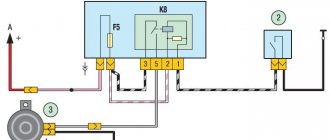
Schematic electrical diagrams, connecting devices and pinouts of connectors
VAZ cars have a fault diagnostic system that allows you to read and decipher error codes. Most VAZ-2110 cars have an old type “January-4” controller installed. The activation of “CHECK ENGINE” is considered a malfunction detection signal. Troubleshooting in such a controller is simple - error codes are calculated starting from the number 12 and ending with 61. For more modern VAZ models, ELM-327 electronic adapters with the OBD-II program are suitable.
Where is the diagnostic connector located?
On different cars of the VAZ family, the socket is located in different parts of the car. Let's look at a few models as an example:
- on the VAZ-2112 , as on the 2110 , as well as the 2111 , the socket is located to the right of the driver’s seat, immediately under the column;
- on models 2108 , 2109 and 21099 , the socket you need is located under the glove compartment, on a special shelf;
- on cars with a europanel it can be found in the center of the console, near the cigarette lighter. A special decorative cover is used to disguise it;
- Lada Kalina cars the connector is near the gear shift lever, it is also hidden under a special cover;
- On a Lada Priora, look right behind the glove compartment, on the wall.
VAZ 2110
see also
Comments 122
I had a diagnostic connector on my '98 car. And since I always had a repair book on hand, I quickly identified all the unclear connectors from it :) but there was no sensor in the gearbox. There is a sensor for the beige one, but the box is already 2110
The TDC sensor was installed before 1995, emnip.
How is driving the Ex-85, I wonder?! )))
A few years ago I bought a friend a Soviet instrument panel 2108 with a test mileage of 00002 at a very ridiculous price.
There is that same TDC sensor, now screwed into the gearbox bell (the one from the USSR). If you are interested, I will send it. The condition is really bad.
Thank you, there is such a thing, but without a tester it’s more likely just for beauty)
How can a tester carry out diagnostics? And what kind of tester?
There are still large quantities of mirror caps in the warehouse (where I worked) both left and right!
take out a few sets if you have more
There are still large quantities of mirror caps in the warehouse (where I worked) both left and right!
I'll buy it if there are any left.
And you want to say that this connector can be used?
Why not, if there is a device
I still have the sensor on the gearbox. I kept racking my brains as to why the hell he was needed there. Now I already know. Another "trick". Near the fuse block (on the right side) in early (as well as in other) models, there is a “specific” connector, somewhat reminiscent of a cigarette lighter connector. This is a connector for a carrying case, which has two magnets on the reverse side for fixing it to the body (it still serves me faithfully). avtohpp-ru.1gb.ru/index.p…rer_ >
I had such a connector. I found the carrier in the garage late, after the car was sold.
I also have a connector, I was wondering what it was for, thanks for the article. I'll have to look at the box and look at the sensor.
The old expansion one and I would install it with great pleasure! Cool little things... History!
What kind of diagnostic device was it?
there’s a sea of them, even a gazelle seems to fit, but I haven’t checked, otherwise www.ebay.co.uk/itm/Lada-S…ain_3&hash=item540583a8d8
for this money you can install an injection engine and still have enough for OBD)
How to diagnose a car
- Connect contact “B”, which has the diagnostic block and “ground”;
- Turn the ignition key to the third position, do not start the car;
- First, the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp displays code 12 with 3 flashes. It shows that the diagnostic programs are working. On the VAZ 2110 this happens in this order: the lamp blinks briefly 1 time (which should be considered the designation of number 1). After a pause lasting at least 2 seconds, it flashes 2 times in a row (two). So we got the number two. And this is repeated 3 times so that the driver understands these signs;
- After the diagnostic program has declared its serviceability, it will begin to display error codes, if there are any, of course. In the same way - flashes and pauses.
Lada 2109 Baltic in L series › Logbook › Brain self-diagnosis. Please help!
Hello everyone) This time there were problems with the brain, a couple of days ago, the “Check Engine” light came on several times and went out, but it didn’t affect the driving in any way. I couldn’t sleep at night, I didn’t give any rest, there was no time to go for diagnostics. Often before I came across an advertisement with a block, a cord and a disk for self-diagnosis, then I decided to look for it, but with my brains (and my brains are gm isfi-2s) I still couldn’t find anything, maybe I was looking poorly, so if anyone then he knows, send it, thanks in advance. And during the search I came across an article on self-diagnosis without any pads, maybe it will be useful to someone.
Everything is very simple. The diagnostic block is used to communicate with the ECU. The diagnostic block is located on a VAZ 2108, VAZ 2109, VAZ 21099 car under the instrument panel on the right side next to the ECU. Vehicle fault codes stored in the ECU memory can be read using a special diagnostic tool or by counting the number of flashes of the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp. To read fault codes with a lamp, it is necessary to connect pin B of the diagnostic block with a jumper to ground with pin A, which is connected to engine ground.
Marking of contacts of the diagnostic block for VAZ 2108, VAZ 2109, VAZ 21099 A - contact connected to ground; B - diagnostic contact for sending a signal to the computer; G—electric fuel pump control contact; M - information output contact (serial data channel) When contacts A and B are connected, turn the key in the ignition switch on the car to position I (ignition), while the engine should not be running. Under these conditions, the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp should flash code “12” three times in a row. This should happen in this order: flash, pause (1-2 sec), flash, flash - long pause (2-3 sec) and so on two more times. Code “12” indicates that the self-diagnosis system is working; if code “12” does not work, it means that the ECU system itself is faulty. After code “12” is displayed, the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp flashes fault codes three times if they exist, or simply continues to display code “12” if there are no fault codes. If more than one fault code is stored in the computer's memory, each of them is displayed three times.
Deciphering error codes
The first character is a letter and indicates a fault block:
- B - body;
- C - suspension;
- P — engine (ECM, gearbox);
- U - data exchange bus.
The second character is a number, code type:
- 0 — SAE (standard);
- 1.2 - OEM (factory);
- 3 - reserved.
The third character is a number, system:
- 1, 2 - fuel system;
- 3 - ignition system;
- 4 — reduction of exhaust gas toxicity;
- 5 - idle;
- 6 - ECU or its circuits;
- 7, 8 — transmission (automatic transmission).
The fourth and fifth characters are numbers, the error code itself.
To diagnose a VAZ 2114, 2113 or update the ECU firmware, car owners, diagnosticians or mechanics need to know the location of the OBD2 diagnostic connector, as well as its pinout and type. To flash the electronic unit or replace it, you also need to know the location of the ECU and the purpose of the pins.
For a VAZ 2114 car, the type of block depends on the year of manufacture and the type of ECU:
Where is the diagnostic connector for the VAZ-2114
VAZ 2108-2115 with a “European panel”, the diagnostic connector is located in front of the gearbox, directly under the cigarette lighter. The block is closed with a decorative cover. On injection models since 2002, a 12-pin rectangular connector has been used.
The location of the connector is indicated on the diagram in position No. 8 . The following are visual photos of the diagnostic block.
Photo of the block location:
About the ECU and its location is written in the article “Diagnostics of VAZ 2114”. The following shows the pinout of the OBD2 connector and the assignment of contacts of the electronic control units that were installed on the Fourteenth VAZ models.
OBD 2 connector
OBD 2 is an international diagnostic standard. It regulates the requirements for diagnostic equipment, unifies error codes - in general, almost everything related to diagnostics.
The VAZ 21099, produced since 2002, began to install a diagnostic connector that complies with the OBD 2 standard. Externally, it differs from the VAZ one in its trapezoidal shape:
You can carry out diagnostics on the injection VAZ 21099 using a car scanner (for example, based on the elm 327 processor). This is done with the preliminary installation of an application sold with a licensed scanner, even using a smartphone. By logging into the installed application, you can easily set error codes and also delete them.
True, the market is flooded with Chinese products that “do not see” the ECU of domestic cars, so you have two options:
- reflash the Chinese scanner;
- purchase a diagnostic cable connected to a laptop, Vag-com brand.
If you have an “old” GM12 block on your car, then the following adapter will help you connect to the scanner or cable:
However, in cases where you need to output errors to the computer, but there is no adapter, you can connect by independently connecting to any of the connectors for diagnostics, using the following correspondence diagram:
OBD1 pinout - 12 PIN (GM12)
Description:
OBD1 (GM12) connector is rectangular in shape, consists of 12 contacts.
Brands and years:
All injection models, except for some models after 2002, which have an OBD-II connector.
Access and location:
Open access. Located next to the ignition switch, partially covered by the steering column cover.
Pinout:
| M | L | K | J | H | G |
| A | B | C | D | E | F |
| Key * | |||||
* Connector Keying - A design element of a removable connector that ensures the correct orientation of the plug and socket.
Example in the photo:
Conclusions and their purpose:
| Conclusion | Color | Purpose |
| A | Weight | |
| B | L-line diagnostics (not always routed) | |
| D | CO potentiometer (not always diluted) | |
| G | Fuel pump control | |
| H | Power supply +12V (not always wired) | |
| M | K-line diagnostics |
OBD2 pinout - 16 PIN
Description:
The OBD2 connector is trapezoidal and consists of 16 pins.
Brands and years:
Gasoline passenger cars and light commercial vehicles manufactured or imported into the United States since 1996 (US CARB and EPA legislation) and in Europe (EOBD) since 2000-2001 (European Union Directive 98/69EG) and Asia (mainly since 1998). ).
Access and location:
Pinout:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| Smaller side of trapezoid | |||||||
Example in the photo:
Conclusions and their purpose:
| № | Color | Purpose |
| 2 | J1850 Bus + | |
| 4 | Body grounding | |
| 5 | Signal Ground | |
| 6 | Line CAN-High, J-2284 | |
| 7 | K-line diagnostics (ISO 9141-2 and ISO/DIS 14230-4) | |
| 10 | J1850 Bus- | |
| 14 | Line CAN-Low, J-2284 | |
| 15 | L-line diagnostics (ISO 9141-2 and ISO/DIS 14230-4) | |
| 16 | Power supply +12V from battery |
Diagnostic connector pins for used protocols
Pins 4, 5, 7, 15, 16 - ISO 9141-2.
Pins 2, 4, 5, 10, 16 - J1850 PWM.
Pins 2, 4, 5, 16 (without 10) - J1850 VPW.
The ISO 9141-2 protocol is identified by the presence of pin 7 and the absence of pins 2 and/or 10 on the diagnostic connector.
If pin 7 is missing, the system uses the SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation) or SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) protocol.
All three data exchange protocols operate via a standard OBD-II J1962 connector cable.
The correct connection diagram for a 12 PIN block with a 16 PIN adapter
see also
Comments 122
I had a diagnostic connector on my '98 car. And since I always had a repair book on hand, I quickly identified all the unclear connectors from it :) but there was no sensor in the gearbox. There is a sensor for the beige one, but the box is already 2110
The TDC sensor was installed before 1995, emnip.
How is driving the Ex-85, I wonder?! )))
A few years ago I bought a friend a Soviet instrument panel 2108 with a test mileage of 00002 at a very ridiculous price.
There is that same TDC sensor, now screwed into the gearbox bell (the one from the USSR). If you are interested, I will send it. The condition is really bad.
Thank you, there is such a thing, but without a tester it’s more likely just for beauty)
How can a tester carry out diagnostics? And what kind of tester?
There are still large quantities of mirror caps in the warehouse (where I worked) both left and right!
take out a few sets if you have more
There are still large quantities of mirror caps in the warehouse (where I worked) both left and right!
I'll buy it if there are any left.
And you want to say that this connector can be used?
Why not, if there is a device
I still have the sensor on the gearbox. I kept racking my brains as to why the hell he was needed there. Now I already know. Another "trick". Near the fuse block (on the right side) in early (as well as in other) models, there is a “specific” connector, somewhat reminiscent of a cigarette lighter connector. This is a connector for a carrying case, which has two magnets on the reverse side for fixing it to the body (it still serves me faithfully). avtohpp-ru.1gb.ru/index.p…rer_ >
I had such a connector. I found the carrier in the garage late, after the car was sold.
I also have a connector, I was wondering what it was for, thanks for the article. I'll have to look at the box and look at the sensor.
The old expansion one and I would install it with great pleasure! Cool little things... History!
What kind of diagnostic device was it?
there’s a sea of them, even a gazelle seems to fit, but I haven’t checked, otherwise www.ebay.co.uk/itm/Lada-S…ain_3&hash=item540583a8d8
for this money you can install an injection engine and still have enough for OBD)