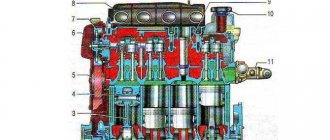
Compression in engine cylinders
Signs of engine wear include high oil consumption and poor starting in cold weather. In this case, the lubricant is consumed more than 150 g per 1000 km. If these signs are detected, then the compression in the cylinders is first checked. It helps to more accurately determine the performance of the power unit: valves, pistons and cylinders. To carry out diagnostics, it is enough to buy a special pressure gauge. It is not at all necessary to contact a car service.
Method for determining engine displacement
To solve this problem, you will need to find out the volume of one cylinder, multiply the resulting number by the number of cylinders in the internal combustion engine . For a rough understanding, the calculation formula is given below:
V engine = Pi * radius squared * stroke height * number of cylinders.
Volume is measured in cubic centimeters, while characteristics are measured in millimeters. If you need to convert between units, simply divide the resulting number by 1000.
Please pay attention! The full and working dimensions of the engine differ in values, which is due to the recesses of the pistons and bulges.
How to find out the volume of a cylinder? To do this, you need to add the values of the working value and the camera size. You can find out the real indicator of the power unit using a calculator. To do this, you need to know the parameters in cm³ , piston and cylinder.
Why do you need to check the characteristics of the internal combustion engine?
The desire to know this value is most often motivated by the desire to increase the compression ratio. This procedure is often of interest to car tuning enthusiasts. Boring the cylinders allows you to increase the compression ratio and pressure on the piston.
The power unit produces more horsepower with the same amount of fuel mixture consumed. However, in an effort to achieve maximum efficiency, the motor often cannot withstand the load and fails after a deafening explosion.
How to find out the main parameter of a unit using the VIN code
VIN is an identification number assigned to each vehicle. This is a set of unique letters and numbers that help you find out the characteristics of the motor. You only need to look at the vehicle’s registration certificate before finding out the desired value. For example, for a standard four-cylinder installation:
- In this formula, D serves to determine the motor diameter (in mm),
- H is used to indicate the stroke of the piston.
In order to indicate engine volume in documentation, cubic centimeters are often used. The indicator is also indicated in liters .
What should the compression be?
To identify the point of maximum wear of engine parts, you need to know the permissible pressure values. It is related to the degree of compression in direct proportion - the more, the higher the pressure.
Today you can find 3 types of engines in operation with different characteristics:
- Old engines with a low compression ratio - up to 8.5.
- Modern gasoline engines in which the air-fuel mixture is reduced in volume by up to 9-11 times.
- Diesel engines capable of compressing the fuel mixture from 16 to 24 times.
The combustion chamber of an engine running on diesel fuel is characterized by a small volume. Therefore, the motor does not require an electric spark, just strong compression.
The amount of compression is influenced by various factors:
- tightness of valve seating;
- cracks in valve seats;
- presence of lubricant in the cylinders;
- ring wear;
- wear of parts of the cylinder-piston group.
Norm and minimum
Through testing, data on the optimal pressure in the cylinders for different types of engines was obtained. When the engine has reached operating temperature and the battery is fully charged, the compression should be:
- On older engines equipped with carburetors, the lowest value is 1 megapascal. In old units - 10 bar. If the engine is new, the pressure can reach 13 bar.
- The optimal pressure in a gasoline engine is 1.5 megapascals. The minimum level is 1.1 MPa.
- For a diesel engine, the normal value is 2.4-3 MPa.
It is important to know! Analysis of parameter measurements allows us to establish a pattern that a compression ratio with a coefficient of 1.5 gives the optimal pressure in the cylinders.
If we more accurately determine the indicated coefficient, then for 4-stroke gasoline engines it is in the range of 1.2-1.3, for diesel engines - 1.7-2.
Signs of poor compression
Identification of the lower compression limit indicates increased engine wear. Friction occurs between the piston rings and the cylinder, which increases the gap between the parts. For this reason, compression is reduced.
The following signs can indicate that the compression is insufficient:
- There is a lot of smoke coming out of the breather. This is a valve that serves to remove crankcase gases from injection and carburetor engines.
- Reduced power of the power unit, especially noticeable on small engines.
- A lot of smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe as the engine oil burns in large quantities.
- High oil consumption due to wear of oil scraper rings and caps.
If at least one of these signs is noticed, then there is a reason to conduct a full engine diagnostics.
This will allow timely measures to be taken to restore its functionality. If we consider the reasons for the decrease in compression, we can highlight the main ones:
- Operating a car with a cold engine, thermostat failure.
- Overheating of the power unit.
- Use of low quality lubricant.
- Maintenance and oil changes are not carried out in a timely manner.
- The service life of the engine has expired.
If the head gasket is burned out or the valves are damaged, then changing the lubricant will not help. In these cases, engine repair will be required with replacement of piston group parts and other elements.
Permissible compression difference in cylinders
If the measured compression differs between cylinders, this complicates matters. The engine will have to be disassembled and overhauled. Not only will it be necessary to replace rings, valves and sealing caps.
Compression less than the minimum value in one cylinder means that there are defects in the piston or cylinder. In this case, all elements of the cylinder-piston group are usually changed, otherwise the difference in compression will remain and the problem will not go away.
The normal value is considered to be a pressure of 10-12 bar, depending on the car model and engine. But the permissible difference in compression in different cylinders has also been established. For example, in cylinders 2 and 3 this value may be 0.5 bar lower, which is quite acceptable. It depends on the load on the pistons - where there is more, there is more wear.
Piston diameter and stroke - how do they affect the performance characteristics of the engine (theoretically)?
It is most often used in special machines and vehicles.
Footnotes
- ↺ Matskerle Yu. Modern economical car/Trans. from Czech V. B. Ivanova; Ed. A. R. Benediktova. - M.: Mechanical Engineering, 1987. - 320 pp.: ill.//Page. 186 - 192 (the book is in the site library). – Approx. icarbio.ru
- ↺ Learn more about effective efficiency. – Approx. icarbio.ru
Comments
Guy, isn't it easier to surf the auto forums than to ask around here?
Why does overheating occur?
Examine the elements of the cooling system. Almost any of them, under certain circumstances, can cause engine overheating. Basically, such problems in most cases are caused by an insufficient amount of coolant in the system, poor cooling of the fluid in the radiator, insufficient sealing of the combustion chamber, and leaks in the system. It is the poor tightness of the system that causes a decrease in excess pressure in the system.
The reason for poor cooling of the fluid in the radiator is external contamination of the radiator with dust, leaves, poplar fluff, as well as a malfunction of the fan clutch or motor, sensor, or thermostat. There may also be internal contamination of the radiator. Previously, this was due to scale, after running the engine for a long time on water. Now the cause of contamination is the use of various radiator sealants. This effect from them is even stronger than from water. It is quite a big problem to clean thin radiator tubes if they are clogged with such a product. Typically, such malfunctions are easy to detect and in order to get to your destination or service station, you need to add fluid to the system and turn on the heater.
A common cause of overheating is insufficient sealing of the combustion chamber. The products of fuel combustion in the cylinder are under high pressure. They seep into the cooling jacket through a poor seal and push coolant away from the walls of the combustion chamber. Also, hot gases additionally heat the wall.
How is compression measured?
The main engine parameter, which is indicated in the operating manual, is the compression ratio. It determines how many times the fuel mixture is compressed before combustion. The cylinder volume divided by the piston stroke is the compression ratio. It does not change if the car owner has not tuned the engine, for example, bored the cylinders or installed a different crankshaft.
But this characteristic should not be confused with compression, which means piston pressure. It is determined by rotating the crankshaft with the starter.
Compression decreases over time due to wear of parts. Its units of measurement can be:
- Bar.
- Atmosphere (atm).
- Megapascal (MPa).
- Kilogram*force per square centimeter (kgf/cm2).
The most modern unit of measurement is the Megapascal, which is equal to 9.9 atmospheres.
How to measure compression
To assess the technical condition of the cylinders and piston group elements, a special device is used - a compression meter.
It includes the following elements:
- Pointer pressure gauge with scale graduation from 0 to 2.4 MPa. For a diesel engine, you will need a device with a scale of up to 4 megapascals.
- Flexible hose with a tip for connecting to the spark plug hole.
- Check valve.
- Pressure relief device.
- Adapter nozzles for different threads in spark plug holes.
A simple configuration of the device is a pressure gauge equipped with a check valve and a conical rubber nozzle. When measuring, you do not need to screw it in, just press it firmly with your hand.
The pressure gauge is used to measure pressure. The check valve is designed to retain air in the device until maximum pressure is reached. It occurs within 5-10 working cycles. Next, the readings are set to “0” by releasing the pressure with a special button. In a diesel engine, compression is measured through the injector holes, which may have different threads. That's why the kit includes adapters.
Checking without a device
There is a simple way to measure compression without special devices. If you need to find out which cylinder is faulty, you can unscrew the spark plugs and rotate the engine with the starter. In this case, the hole is closed with a finger and the release and intake of air is checked. If the malfunction is serious, for example, a burnt valve, then the air in the cylinder will be pushed out and sucked in less easily.
Oil check
If diagnostics reveal a low compression value, then you can find out what the specific reason is. 30 ml of engine oil is poured into all cylinders and the pressure is measured again.
- If the compression has increased to a normal value, then the problem is the wear of the pistons and cylinders, or the piston rings.
- If, after adding oil, the pressure is poor only in some cylinders, then rings may break, valves or pistons may burn out.
More accurate diagnostics can only be done with a compression meter.
How to measure compression pressure
Basic rules for measurement:
- The engine is warmed up to operating temperature ;
- The fuel system is turned off;
- the spark plugs are unscrewed (except for the cylinder, which is being checked);
- battery is charged;
- air filter - clean;
- The gearbox is switched to neutral speed.
To obtain accurate information about the engine, the compression pressure in the cylinders is measured. Before measurement, the engine is warmed up to determine the clearances between the piston and cylinder. The compression gauge, pressure gauge, or rather compression gauge, is screwed in instead of the spark plug. Then the engine is started by the starter with the accelerator pedal depressed (throttle valve open). The compression pressure is displayed on the compression gauge needle. A compression gauge is a tool for measuring compression pressure.
Compression pressure is the maximum achievable pressure at the end of the engine's compression stroke, when the mixture is not yet burning. The amount of compression pressure depends on
- compression ratio;
- engine speed;
- degree of cylinder filling;
- combustion chamber tightness.
All these parameters, except for the tightness of the combustion chamber, are constant and are set by the design of the engine. Therefore, if the measurement shows that one of the cylinders does not reach the value specified by the manufacturer, then this indicates a leak in the combustion chamber. The compression pressure must be the same in all cylinders.
How to properly check engine compression
Before checking the compression, you need to fully charge the battery and make sure the starter is working properly. Otherwise, the measurement will be inaccurate and the readings will be underestimated. As a result of the error, you can begin to repair the motor, although you need to look for other reasons.
Doctors use different diagnostic methods:
- on a cold engine;
- on a warm engine;
- with closed or open throttle.
The most accurate data is provided by diagnostics on a warm engine, which is carried out in the following order:
- Start the engine and warm it up to a temperature of 70 degrees.
- On a diesel engine, unscrew the injectors; on a gasoline engine, remove the high voltage wires and unscrew the spark plugs.
- Disconnect the wire plug from the injectors or turn off the gasoline pump by removing the corresponding fuse.
- Install the compression gauge nozzle on cylinder 1.
- Press the gas pedal to open the throttle.
- Turn the engine 5-10 revolutions with the starter.
- Record the compression readings and repeat the procedure on the other cylinders.
Attention! The injector plugs may not be disconnected, but when measuring compression, a little gasoline will penetrate into the crankcase. This does not affect the accuracy of measurements.
The fuel supply on a diesel power unit with a mechanical fuel pump is turned off with a shut-off lever.
How often to check compression
For prevention, diagnostics are carried out when replacing spark plugs. This procedure should be carried out every 25-50 thousand km.
In addition, emergency diagnosis is carried out for the following signs:
- The engine consumes a lot of oil - more than 200 ml per 1000 km.
- Blue smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe.
- The car has become harder to start in winter.
- Unstable idle, vibration.
The last symptom indicates a failure of the ignition system or several spark plugs. Before measuring compression, these faults must be eliminated. On diesel engines, wear of valves, pistons and cylinders shows the same signs. Cold starts are especially noticeable - diesel fuel cannot ignite.
Methods for restoring compression
There are several ways to increase the pressure in the engine if the rings are stuck:
- Pour 100 ml of engine oil into each cylinder. It is necessary to give time for the rings to “throw away”. Periodically you need to turn the crankshaft.
- The second method is more effective. A mixture of kerosene, acetone and motor oil is prepared in a ratio of 1:1:1. 50 g is poured into each cylinder, the spark plugs are put in place, and the engine is left alone for 10 hours. Next, the spark plugs are removed, and the engine is cranked by the starter several revolutions. After installing the spark plugs, you need to start the engine and warm it up to 40 degrees. Then the oil is drained and the system is washed with a special product. All that remains is to add fresh oil and replace the filter.
In addition, special chemicals for normalizing compression can be found on sale. Such products contain additives that are poured into the engine. But their effectiveness is questionable, and responsibility for use lies with the car owner.
Engine compression ratio - what is it?
The ratio of the total volume of the cylinder to the volume of the combustion chamber is called the compression ratio - E.
(Compression ratio of the Lada Niva 4×4 engine is 9.3. (see here))
Everything is short and clear. But is that enough? The design of the power plant is only a method or system that converts the thermal energy of burned fuel into mechanical energy of the rotating parts of the engine. The concepts of “compression”, “expansion”, “working fluid” also oblige us to consider the physical and chemical processes occurring in the engine cylinders. And these processes are impossible without temperature, which, in turn, is determined by the degree of compression. The efficiency of using expanding gases depends on the degree of expansion. And so, when considering these processes in the most general form, it is possible and necessary to understand something. Everything is in order.
The compression ratio is one of the engine characteristics. It shows how many times the volume of the working mixture or air decreases when the piston moves from BDC to TDC. Using this characteristic, you can determine the type of fuel used in the engine; outdated or advanced engine model; This is a diesel engine with separate combustion chambers or a diesel engine with direct injection.
Increasing the compression ratio increases engine power and improves its efficiency. The possibility of increasing the compression ratio is determined mainly by the properties of the fuels, the toxicity of the exhaust gases and the load on engine parts; for gasoline car engines E = 6.5 -14, and for diesel engines E = 15-24.
In diesel engines, as the compression ratio E increases, the temperature and air pressure increase at the start of injection. As a result, ignition delays are reduced, the rate of pressure rise is reduced, and engine operation becomes smoother. However, at large E (due to higher pressures in the cylinder), it is necessary to increase the mass of parts of the crank mechanism to increase strength. This leads to an increase in mechanical losses. It must be remembered that as a result of combustion of the air-fuel mixture, the volume of the cylinder is filled with a mixture of nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor, and that at high temperatures (over 2000°C) in the combustion chamber, water dissociates into hydrogen and oxygen, and carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide and oxygen. A significant amount of heat is spent on this - the increase in temperature of the working fluid is inhibited.
Increasing the compression ratio in gasoline engines is limited due to the possibility of detonation. Knocking combustion that continues for a period of time can cause engine damage.
The compression ratio is an engine characteristic specified by the designer. There is no need to check it, and only when repairing an engine must you strictly follow the technical conditions for assembling a particular engine.
Is the compression ratio constant? Or is the compression ratio a variable value?
If we assume that the compression ratio is a constant value, then we get two other constant values - temperature and pressure. But this cannot happen. It is impossible to consider the operation of an engine, taking into account only its design.
In order for temperature and pressure to appear, something needs to be compressed (compression ratio). This something is air or an air-fuel mixture (working fluid).
The engine load is regulated by throttling the air, which is an indispensable condition for maintaining an approximately constant composition of the air-fuel mixture in a gasoline engine. In a diesel engine, the load is controlled by changing the amount of fuel supplied to the combustion chamber.
In other words, we control engine power by changing the amount of working fluid in its cylinders.
Modern cars use electronic control systems that can quickly and accurately calculate the composition and quantity of the working fluid, supply it to the engine cylinders in a timely manner and in the right quantity, taking into account many factors affecting the operation of the power plant as a whole.
Let's remember some engine operating modes - idle, partial load and maximum load. For each of these engine operating modes, a certain amount of working fluid is required in accordance with the position of the fuel pedal.
For idle mode, a minimum amount of working fluid is required, for maximum load mode - a maximum.
If you fill the volume between the piston located at BDC and the block head with the maximum amount of working fluid (maximum load), and then move the piston to TDC, then the working fluid will be compressed to a certain density. After the calculations, we will obtain the actual degree of compression of the working fluid. This actual compression ratio cannot be higher (for naturally aspirated engines) than the compression ratio specified when the particular engine was designed.
Chain or belt?
Here, dear readers, is another important feature that it is very advisable to take into account when choosing the engine of your future car. The fact is that each internal combustion engine includes a timing mechanism - a gas distribution mechanism, which must rotate strictly synchronously with the crankshaft. The transmission of rotation from the crankshaft to the camshafts can be done either by a belt or a chain , let's look at the pros and cons of each option.
- Belt
The advantage of the belt is that replacing it is a routine operation and is inexpensive , but the main disadvantage of the belt drive is the fact that the belt is not made of iron and may well break . Most modern engines in the event of such a break suffer serious damage and the car owner ends up with very expensive repairs. Therefore, an engine with a timing belt drive must be monitored, periodically checking the belt tension, and maintenance simply must be carried out strictly according to schedule.
- Chain
In contrast to the belt drive, the chain is a much more reliable element of the engine, which is understandable, because it is still made of steel. A chain, like a belt, needs to be replaced, but much less often than a belt, and before it breaks, it first makes noise for a long time, which is why its break is not sudden. On the other hand, replacing a chain costs the owner much more than replacing a belt, and it is quite difficult to do it yourself.
The longevity of a timing belt greatly depends on the quality of its installation. A heavily overtightened or undertightened belt will break very quickly, but the chain will first stretch and begin to rumble, hinting that it is time to replace it.
In general, the conclusions are:
- If you know how to take care of the car yourself and plan to drive it for quite a long time (more than 150 thousand km), then timing belt will be more suitable for you
- If you don’t want to check the belt tension or don’t intend to drive this car for more than 150 thousand km, then it’s better for you to choose a motor equipped with a timing chain. In this case, such an important maintenance item as replacing the timing drive will not exist for you at all.
When choosing a car model, studying its engines, pay attention to what timing drive they are equipped with.
What is compression ratio
This degree is the ratio of the volume of the engine cylinder to the volume of the combustion chamber. Otherwise, we can say that the compression value is the ratio of the volume of free space above the piston when it is at bottom dead center to the same volume when the piston is at the top point.
It was mentioned above that compression and compression ratio are not synonymous. The difference also concerns the notation; if compression is measured in atmospheres, the compression ratio is written as a certain ratio, for example, 11:1, 10:1, and so on. Therefore, it is impossible to say exactly what the compression ratio in the engine is measured at - this is a “dimensionless” parameter that depends on other characteristics of the internal combustion engine.
Effect on power
The more the working mixture is compressed, the higher the pressure generated in the combustion chamber. Consequently, the piston receives significantly more energy, which naturally transfers to the crankshaft.
The conclusion is obvious: the higher the compression ratio, the more powerful the engine. But this indicator cannot increase indefinitely: when excessively high pressure is created, an extremely undesirable phenomenon can occur - premature ignition, called detonation. Because of this, pressure begins to build up on the piston even before it reaches the top position. This causes:
- powerful and sharp shock loads;
- constant overheating even after short-term operation;
- destruction of piston pins and rings;
- noticeable loss of dynamics and power.
Therefore, the compression ratio must be determined taking into account other performance characteristics and design features of a particular engine.
Compression calculation
Let's look at how to find out the engine compression ratio.
It is calculated by the formula:
Here Vр means the working volume of an individual cylinder, and Vс is the value of the volume of the combustion chamber. The formula shows the importance of the chamber volume value: if, for example, it is reduced, the compression parameter will become larger. The same will happen if the volume of the cylinder increases.
To find out the displacement, you need to know the cylinder diameter and piston stroke. The indicator is calculated using the formula:
Here D is the diameter and S is the stroke of the piston.
Since the combustion chamber has a complex shape, its volume is usually measured by pouring liquid into it. Once you know how much water fits in the chamber, you can determine its volume. For determination, it is convenient to use water because of its specific gravity of 1 gram per cubic meter. cm - how many grams are poured, so many “cubes” in the cylinder.
An alternative way to determine the compression ratio of an engine is to refer to its documentation.
Calculation of internal combustion engine volume with a calculator
To calculate the volume of the engine you are interested in, you need to enter 3 numbers in the appropriate fields - the result will appear automatically. All three values can be found in the car’s passport data or technical data. characteristics of a particular part, or a caliper will help determine what piston volume.
Thus, if, for example, you find that the volume is 1598 cm³, then in liters it will be designated as 1.6 liters, and if the number is 2429 cm³, then 2.4 liters.
Long-stroke and short-stroke piston
Also note that with the same number of cylinders and engine displacement, the cylinder diameters, piston strokes and power of such engines may also be different. An engine with short-stroke pistons is very power hungry and has low efficiency, but achieves great power at high speeds. And long-stroke ones are located where traction and efficiency are needed.
Therefore, the question “how to find out engine size by horsepower” can be given a firm answer - no way. After all, although horsepower has a connection with engine volume, it will not be possible to calculate it from them, since the formula for their relationship also includes many different indicators. So the cubic centimeters of an engine can be determined solely by the piston parameters.
What does the compression ratio affect?
It is important to understand what the engine compression ratio affects: compression and power directly depend on it. If you make the compression greater, the power unit will receive greater efficiency, since the specific fuel consumption will decrease.
The compression ratio of a gasoline engine determines the octane number of fuel it will consume. If the fuel is low octane, it will lead to the unpleasant phenomenon of detonation, and too high an octane number will cause a lack of power - an engine with low compression simply will not be able to provide the required compression.
Table of basic ratios of compression ratios and recommended fuels for gasoline internal combustion engines:
| Compression | Petrol |
| To 10 | 92 |
| 10.5-12 | 95 |
| From 12 | 98 |
Interesting: turbocharged gasoline engines operate on fuel with a higher octane number than similar naturally aspirated internal combustion engines, so their compression ratio is higher.
It is even greater for diesel engines. Since diesel internal combustion engines develop high pressures, this parameter will also be higher. The optimal compression ratio of a diesel engine ranges from 18:1 to 22:1, depending on the unit.
Engine chip tuning to increase performance
An increase in power is possible without intervention in the design of the power unit. Tuning through programming makes it possible to customize engine parameters for yourself. The stages of chip tuning include:
- changing the fuel-air mixture ratio,
- changing the ignition angle,
- adjustment of engine operating modes according to crankshaft speed.
For naturally aspirated engines, chip tuning gives an increase of about 10%, for turbocharged engines - up to a 30% increase in power and torque. The difference in chip tuning for turbocharged engines is that the turbine pressure and the moment of its inflation are adjusted.
Changing the compression ratio
Why change the degree?
In practice, such a need arises rarely. You may need to change compression:
- if desired, boost the engine;
- if you need to adapt the power unit to operate on non-standard gasoline, with an octane number different from the recommended one. This is what, for example, Soviet car owners did, since there were no kits for converting a car to gas on sale, but there was a desire to save on gasoline;
- after an unsuccessful repair, in order to eliminate the consequences of incorrect intervention. This may be thermal deformation of the cylinder head, after which milling is required. After the compression ratio of the engine has been increased by removing a layer of metal, operation on the gasoline originally intended for it becomes impossible.
Sometimes the compression ratio is changed when converting cars to run on methane fuel. Methane has an octane number of 120, which requires increasing the compression for a number of gasoline cars, and lowering it for diesel engines (the coolant is in the range of 12-14).
Converting diesel to methane affects power and leads to some loss of power, which can be compensated for by turbocharging. A turbocharged engine requires an additional reduction in the compression ratio. It may be necessary to modify the electrics and sensors, replace diesel engine injectors with spark plugs, and a new set of cylinder-piston group.
Engine boost
To produce more power or to be able to drive on cheaper types of fuel, the internal combustion engine can be boosted by changing the volume of the combustion chamber.
To obtain additional power, the engine should be boosted by increasing the compression ratio.
Important: a noticeable increase in power will only be on an engine that normally operates with a lower compression ratio. So, for example, if a 9:1 engine is tuned to 10:1, it will produce more additional horsepower than a stock 12:1 engine boosted to 13:1.
The following are possible methods for increasing the engine compression ratio:
- installation of a thin cylinder head gasket and modification of the cylinder head;
- cylinder boring.
By refining the cylinder head we mean milling its lower part in contact with the block itself. The cylinder head becomes shorter, which reduces the volume of the combustion chamber and increases the compression ratio. The same thing happens when installing a thinner gasket.
Important: these manipulations may also require the installation of new pistons with enlarged valve recesses, since in some cases there is a risk of the piston and valves meeting. The valve timing must be re-adjusted.
Boring the BC also leads to the installation of new pistons of the appropriate diameter. As a result, the working volume increases and the compression ratio becomes higher.
Counting example
This is what the generally accepted calculation formula for an automobile internal combustion engine looks like: “SSD = (RO+OKS)/OKS.” The compression ratio here is o, the working volume of the cylinder is “RO”, and the volume of the combustion chamber is “OKS”.
To calculate “PO,” you must first decompose the single engine volume or displacement into the number of cylinders used. For example, the displacement of the “four” engine is 1997 cm3. To determine the capacity of one cylinder, you need to divide 1997 by 4. You get about 499 cm3.
To calculate the “OCS” parameter, specialists use a tube or pipette calibrated in cm3. The chamber refers to the place where the fuel ignites directly. The chamber is primed and then the volume is measured using a liquid burette. If you don't have a graduated tube, you can pump out the liquid with a syringe and then measure it in a measuring cup or on a scale. In this case, it is advisable to use clean water for calculations rather than gasoline or diesel fuel, since its specific gravity is more related to the volume in cm3.
Attention! To accurately measure “OKS”, the thickness of the cylinder head gasket is additionally added, the shape of the piston crown and other features are taken into account. Therefore, it is recommended to entrust the calculation of this value to specialists.
Deboosting for low octane fuel
This operation is carried out when the issue of power is secondary, and the main task is to adapt the engine to a different fuel. This is done by reducing the compression ratio, which allows the engine to run on low-octane gasoline without detonation. In addition, there are certain financial savings on the cost of fuel.
Interesting: a similar solution is often used for carburetor engines of old cars. For modern electronically controlled fuel injection engines, deforcing is highly not recommended.
The main way to reduce the engine compression ratio is to make the cylinder head gasket thicker. To do this, take two standard gaskets, between which an aluminum gasket insert is made. As a result, the volume of the combustion chamber and the height of the cylinder head increase.
Motor location
There are only two options here: longitudinal and transverse engine arrangement, but this characteristic for you and me, dear readers, has no meaning at all. The only reason why designers change the position of the engine is to fit the engine under the hood.
- The longitudinal arrangement of the engine is used on rear-wheel drive cars and cars with permanent all-wheel drive .
- Transverse - usually used on front-wheel drive , as well as on cars with all-wheel drive , when the rear wheels are connected using a clutch.
There is an opinion that the longitudinal arrangement of the engine allows for a lower level of vibration, but on modern cars this difference is very insignificant.
Some interesting facts
Methanol race car engines have a compression ratio of over 15:1. By comparison, a standard carbureted engine consuming unleaded gasoline has a maximum compression of 1.1:1.
Of the production models of gasoline engines with 14:1 compression, there are models on the market from Mazda (Skyactiv-G series), installed, for example, on the CX-5. But their actual coolant is within 12, since these engines use the so-called “Atkinson cycle”, when the mixture is compressed 12 times after the valves are closed late. The efficiency of such engines is measured not by compression, but by expansion ratio.
In the middle of the 20th century, in the global engine industry, especially in the USA, there was a tendency to increase the compression ratio. Thus, by the 70s, the bulk of American automobile industry samples had a coolant ratio from 11 to 13:1. But the normal operation of such internal combustion engines required the use of high-octane gasoline, which at that time could only be produced by the ethylation process - by adding tetraethyl lead, a highly toxic component. When new environmental standards appeared in the 1970s, leaded lead was banned, and this led to the opposite trend - a decrease in coolant in production engines.
Modern engines have an automatic ignition angle control system, which allows the internal combustion engine to operate on “non-native” fuel - for example, 92 instead of 95, and vice versa. The OZ control system helps to avoid detonation and other unpleasant phenomena. If it is not there, then, for example, if you fill an engine with high-octane gasoline that is not designed for such fuel, you can lose power and even fill the spark plugs, since the ignition will be late. The situation can be corrected by manually setting the OZ according to the instructions for a specific car model.