current passing through the fuse-link exceeds the calculated rating, it is destroyed. This breaks the electrical circuit and prevents overheating of the electrical wiring and spontaneous combustion of the car.
Examination
First of all, the electrical circuit “rings” to the housing. In this case, the battery terminals are disconnected. It must be remembered that the second wire from the engine goes to the housing; it must have zero contact resistance. The supply conductor is checked for short circuit.
If the wiring is intact, proceed to checking the voltage of the electrical circuit assembly. Measuring points are determined according to the diagram in the car manual. Also, the power at the battery terminals must be at least 12 V when the engine is off. When operating, a value above 13.6 V is measured.
With a multimeter you can measure resistance, contact integrity, and check voltage. The presence of oxides or mechanical damage is determined visually.
MAIN CAUSES OF FUSE BLOCKING
Frequent burnout of protective devices in a car cannot be considered the norm, since it indicates existing malfunctions. Some of the most common problems include the following:
- damage to a specific electrical unit or section of wiring, as a result of which current is supplied along a shorter path with less resistance. Many people remember from a school physics course that in such conditions the current strength increases. If the protection is triggered and melts, the car’s electronics remain intact, but if it doesn’t melt, the equipment suffers;
- a voltage surge resulting from an increase in current load - this often occurs, for example, when an electric motor that drives a certain mechanism is blocked;
- discrepancy between the installed fuse and the current voltage in the car’s electrical network, for example, if a model rated at 2 A is installed in place of a 5 A device;
- poor contact of the fuse with the block - in this case, both the block and the fuse body melt. If such cases occur frequently, you need to think about the quality of the fuses purchased - most likely it is extremely low. It makes sense to purchase a new set and replace all the fuses in the block, otherwise you may need to replace the entire block;
- fuse wear when areas with a smaller cross-section form in its fusible part.
Of course, the design of the fusible “protector” was initially designed for its one-time operation, but if a fuse protecting the same group of devices constantly burns out, this is a serious reason for checking. Quite often the following situation occurs - a newly installed fuse blows out almost immediately. In this case, the car owner needs to find out which electrical appliance is causing this problem.
In such a situation, it is not necessary to take the car to a service center; you can determine the cause yourself. To do this, you should gradually turn off all electrical appliances that are protected by the “problem” fuse. Each time the device is turned off, do not remove the device, as it may burn out. It should be checked in a simpler way - with the end of a screwdriver with an insulated handle, you need to touch the fastening terminals; if sparking is observed, disconnecting consumers should be continued until it stops - the device being turned off at this moment is the reason for frequent replacement of the fuse.
The fuse element has blown: what to do?
It is undesirable to resume operation of the circuit without identifying the causes of the failure. Maybe it’s not a fuse at all, but the car is giving all the signs that the battery is completely dead. If this is not the case, then at a minimum, the destructive current will again disable the fuse, and at maximum, it will finish off the executive electrical equipment. The first step is to diagnose the electrical circuit, and we will tell you how.
Suspicion No. 1 is a short circuit, the search for which should begin with a visual inspection. Doubtful locations are places where wire insulation is likely to be damaged. This category includes welding connections, loose and tensioned sections of wiring. Errors during assembly cannot be ruled out, as well as connections that call into question the reliability of current transmission. To exclude such cases, inspect the connecting blocks and wire tips.
Did the visual inspection yield no results? Let's use a multimeter or a test lamp. Control devices are connected to the fuse socket, and their readings are used to judge the state of affairs in the circuit. The difference between a conditioned circuit and a short circuit is the voltage. A short-circuited circuit has a voltage other than zero, while a healthy branch protected by a fuse has a voltage of zero.
Electrical circuit diagnostics are based on this simple difference:
- Remove the fuse.
- Connect the contacts of the socket for the fuse element through a 12V lamp or with a multimeter (in “constant voltage” mode). If the lamp lights up or the device shows a voltage other than zero, then there is a short circuit.
- Disconnect all electrical equipment of the damaged circuit one by one. We sequentially disconnect each of the blocks responsible for a specific piece of equipment in the electrical circuit until the lamp goes out or the multimeter gives zero voltage. A section of the circuit, after disconnecting which the state of affairs in the circuit returned to normal, is considered defective. Further troubleshooting work is carried out here.
Having localized and eliminated the cause of the circuit protection tripping, we safely install a new fuse and check the operation of the branch.