VAZ 2107 engine structure
The 2107 power plant can be called revolutionary for the line of car engines of the Togliatti Automobile Plant. This is the first of the so-called classic cars to receive an advanced injection system.
The “Seven” injection system operates in rather difficult conditions, with constant high loads, especially on our roads. For this reason, the engine requires good and timely maintenance. Even the slightest blockage will negatively affect the fuel supply, resulting in an increase in fuel consumption and a decrease in the efficiency of the internal combustion engine.
Lubrication system
One of the main areas of the VAZ 2107 engine is the lubrication system, which functions by supplying oil to the rubbing surfaces. Thanks to it, friction is reduced and the efficiency of the power plant is increased. Oil is filled through the oil filler neck, which is tightly closed with a lid. Old, no longer needed lubricant is drained from the system through another hole - it is closed with a rubber plug.
Important characteristics of the lubrication system:
- the system holds exactly 3.75 liters of oil, the level of which can be monitored using an indicator gauge;
- the pressure on a heated internal combustion engine at average crankshaft speed is 0.35–0.45 MPa;
- The lubrication system functions in a combined way - under pressure and by splashing.
The main problems of the lubrication system include:
- oil filter clogged;
- problems with crankcase ventilation;
- lubricant leakage through loose connections;
- destruction of crankshaft seals;
- problems with fluid pressure.
The reasons that cause problems to occur are quite varied. You must understand that long-term engine operation is directly related to the lubrication system - it determines the durability of the power plant. After all, even a short-term interruption in the supply of lubricant to the rubbing internal parts of the engine can lead to major repairs and even replacement of an expensive unit.
The lubrication system ensures the durability of the power plant
Find out which engine can be installed on the VAZ 2107: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/dvigatel/kakoy-dvigatel-mozhno-postavit-na-vaz-2107.html
Cooling system VAZ 2107
It is designed to maintain the desired thermal regime of the motor installation by correlating the heat removal from the hottest components and parts. The “seven” operates a sealed liquid system with forced circulation. Some of its important components are the pump, expansion tank, heater core with electric fan and thermostat.
- The centrifugal pump is driven by the crankshaft. It consists of a cover supported by four studs and a body connected to the cover through a sealing gasket. The pump also has a roller with an impeller, rotating on a bearing.
- The expansion tank is integrated into the cooling system for a reason. The element accepts excess antifreeze, which, when expanded, tends to create high pressure that can rupture all hoses, tubes and radiator honeycombs. The same force is possessed by the vacuum discharge formed when the liquid cools (reduces). The expansion tank is designed to eliminate both phenomena. It is a durable tank element with a filler neck and fittings. A special role is played by the tank lid, equipped with valves to release excess pressure.
- The heater core is a structural part with two reservoirs and an iron core. It is installed on rubber cushions and fixed to the body of the “seven” with two bolts. The element is connected to the expansion tank in a sealed manner. Equipped with an electric fan activated by a sensor. On the “sevens” of the early year of production, an electric fan was not installed; the blades were mechanically rotated by the motor. In injection systems, the electric fan receives a command from the computer through a relay and an antifreeze temperature sensor.
- The thermostat maintains the desired thermal regime of the power unit and helps it start quickly. Equipped with two valves: main and bypass. Thanks to the thermostat, the engine warms up quickly.
The operating principle of engine cooling can be represented as follows: antifreeze circulates through all zones of the system, heats up, then enters the radiator and the pump.
The cooling system of the VAZ 2107 is designed to maintain the desired thermal conditions of the engine installation
More information about the design of the cooling radiator: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/sistema-ohdazhdeniya/radiator-vaz-2107.html
Piston group
This includes 4 required elements.
- Pistons on the VAZ 2107 are sorted by pin diameter into 3 classes every 0.004 mm. During their manufacture, special attention is also paid to weight, so when overhauling a motor unit, it is not necessary to use pistons of the same group - it is enough that they are suitable for the “seven” engine. There is a direction arrow on the bottom of the piston.
- The piston pin is a structural element held in place by retaining rings.
- Connecting rods on the VAZ 2107 are used with a pressed-in bushing made of combined iron. They, too, like pistons, are classified into 3 classes, depending on the diameter of the sleeve. The connecting rods are made of forged steel.
- The rings in the “seven” piston group are cast iron. Two of them are barrel-shaped, semi-chrome plated and compression, one is oil scraper.
The VAZ 2107 piston group is selected according to one size
Cylinder block
The block is made of a special type of cast iron - high-strength. Liners for VAZ cylinders are not needed, since boring is meant on site. The cylinders are honed from the inside, which makes them highly accurate. They are divided into 5 classes, alternating by 0.01 mm.
Engine
The VAZ-2107, -21072, -21074 cars are equipped with four-cylinder, four-stroke carburetor engines 2103, 2105 and 2106 with different cylinder capacities. The 2105 engine, which has a camshaft belt drive, is used only on VAZ-21072 cars, of which a small number are produced. Therefore, it is not described in this section. and its structure can be found in the section VAZ-2105, VAZ-2104.
The 2103 and 2106 engines, which are described below, differ from each other in the cylinder block and pistons with piston rings. The engine layout is simple and easy to maintain. All engine components that require adjustment and maintenance (ignition distributor, spark plugs, carburetor, air filter, valve lever adjusting screws, chain tensioner nut, oil filter, generator) are installed in easily accessible places.
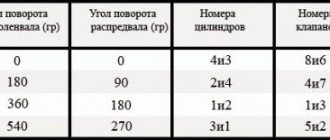
The cylinders are numbered from the generator drive pulley and water pump. On the left side of the cylinder head, near its lower plane, the number of each cylinder is cast, as well as the order of operation of the cylinders (1-3-4-2). The engine cylinders are combined with the upper part of the crankcase and form a single casting - the cylinder block. This arrangement ensures structural strength, rigidity, compactness, reliability and reduces engine weight.
The crankshaft is mounted on five supports at the bottom of the cylinder block. The front and rear ends of the crankshaft are sealed with self-clamping rubber seals. Each engine cylinder has one intake and one exhaust valve. Pistons 15 have two compression rings 16 and 17 and one oil scraper ring 14 with a spring. The piston is connected to the connecting rod by piston pin 33, pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod.
The camshaft 27 is mounted on the cylinder head in the housing 26 and is driven by a double-row roller chain 20 from the crankshaft. The advantage of the drive is its simplicity of design and lower weight compared to other types of transmissions. Cylinder block 18 is the basic part of the engine and is used for installing and fastening mechanisms, devices and auxiliary units of the engine. The block is cast from special low-alloy cast iron. Engine cooling ducts are made along the entire height of the cylinders, which improves the cooling of the pistons and piston rings and reduces block deformation from uneven heating. To increase rigidity, the lower plane is lowered 50 mm below the axis of the crankshaft.
The block cylinders by diameter are divided into five classes through 0.01 mm, designated by the letters A. B, C, D, E:
| Class | Cylinder diameter of VAZ 2103 | Cylinder diameter VAZ 2105, -2106 |
| A | 76,000-76,010 | 79,000-79,010 |
| B | 76,010-76,020 | 79,010-79,020 |
| C | 76,020-76,030 | 79,020-79,030 |
| D | 76,030-76,040 | 79,030-79,040 |
| E | 76,040-76,050 | 79,040-79,050 |
The cylinder class is indicated on the bottom plane of the block opposite each cylinder. The cylinder and the piston mating to it must have the same class. During repairs, cylinders can be bored and honed to accommodate an increased piston diameter (by 0.4-0.8 mm), taking into account the provision of a gap between the piston and cylinder of 0.05-0.07 mm. To ensure repair of the crank mechanism, parts of repair sizes are produced pistons and piston rings, increased in diameter) by 0.4 and 0.8 mm; main and connecting rod bearing shells for the crankshaft journals, reduced in diameter by 0.25; 0.5; 0.75 and 1 mm.
At the bottom of the cylinder block there are five crankshaft main bearing supports with thin-walled steel-aluminum liners. The bearings have removable covers 2, which are attached to the block) with self-locking bolts. The holes for the crankshaft bearings in the cylinder block are processed together with covers. Therefore, bearing caps are not interchangeable and there are risks for differences on the outer surface. The bearing supports and their corresponding caps are measured from the front end of the cylinder block. The rear support has slots for installing thrust half-rings 36, which hold the crankshaft from axial movements.
The axial clearance should be 0.06-6.26 mm. If the gap exceeds the maximum permissible (0.35 mm), it is necessary to replace the half rings with repair ones, increased by 0.127 mm. It should be borne in mind that the grooves located on one side of the half rings 36. must face the thrust surfaces of the crankshaft. Since October 1981, engines have been equipped with a front steel-aluminum half-ring and a rear metal-ceramic half-ring, impregnated with oil.
On the left side of the block there is a drive shaft 12 for the oil pump, ignition distributor and fuel pump. Rolled steel-aluminum bushings 51 are pressed into the holes for the roller bearings. By processing them together in the block, the necessary alignment of the bearings is ensured. When checking the technical condition of the block and making repairs, it is necessary to ensure that the lubrication hole in the front bushing aligns with the channel in the cylinder block.
In the front part of the cylinder block there is a cavity for the chain drive of the gas distribution mechanism. This cavity is closed by a cover 8. A holder 35 of the rear oil seal is attached to the rear side of the cylinder block, 6 the cover 8 and the holder 35 are equipped with self-clamping oil seals. On the left side, an oil filter, a fuel pump are attached to the cylinder block, a crankcase ventilation system and electrical oil pressure sensors are installed. A water pump and generator are installed on the right side of the cylinder block. At the bottom of the cylinder block on the right and left sides there are bosses for installing the engine on the suspension brackets.
An ignition distributor is installed on the upper plane in the front left part. The bottom of the cylinder block is closed with a stamped steel crankcase 43; the crankcase has a baffle to calm the oil. A cork rubber gasket is installed between the crankcase and the cylinder block.
Cylinder head 19 is common to four cylinders, cast from aluminum alloy, and has wedge-shaped combustion chambers. Valve guides and seats made of cast iron are pressed into the head. The intake valve seat dimensions are larger than the exhaust valve seat dimensions. Between the head and the cylinder block there is a gasket made of asbestos material on a metal frame, impregnated with graphite; along the edges of the cylinder holes, the gasket has a mild steel edging. The hole in the oil supply channel to the camshaft is edged with copper tape. To prevent the gasket from sticking to the block and cylinder head, it is recommended to rub it with graphite before assembly. The cylinder head is attached to the cylinder block with eleven bolts.
To ensure a uniform and tight fit to the block and to avoid warping, the bolts must be tightened on a cold engine in two steps using a torque wrench and in a strictly defined sequence (from center to periphery, left and right alternately). In the first tightening step, a pre-tightening torque of approximately 39.2 Nm (4 kgf-m) for ten main bolts and 14.7 Nm (1.5 kgf-m) for one bolt at high tide is carried out. In the second step, the final tightening is performed - the tightening torque is 115.7 N-m (11.5 kgf-m) for ten bolts and 37.24 N-m (3.8 kgf-m) for a bolt at tide.
The cylinder head bolts should be tightened after the first 2000-3000 km. and later after removing the cylinder head or when there are signs of gas breakthrough or coolant leakage between the block and the cylinder head. The top of the cylinder head is closed with a stamped steel cover. At the top of the cover there is a neck for pouring oil into the engine. To eliminate oil leaks, a rubber-cork mixture gasket is installed between the cylinder head and the cover. The cover is attached to the cylinder head using studs and nuts. To improve the fit of the lid to the neck, wide hard washers are installed under the nuts.
The engine assembly with clutch and gearbox is installed on the car on three elastic supports. The supports support both the mass of the power unit and the load. arising when starting a car, accelerating and braking. Using two front supports 37 the engine is attached to the cross member of the front suspension of the car, and the rear mount 38 is attached to the cross member of the rear suspension of the car. The front supports have rubber cushions 47, in which steel washers with fastening bolts are vulcanized. To increase rigidity, there are 45 springs in the hole inside the cushions.
To limit strokes, buffers 46 are used, which are a rubber rod with a vulcanized steel bushing. The cushion is attached to the intermediate plates, and these, in turn, to the brackets 44 of the front engine mount. The brackets are secured to the cylinder block flange with four studs. The rear support 38 consists of three steel plates vulcanized to the rubber separating them. The top plate is attached to the rear transmission cover, and the bottom plates are attached to the rear engine mount cross member.
To prevent the crossbar flanges from being dented when tightening the support mounting bolts, spacer bushings are installed between the flanges. The suspension design of the power unit ensures minimal engine vibrations and eliminates the transmission of vibration to the body.
continuation>>
Announcements of articles from friendly sites
VAZ 2107 car engine
The engine is the heart of any car. It’s not for nothing that the word “car” means “self-propelled” when translated from Latin. It is the power unit that distinguishes any bicycle from a car. The engines of the VAZ classic family, to which the VAZ 2107 belongs, were for their time advanced in their class - quite quiet, economical, and unpretentious. The weight of the power unit and the weight of the car are 10% and 90%, which is not bad for the development of traction. Let's talk more about the engine.
All engines of the classic family, including the VAZ 2107, are gasoline, four-stroke. All units have four cylinders, four pistons, which are arranged in a row, and a carburetor is installed. The unit is eight-valve, two valves for each cylinder. The camshaft (or timing mechanism, gas distribution) is located on top. At the top is the supply of the mixture of fuel and air, which is supplied by the carburetor.
Initially, the VAZ 2107 was equipped with a carburetor, a “six” engine, like the VAZ 2106, its volume was 1.6 liters. In the future, we will keep in mind this particular carburetor engine.
You can also install the 21067 engine, its volume is 1.6 liters. The mass of these two types of engines is almost the same
In addition to this standard, the old VAZ 2107 models were equipped with power units 2103 and 2104, with a different cylinder size, which was not 79 mm, but 76. Accordingly, the engine power was slightly less.
In all power units, the cylinder operating order is 1-3-4-2.
Power unit, section in the frontal plane
The power of the units installed on the VAZ 2107, and most of all in the VAZ 2106, is 54.8 kW, or 74.5 hp. There is a direct relationship: the larger the cylinder volume, the higher the engine power. A carburetor adds more reliability to the engine, compared to an injection engine, in case of engine failure, the ability to give it a “light”, etc.
The assembled engine weighs about 120 kg, so it is not recommended to try to remove the power unit without having an electric hoist or overhead crane at hand.
The engine structure is as follows:
- The cylinder block is a high-strength cast iron. It contains 4 high-precision cavities - cylinders in one row. The figure shows a diagram of the cylinder block and the coolant passages in it. Its mass is large; it is the heaviest part of the power unit.
- The crankshaft is also made of high strength cast iron and rests on five bearings called journals. The mass of the crankshaft is large, and the precision of its processing is also great; its journals are hardened by high-frequency currents. The figure shows the diagram, structure and main tolerances in the production of the crankshaft.
- Connecting rods are made of high-strength forged steel, as it experiences heavy loads. There are 4 of them, one for each cylinder. The piston pin is pressed into the connecting rod. Since the connecting rods cannot be replaced from one to the other, they are marked according to the cylinders. The figure shows the structure and main dimensions of the piston (right) and connecting rods (left) and their maximum tolerance diagram in mm.
- Pistons are cast from light aluminum alloys, with tin coating on the outer surfaces. This technology makes it possible to improve the running-in of the piston to the cylinder wall. Three rings are installed on the pistons, two of which are called compression rings, and one oil scraper ring.
- The cylinder head is made of light aluminum alloy, its weight is relatively small, and between it and the cylinder block there is a special gasket that is not subject to shrinkage. The figure shows the structure of the BC head and valves.
- The camshaft with sprocket and valve train, together with the chain, constitute the timing mechanism. The chain drive works together with the chain tensioner and damper.
- The flywheel is located at the rear pole of the crankshaft. The flywheel has a cast iron ring gear that meshes with the starter to start the engine. To increase engine power, you can reduce the weight of the flywheel by installing a lightweight version.
- The schematic diagram of the unit includes many others, for example, the engine lubrication diagram will also be presented, for example, this way:
In this diagram, without going into detail, you can see special channels and cavities in cast parts, the so-called lubrication passages and cavities for the circulation of coolant in the cylinder block.
It should be noted that the power of the unit cannot be maximum or close to it for a long time, without an adequate cooling and lubrication system.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that if you choose whether to choose a carburetor or an injector, then we can say that the first option is simpler and more reliable to repair, but the second is more modern and economical.
Source
VAZ 2107 Zhiguli
VAZ 2107 (Lada Nova, Lada Riva, Lada 1500) or “Seven” is a popular and latest rear-wheel drive classic model from AvtoVAZ in a sedan body. The car is a modified VAZ 2105, from which it differed in a higher level of comfort and the use of powerful and large-capacity 2107 1.7 and 1.6 liter injection or carburetor engines.
Some time later, after the car was discontinued, a replacement for the classic family was introduced - the Lada Granta.
In the articles you will find out which engines were used in the 2107, their malfunctions, of which there are quite a few... on the Internet you can always find owners whose VAZ 2107 engine speed fluctuates or the engine troits, noise and knocking in the engine is heard during operation, etc. Where to look for the root of evil and the cause of these phenomena, where to start repairing the 2107 engine, all information is now collected in one place and in an extremely compressed form.
In addition, you will find the complete technical characteristics of the VAZ 2107 engine, including engine weight and service life; no less important is the moment of changing the engine oil and what kind of oil to pour. In addition to the routine things described above, information on tuning the 2107 engine has been added to the articles, a sports engine is the dream of any 7 owner, and how to boost it correctly is also described here. We touched on the topic of the Priora engine on the classics and its brother engine 2112. To familiarize yourself with the material, select your model.
Model VAZ 2107:
1st generation (1975 - 2005): VAZ 2107 (71 hp) - 1.5 l. VAZ 21071 (59 hp) - 1.2 l. VAZ 21072 (64 hp) - 1.3 l. VAZ 21074 (75 hp) - 1.6 l. VAZ 21077 (64 hp) - 1.3 l. VAZ 21078 (75 hp) - 1.6 l.
Characteristics of the car 2107
Dimensions Length: 4145 mm Width: 1620 mm Height: 1435 mm Wheelbase: 2424 Front track: 1365 Rear track: 1321 Ground clearance: 170 mm Maximum trunk volume: 325 l Curb vehicle weight: 1060 kg Permissible gross weight: 1460 kg Turning circle: 9.9 m
Carburetor-type engine versions are marked 2103 and 2106. The main malfunctions are associated with floating engine speeds, tripping and overheating. Thanks to its simple design, repairing the power unit is quite easy.
Injection versions of the VAZ 2107 engine are considered more modern. In the VAZ 2107, the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders is obtained thanks to a separate injection system. The injector has 4 nozzles, which are controlled by a microcontroller. Fuel supply is regulated depending on various parameters of the vehicle’s condition.
The efficiency of the VAZ 2107 injection engine is higher than that of the carburetor engine. The engine is resistant to idling and rarely stalls when starting from a standstill thanks to sophisticated electronics. The motor has low noise thanks to automatic chain tension adjustment.
Specifications
Before we begin to describe the malfunctions, it is worth considering the engine options that were installed on the VAZ 2107 carburetor. The characteristics and design of the engine are quite simple. The engine has an in-line longitudinal arrangement of cylinders.
So, for the VAZ 2107 with carburetor versions of power units, engines marked 2103 and 2106 were installed.
VAZ 2103
| Name | Index |
| Volume | 1.5 liter (1452 cm3) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Power | 80 hp |
| Fuel | Gasoline with the possibility of installing gas cylinder equipment |
| Cooling | Liquid |
| Injection system | Carburetor |
| Fuel consumption | 6,7 |
| Cylinder diameter | 76 |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
VAZ 2106
| Name | Index |
| Volume | 1.6 liter (1569 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Power | 75 hp |
| Fuel | Gasoline with the possibility of installing gas cylinder equipment |
| Injection system | Carburetor |
| Fuel consumption | 6,7 |
| Cylinder diameter | 79 mm |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
The engines were equipped with gearboxes manufactured by VAZ - 4-speed manual transmission and 5-speed manual transmission. Unlike new models, all power units have a timing chain instead of a belt. Unlike the “fives”, the seventh model of the Zhiguli has higher engine power and displacement.
Maintenance of the VAZ 2107 engine is quite simple. So, the engine requires scheduled maintenance every 10,000 km. Many motorists are wondering what kind of oil to pour into the engine? Considering the design of the engine, the most suitable option is “semi-synthetic”.
Many car enthusiasts argue that it is better to pour “mineral water” or “synthetic” in general. Of course, an engine with high-quality oil will run longer, but in the case of the “seven” even the manufacturer recommends using “semi-synthetic”. But for power units equipped with an injector rather than a carburetor, it is already recommended to use a higher criterion motor oil - “synthetic”.
Electrical diagram VAZ-2107 carburetor
Electrical diagram of VAZ 2107, 21074 produced in 1988-2001 with generator 37.3701
- block headlights
- side direction indicators
- accumulator battery
- starter relay
- carburetor electro-pneumatic valve
- carburetor microswitch
- generator 37.3701
- gearmotors for headlight cleaners *
- Fan motor switch sensor
- engine cooling fan motor
- sound signals
- distributor
- spark plug
- starter
- coolant temperature gauge sensor
- engine compartment lamp
- low oil pressure warning sensor
- low brake fluid level indicator sensor
- windshield wiper motor
- carburetor electro-pneumatic valve control unit
- ignition coil
- headlight washer pump motor *
- windshield washer pump motor
- mounting block
- windshield wiper relay
- hazard warning and direction indicator relay
- brake light switch
- reverse light switch
- ignition relay
- ignition switch
- three lever switch
- hazard switch
- socket for portable lamp**
- heater fan switch
- additional resistor for the electric motor of the heater (stove)
- rear window heating indicator lamp
- low brake fluid level warning lamp
- signaling unit
- heater fan electric motor
- glove compartment lamp
- light switches on the front door pillars
- switches for warning lights of open front doors ***
- front door open warning lights ***
- connection block
- cigarette lighter
- watch
- instrument light switch
- diode for checking the serviceability of the low brake fluid level indicator lamp
- fuel level indicator
- fuel reserve indicator lamp
- speedometer
- turn signal indicator lamp
- carburetor choke indicator lamp
- battery charge indicator lamp
- carburetor choke warning switch
- instrument cluster
- econometrician
- light switches on the rear door pillars
- coolant temperature gauge
- tachometer
- parking brake indicator lamp ("handbrake")
- low oil pressure warning lamp
- high beam indicator lamp
- indicator lamp for turning on external lighting
- voltmeter
- parking brake indicator switch ("handbrake")
- outdoor light switch
- rear window heating switch with backlight
- rear fog light switch with on/off indicator *
- fog light circuit fuse
- lampshade ****
- tail lights
- level indicator and fuel reserve sensor
- connectors for connecting to the rear window heating element *
- license plate lights 2107
Wiring diagram VAZ-2107 carburetor - full view:
Electrical equipment VAZ 2107
Wiring type: single-wire, negative on the car body (ground).
Battery: 6ST-55, capacity 55 Ah. Batteries with a capacity of 60 and 65 Amperes are also suitable, but you need to check the dimensions. Typically it is 242mm x 175mm x 192mm.
Operating voltage in the network: 13.6 -14.6 volts. The generator (G221) must deliver a current of no more than 1/10 of the battery capacity, i.e. approximately 2 to 5.5 Amps.
Ignition coil - B117 or B117-A (for carburetor engines) Starter - ST221
Lamp type:
— low and high beam lamp: H4 or AKP2-60+55 (in Russian) — side marker lamp and side turn signals: T4W or A12-4-1 — turn signal lamp in the headlight, fog lights, reverse and brake lights: P21W or A12-21-3 - license plate and interior lighting lamp: C5W or AC12-5-1
Fuel consumption
- Fuel consumption in urban conditions is 9.4 liters per 100 km.
- On a flat road at cruising speed it will already be 6.9 liters per 100 km.
- In mixed mode, consumption will be from 8 to 9 liters per 100 km. Such figures do not allow us to call this engine economical, but in this case a lot depends on the driver himself.
- Another parameter that depends on the driver is oil consumption per 100 km. For the average driver of a car with this engine, it is 700 g per 100 km. This, of course, is not small, but with careful driving you can reduce this consumption down to 450-500 g/100 km.
- The weight of the 2103 engine when fully assembled is 121 kg.
General technical characteristics of VAZ 2107 cars
| 2107 | 210720 | 21074 | 2107420 |
| Body type | Sedan | ||
| Number of places | 5 | 5 | |
| Number of doors | 4 | 4 | |
| Body length, m | 4,145 | 4,145 | |
| Body width, m | 1,62 | 1,62 | |
| Body height, m | 1,446 | 1,446 | |
| Wheelbase, m | 2,424 | 2,424 | |
| Ground clearance, m | 0,164 | 0,164 | |
| Curb weight, kg | 1060 | 1060 | |
| Maximum speed, km/h | 150 | 150 | |
| Acceleration time to 100 km/h, s | 17 | 16 | |
| Fuel consumption in the urban cycle, l | 9,6 | 9,6 | |
| Fuel consumption on the highway, l | 6,9 | 6,9 | |
| Fuel tank volume, l | 42 | 42 |
What engines is the VAZ 2107 equipped with?
The VAZ 2107 model was produced from 1982 to 2012. Over the 30 years of its existence, the car has been repeatedly refined and changed to more accurately meet modern requirements. Initially, the “seven” was conceived as a small-class rear-wheel drive car in a sedan body. However, in some countries the VAZ 2107 was refined and modified, which is why it can be considered a universal car model.
Depending on the year of manufacture and the country of origin (at different times, the VAZ 2107 was produced not only by the Russian AvtoVAZ, but also by factories in European and Asian countries), the model was equipped with different types of propulsion systems:
- LADA-2107 (engine 2103, 1.5 l, 8 cells, carburetor);
- LADA-21072 (engine 2105, 1.3 l, 8 cl., carburetor, timing belt drive);
- LADA-21073 (engine 1.7 l, 8 cells, mono injection - export version for the European market);
- LADA-21074 (engine 2106, 1.6 l, 8 cl., carburetor);
- LADA-21070 (engine 2103, 1.5 l, 8 cl., carburetor);
- LADA-2107–20 (engine 2104, 1.5 l, 8 cells, distributed injection, Euro-2);
- LADA-2107–71 (engine 1.4 l, 66 hp, engine 21034 for A-76 gasoline, version for China);
- LADA-21074–20 (engine 21067–10, 1.6 l, 8 cl., distributed injection, Euro-2);
- LADA-21074–30 (engine 21067–20, 1.6 l, 8 cl., distributed injection, Euro-3);
- (engine 21067, 1.6 l, 53 kW/72.7 hp 8 cells, injector, catalyst) (2007);
- LADA-21077 (engine 2105, 1.3 l, 8 cl., carburetor, timing belt drive - export version for the UK);
- LADA-21078 (engine 2106, 1.6 l, 8 cl., carburetor - export version for the UK);
- LADA-21079 (rotary piston engine 1.3 l, 140 hp, originally created for the needs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the KGB);
- LADA-2107 ZNG (engine 21213, 1.7 l, 8 cells, central injection).
That is, in total there were 14 versions in the VAZ 2107 line - either with carburetor engines or with injection ones.
Read about the design of VAZ 2107 injection engines:
Technical characteristics of VAZ 2107 (carburetor)
The VAZ 2107 was initially equipped with a 1.5 and 1.6 liter carburetor.
In the USSR in the 1980–1990s, almost all produced models were equipped with engines of this size - this power was quite enough for trips around the city and country roads. The engine uses AI-92 gasoline to create the air-fuel mixture. There were also 1.3 and 1.2 liter carburetors, but they were not particularly popular.
The carburetor on the “seven” does not have large dimensions: the device is 18.5 cm wide, 16 cm long, 21.5 cm high. The total weight of the entire assembled mechanism (without fuel) is 2.79 kg. The engine works with spark plugs of a certain type - brand A17DVR or A17DV-10*.
The maximum power was calculated according to GOST 14846: 54.8 kW (or 74.5 horsepower).
The diameter of the working cylinders is 79 mm, while the piston stroke can reach 80 mm. The established order of operation of the cylinders is carried out according to the 1-3-4-2 scheme (every auto mechanic needs to know this scheme, since if the cylinders are not started in an coordinated manner, the operation of the carburetor will be disrupted).
The crankshaft size is 50.795 mm, the shaft itself rotates at a speed of 5400 rpm. When viewed from the front of the car (radiator side), the crankshaft rotates clockwise. The flywheel installed on the model has an outer diameter of 277.5 mm.
Check out the possibilities for tuning the VAZ 2107 carburetor:
The lubrication system on VAZ 2107 carburetors is combined, that is, the rubbing parts are lubricated both under pressure and by splashing. If you follow the recommendations of AvtoVAZ engineers, then you need to fill the carburetor engine of the “Seven” with oils that meet the API SG/CD standard. It is also recommended to select a lubricant according to the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers in the USA) classification. Thus, if you combine these two principles for selecting oils, then it is better to fill the “Seven” carburetor engine with:
- oils produced by Lukoil in the Lux and Super versions;
- Esso brand oils;
- Shell Helix Super lubricants;
- Norsi Extra oils.
AvtoVAZ has established acceptable oil consumption during vehicle operation.
Thus, a loss of 0.7 liters of oil per 1000 kilometers is considered acceptable (of course, if there are no leaks).
Where does this rate of 700g per 1000 come from??? This is more like the GAZ-53 norm, at least in the farm where I worked at one time they gave a liter of oil for about 200 liters of gasoline. I wrote purely on my own occasion - I always kept MAX oil. in the crankcase, and did not leak or drip from anywhere, and when replacing the level was 2 matches below MAX. there was, and it was over 8000. This is normal oil consumption, as in the book “natural oil consumption for waste.” And when did it become when replacing MIN. I put it on capital, and, as it turned out, it was not in vain
Advanced
https://www.lada-forum.ru/index.php?showtopic=12158
The service life of a carburetor engine before major overhaul is relatively short - approximately 150–200 thousand kilometers. However, due to the simplicity of the design, overhauls will not require large investments, and the updated engine will operate in the same mode as the new one. In general, the service life of the VAZ 2107 engine greatly depends on the driver’s driving style and care:
It depends on how you drive and what kind of oil you use. Ideally - 200 thousand, then capital is guaranteed
Enlightened
I used 270 thousand, I would have used more, but an accident forced me to disassemble it and replace everything that was needed without boring.
Sailor
https://otvet.mail.ru/question/70234248
The device of the injection model VAZ 2107
The platform for the creation of the VAZ 2107 was the model 2105. Its serial production began in 1982. A model with a capacity of 1.45 liters was available for sale in Asian markets. To withstand competition in the European market, engineers developed a model with an injection unit. Subsequently, the injector began to be installed on all engines.
Characteristics of VAZ 2107
| Performance indicators | Meaning |
| Maximum speed, km/h | 150 |
| Fuel consumption l: | |
| City | 9,6 |
| Route | 6,9 |
| Mixed | 8 |
| Euro toxicity standard | Euro 2 |
| Engine | |
| Power unit volume, cm3 | 1451 |
| Fuel type | petrol |
| Number and arrangement of cylinders | 4/R |
| Supply system | Distributive injection |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Maximum torque, N*m at rpm | 115 at 3450 |
| Maximum power, hp | 71 |
| Transmission | |
| Transmission type | Mechanical |
| Number of steps | 5 |
| type of drive | Rear |
| Suspension | |
| Front suspension device | Independent multi-link |
| Rear suspension device | Dependent, on coil springs |
| Front brake mechanism | Disk |
| Rear brake mechanism | Drum |
Initially, the seven was equipped with an engine with a capacity of 1.5 liters, but during the production process the power range was expanded.
Modifications of engines installed on the VAZ 2107.
| Options | Model range of VAZ engines | ||||
| 2103 | 2104 | 2106 | 21067 | 21067-20 | |
| Cylinder diameter, piston stroke | 76 80 | 76 80 | 79 80 | 79 80 | 79 20 |
| Working volume | 1,5 | 1,5 | 1,6 | 1,6 | 1,6 |
| Compression ratio | 8,5 | 8,5 | 8,5 | 8,5 | 8,5 |
| Supply system | carburetor | Distributive injection | carburetor | Distributive injection | Distributive injection |
| Rated power, kW | 52,5 | 52,5 | 54,8 | 54,5 | 53,5 |
| Rated speed | 5600 | 5000 | 5600 | 5000 | 5300 |
| Fuel brand | (AI-92) | (AI-92) | (AI-92) | (AI-92) | (AI-95) |
| Spark plug | A17DVR, FE65CPR, A17DV-10 | А17ДВРМ, BRISR, SUPER, LR 15YC | A17DVR, FE65CPR, A17DV-10 | А17ДВРМ, BRISR, SUPER, LR 15YC | А17ДВРМ, BRISR, SUPER, LR 15YC |
| Toxicity standard | Euro-0 | Euro 2 | Euro-0 | Euro 2 | Euro-3 |
Characteristics and principle of operation of the engine
The operation of the fuel injection system is to supply fuel separately to each cylinder. This mechanism is called distributor injection. All modern cars are equipped with a distribution or electronic injection system.
The injection mechanism is classified according to its operating principle, installation location and number of injectors. “Seven” is equipped with 4 nozzles, which are controlled by an electronic control unit. The ECU prepares the mixture depending on the engine load, throttle position and other parameters read by special modules.
The main control element of the VAZ 21074 injector is an electronic control unit. Using built-in sensors, the ECU monitors the quality of the air-fuel mixture supplied to the combustion chamber, sets the ignition timing depending on the speed, and turns the fuel pump on and off. In addition, it regulates the idle speed, controls the emission of CO in the exhaust gases and determines the operating mode of the cooling fan.
The VAZ 21074 injector works in the following order.
The pump supplies fuel from the gas tank through filters to the fuel rail. Next, the fuel is supplied to the injectors. The pressure in the injectors is maintained by a special regulator within 300 MPa. Excess fuel is sent back to the tank. The injector is a sprayer with a solenoid valve, which operates from ECU pulses.
By reading readings from the piston position module in the cylinder, the central unit determines the moment of opening and closing of the injector. The optimal quality of the air-fuel mixture is prepared based on the readings of the mass air flow sensor and the throttle position.
Other parameters are also taken into account:
- cooling system temperature - necessary to determine the degree of engine warm-up and adjust idle speed. The temperature correction affects the degree of richness of the mixture;
- oxygen concentration - used to measure the oxygen content in exhaust gases;
- on-board network voltages - read by the speed sensor to transmit pulses in a certain order.
Disadvantages and advantages of the model
The VAZ 2107 engine injector has a number of advantages over carburetor modifications:
- the electronic control mechanism ensures stable operation of the engine under any operating conditions;
- the presence of a catalyst and an optimal air-to-fuel ratio reduces the amount of harmful substances in the exhaust gases;
- starts well in cold weather and stalls less often if started incorrectly;
- valve clearances and chain tension are adjusted automatically, which reduces the noise of the power unit;
- smooth torque diagram - the highest point is reached in a wide rev range.
Disadvantages of the injection model of the VAZ engine
In addition to its advantages, the injection VAZ 2107 has some disadvantages:
- The location of the engine and other units in the engine compartment remains the same as in the old-style “classic”. This makes it difficult to access some parts. However, the injection system is quite reliable, so it does not require frequent maintenance during operation.
- The injection “seven” is equipped with a catalyst, which is easily damaged when driving through obstacles. Therefore, you need to be careful when driving on uneven roads.
- An engine with an injector is more demanding on fuel quality than a carburetor variation. When using low-quality gasoline, the system may become contaminated, requiring unscheduled maintenance of the unit.
- If the injection system breaks down, it will not be possible to repair it and adjust it “on the knee” in a garage. You'll have to go to a service station.
Major repairs yourself
Before proceeding with a major overhaul of the VAZ 2107 engine, it is strongly recommended that you familiarize yourself with special literature in order to better understand the procedures being performed.
Upon completion of the repair, the vehicle must be run in to break in all parts. Typically, break-in occurs within the first 5,000 kilometers.
Engine prepared for major overhaul.
Before disassembling, the engine oil must be drained. To do this, warm up the engine to approximately operating temperature and turn it off. If there is a ditch, then the car is driven into it.
If it is not possible to drive into a ditch, you must park the car on a flat surface.
Place a 10-liter container made of heat-resistant material under the oil drain hole. Unscrew the plug and drain the oil.
After this, drain the antifreeze from the cooling system through the drain hole at the bottom of the engine cooling radiator.
IMPORTANT!
The oil can reach temperatures of about 100 degrees. If you try to start the car with the oil and antifreeze drained, the engine will completely fail.
When all the working fluids have been drained, unscrew all the supports and disconnect the bolted connections of the flywheel to the gearbox. Using a winch, remove the engine from the hood space and install it on a stand for repair.
Disassembling the engine does not require a special approach: simply unscrewing the threaded connections.
Photo of the removed cylinder head.
Everything is removed: the cylinder head, electrical components, including the starter and generator, connecting rods, crankshaft, oil pump, and so on. The result should be a separately disassembled cylinder block and crankshaft. Removing the head and all elements is a simple procedure.
It will be difficult when assembling gas distribution and other engine mechanisms that require precise alignment of the position of the working parts. Installing the head will require compliance with the timing marks and other mechanisms.
The removed cylinder head and crankshaft, along with the purchased pistons, are taken to a grinding specialist. The specialist takes all measurements, including all crankshaft dimensions, for subsequent engine boring. Boring is necessary to compensate for wear of non-replaceable parts. The specialist bores the pistons already purchased to size.
Modifications of the VAZ-2107 car
VAZ-2107 . Basic version of the sedan, with an 8-valve carburetor VAZ-2103 engine, 1.5 liters.
VAZ-2107-20 . The same VAZ-2107, but with a 1.5-liter VAZ-2104 injection engine that meets the Euro-2 environmental standard.
VAZ-2107-71 . The car for the Chinese market was equipped with a VAZ-21034 engine, with a volume of 1.4 liters and a power of 66 horsepower, specially tuned for A-76 gasoline. The pistons were taken from a VAZ-2108.
VAZ-21070 . Modification of a car with an 8-valve, carburetor VAZ-2103 engine, volume 1.5 liters.
VAZ-21072 . Modification with an 8-valve carburetor VAZ-2105 engine, volume 1.3 liters.
VAZ-21073 . An export modification for the European market, which was equipped with a 1.7-liter injection engine with a capacity of 84 horsepower. The engine of this car had a catalytic converter that satisfied environmental protection requirements.
VAZ-21074 . Modification with an 8-valve, carburetor VAZ-2106 engine, volume 1.6 liters.
VAZ-21074-20 . Modification with a 1.6-liter VAZ-21067-10 injection engine, which complies with the Euro-2 environmental standard
VAZ-21074-30 . Like the previous model, but with a VAZ-21067-20 engine, which meets the Euro-3 environmental standard
VAZ-210740 . Modification produced in 2010, equipped with a VAZ-21067 injection engine with a catalyst. Engine capacity is 1.6 liters, power is 72.7 horsepower.
VAZ-21076 . Export modification with a VAZ-2103 carburetor engine.
VAZ-21077 . Export modification with right-hand drive for the UK market. The car was equipped with a VAZ-2105 carburetor engine with a volume of 1.3 liters.
VAZ-21078 . Another export modification for the UK, but with a 1.6-liter VAZ-2106 carburetor engine
VAZ-121079 . The modification, developed specifically for the needs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the KGB, was equipped with a powerful VAZ-413 rotary piston engine with a volume of 1.3 liters and a power of 140 horsepower.
VAZ-2107 ZNG . The car is equipped with an 8-valve, fuel-injected VAZ-21213 engine with a volume of 1.7 liters.
Description of design
description of the VAZ 2107 engine design
Depending on the modification, one of four engines can be installed on a VAZ 2107 car: 2103, 2104 (1.5 l volume) or 2106, 21067 (1.6 l volume).
VAZ 2107 car engine
- gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve, with an overhead camshaft. Engines 2103 and 2106 are carburetor, and engines 2104 and 21067 are with distributed fuel injection.
The 2104 engine is based on the 2103 engine, so the cylinder block, connecting rod and piston group, timing drive and crankshaft have the same design and dimensions.
Malfunctions of the VAZ 2107 injection engine
Problems with the 7 injection engine usually manifest themselves as follows:
- The engine is running erratically.
- Fuel consumption of the VAZ 2107 has been increased.
- There is an increased CO content in the exhaust gases.
- Dips when pressing the accelerator pedal.
- The engine “does not pull” (reduced power).
- To diagnose injection system faults, special equipment is required. In particular, in order to read error codes and check sensor readings and the operation of the engine ECU, a special computer (tester) is required. Therefore, repairs and diagnostics of the VAZ 2107 injector are carried out at specialized service stations. The most common cause of injector failure is clogged injectors.
Where is the engine number
The engine number is unique to each vehicle. This is a kind of model identification code. On injection-powered "sevens" this code is stamped out and can be located only in two places under the hood (depending on the year of manufacture of the car):
- on the bottom shelf of the air supply box on the right;
- on the cylinder block.
All designations within the engine number must be clearly readable and not cause double interpretation.