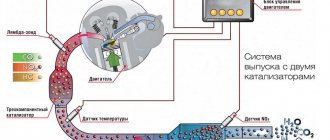
What is a direct-flow exhaust system
To understand why to install a direct-flow muffler, you need to know how the car exhaust system works as a whole and what its tasks are.
Main goals:
- Filling the cylinders with a prepared fuel-air mixture, and in diesel cars - forming the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber;
- Ensuring the removal of spent fuel gases from the engine and passenger compartment outside the vehicle;
- Reducing the emission of toxic gases and harmful substances into the atmosphere thanks to the built-in catalytic converter;
- Reducing noise levels in the cabin and surrounding area.
The operating principle of the exhaust system is partly based on the law of inertia.
Thanks to the action of this law, a vacuum zone is formed behind the exhaust valve into which gases rush, and their place is immediately taken by a fresh portion of the fuel mixture.
This happens due to the fact that the phases of fuel intake and exhaust gases overlap each other, as is provided for in the design of modern engines.
After the exhaust valves are closed, next to the high-pressure zone formed as a result of exhaust gases escaping under pressure, another low-pressure zone is formed in the manifold, which moves along the exhaust pipe at the speed of sound.
Entering the muffler, the vacuum zone encounters resistance in the form of partitions, is reflected and goes in the opposite direction to the valves.
The ideal case is when this zone approaches the motor at the moment the valves open, but this depends on the frequency of the engine and the distance to the obstacle.
And since in modern cars such a distance is large, the vacuum zone from one cylinder, as a result, at the moment the valve opens, ends up in another, and not in the one from which it left.
Thanks to the design of the “spider” (exhaust manifold), where pipes of the same length are provided, the effect of vibration damping occurs, since the vacuum zones go from 4 pipes into one, where resistance is created at the junction of the latter, and they also partially dampen each other.
But the muffler plays a leading role in noise reduction, because the exhaust manifold and other elements are unable to greatly reduce noise.
But on many sports cars such a device may not be found; the role of a muffler there is played by a special turbine, which smoothes out vibrations and reduces the force of the exhaust by grinding the outgoing gas flow.
Bass exhaust
Tuning the exhaust system is a common “pamper” for car enthusiasts who want to give their vehicle maximum originality. A growling/roaring/bass exhaust on a diesel engine is just a refinement of the design of the exhaust system, feasible both for auto repairmen and directly for car owners who have already tried their hand at improving certain elements.
Muffler can with bass sound
How to make the exhaust bassy? Modify the muffler - in other words, use the formula: the smaller the diameter of the exhaust device available to you, the less amount of gases penetrates through it in a limited time period and, accordingly, the lower the noise level accompanying the described process. Therefore, in order to create a bassy exhaust with your own hands, you need to increase the diameter of the exhaust pipe, allowing more exhaust flow to pass through it.
Types of devices
The standard exhaust system of a modern car includes a resonator (the first one comes from the engine) and the muffler itself.
The resonator cuts off low-frequency vibrations, and the muffler cuts both low-frequency and high-frequency vibrations, which together leads to a good result.
But the above scheme, both jointly and separately, may include the following types of mufflers:
- Made of aluminized steel;
- Stainless steel;
- Silencers, limiters, absorbers and reflectors;
- Resonator type;
- Direct-flow (sports) analogues.
Aluminized steel
Devices made of aluminized steel are characterized not only by a long service life, from 5 to 10 years, but also by a high price.
It will be difficult to choose such a muffler for your car, since only a few companies produce such devices, and making it yourself will be problematic.
Stainless steel
The devices are in the inexpensive segment, but their service life is only from 2 to 5 years. A big plus is that you can match the element to almost any car.
Limiters
They are usually used as an additional device installed in front of the main one.
The operating principle is based on creating low acoustic resistance.
Structurally, this is done like this: in the pipe, a large diameter turns into a small one, then there is a sharp increase in volume according to the principle of a large bottle with a narrow neck. The sound, entering a large space, decreases.
Reflectors
Used as a secondary muffler installed after the main one.
Exhaust gases entering the device encounter a group of acoustic mirrors on their way. Reflecting from them, the gases dissipate their energy one by one, and the output is a weak sound.
Absorbers
Can be used as a main muffler. The principle of operation is based on the absorption of vibrations by a porous material, usually glass wool, the fibers of which are heated by oscillating, thereby converting sound into thermal energy. Structurally close to direct-flow analogues.
They are considered ineffective because they absorb only high-frequency vibrations and transmit low-frequency ones.
Resonator type
As a rule, they are used first in exhaust systems as additional ones.
The principle of noise absorption is based on the presence of chambers of different sizes, through which the sound is effectively muffled.
Everything is arranged like this: a pipe with slots runs through the center of the resonator, which is surrounded by chambers of different volumes. Through the slots, exhaust gases penetrate into the chambers, where their energy is lost.
After this, the sounds enter the main device, where they are further reduced.
Direct flow
They are also called sports mufflers. As a rule, they are made of stainless steel. Installed on sports and tuned cars.
After installing a direct-flow muffler, the suction of the air-fuel mixture into the cylinders is improved, and the resistance in the exhaust system created by conventional analogues is reduced.
A direct-flow muffler is structurally somewhat similar to a resonator; there is the same pipe with holes and empty cavities separated by partitions. Only the cavities themselves are filled with basalt wool (or other material), which can withstand high temperatures.
Consisting of long mineral fibers, basalt wool absorbs sounds well, but only until it is blown out of the direct flow and even special protective metal mesh does not save the situation.
If the direct-flow muffler, when you tap on it, begins to sound like an empty metal container, then it needs to be filled again with cotton wool or replaced. And the sound produced by the exhaust system will be different.
Sounds made and their features
After installing a direct-flow exhaust system, the sound emanating from the car immediately changes; as a rule, it is low-frequency “growling”, “bass” and “mumbling”.
This happens because mineral wool placed in the co-current cavities removes only the high frequencies, while leaving the low bass unchanged.
The resistance to exhaust gases is also greatly reduced, and this affects the increase in engine power (but only in combination with other measures).
But the nature of the sounds largely depends on the number of holes and their diameter in the central pipe, as well as the characteristics of the material embedded in the cavity.
As was noted, mineral wool does not support low frequencies, and in most cases the engine produces sounds in the low range.
Therefore, it is not surprising when a car with direct flow makes sounds of engine operation through the muffler, and the higher the frequency the latter operates, the more it clogs the ears.
This is felt especially well inside the car, when such sounds, coinciding in frequency with body vibrations (and they are close to the frequency of the engine), lead to resonant vibrations inside the car and the strength of the sound increases significantly.
Therefore, it is almost impossible to make a quiet direct-flow muffler.
Noise standards and liability for exceeding them
Responsibility for loud exhaust from a muffler is provided for under Article 8.23 of the Code of Administrative Offenses. The driver is charged for operating a vehicle with excess noise levels in accordance with the Technical Regulations of the Customs Union 018/2011 “On the safety of wheeled vehicles”, paragraph 9.9.
Table: dependence of the maximum permissible sound level on the vehicle category
| Vehicle category | Sound level (in decibels) |
| M1, N1, L | 96 |
| M2, N2 | 98 |
| M3, N3 | 100 |
Category M1, N1 and L are passenger cars with no more than 8 seats, trucks with a permissible maximum weight of no more than 3.5 tons, motorcycles/mopeds/ATVs. Category M2 and N2 are cars with more than 8 seats (except for the driver), but whose maximum weight does not exceed 5 tons, and trucks with a permissible maximum weight from 3.5 to 12 tons, respectively. Category M3 and N3 are full-fledged buses and trucks with a permissible maximum weight of more than 12 tons (trucks, most dump trucks).
Power and forward flow, three different opinions
Many owners of VAZ cars or, for example, Mitsubishi Lancer 10, Mazda 3, installing direct-flow exhaust systems on their vehicles pursue several goals, as a rule, there are two of them:
- Tuning your car;
- Increase the engine power, they say installing a sports analogue will leave many behind when starting at a traffic light.
The first opinion is that this is true. There is no debate about tuning; we are missing this point. But there is another opinion about increasing power, and it is the opposite.
The second opinion is that a sports muffler without deep tuning of the engine will not give an increase in power and partly it coincides with the opinion of experts.
The third opinion from professionals is that a noticeable increase in engine power is possible only after significant processing, and a direct-flow muffler is a secondary part of the issue.
The tuned power unit produces more exhaust gases, and, therefore, the standard exhaust system will not cope with its tasks, especially at high speeds.
Therefore, it will be necessary to increase the diameter of all pipes, install a tuned manifold, and only then a direct-flow muffler.
It is on sports cars that they install not simple engines, but ones that require special attention. And the direct-flow exhaust system fits into the overall picture of the tuning engine.
Why install forward flow at all?
Each engine produces a certain amount of exhaust gases per unit of time. The designers took this into account, and therefore designed the exhaust system in such a way that it could cope with the removal of unnecessary residues.
When owners begin to modify the engine, increasing its power, it is also necessary to improve the exhaust system, as the amount of exhaust gases will increase. The original system cannot cope with such a large volume that it will significantly dampen the car. All new improvements, in this case, will be in vain.
That is why it is important, when remaking the engine, to improve the exhaust. There is practically nothing left from the standard installation. The manifold, pipes with a larger diameter and the muffler are replaced. Thanks to this, exhaust gases will begin to leave faster without stagnating in the cylinders, which will naturally increase power. But then you will have to sacrifice quiet sound. The total engine power, with direct flow installed, increases by 15%.
Next, you need to figure out why the forward flow has such a strong hum. Typically, loud noise is caused by constantly and rapidly moving exhaust gases. To reduce the speed, and therefore reduce the sound, use a muffler. Its function is to reduce the speed of gases. The muffler is a certain labyrinth, through which gases significantly reduce their speed. This also reduces noise.
Making a direct-flow muffler with your own hands
If you want to manufacture and install direct flow on your car, then it is better to conduct such experiments with domestic cars, for example, VAZ.
It is better to tune the exhaust system of Mitsubishi Lancer 10, Mazda 3 and other foreign cars by contacting special companies that do this professionally.
We discussed the design of the direct flow above. The difference between a sports muffler and a regular muffler is shown below.
We will be tuning the exhaust system of a VAZ-2110 (8 valve 1.6 liter volume).
To do this you will need the following materials and tools:
- Metal pipe with a diameter of 52 millimeters (a little more than 2 inches);
- Grinder with a disc for cutting metal 1 (1.6) mm;
- Welding machine, preferably inverter;
- Metal sponges (brushes) for cleaning dishes - at least 50 pcs.
Work progress
Dismantle the old device or prepare a similar one taken, for example, from disassembly.
Cut out the gutter and all the insides as shown below.
Leave a 4 cm protrusion on both sides so that a new pipe can be welded into this area.
Prepare a new pipe by cutting it to size and drilling holes with a diameter of 6-8 mm in it at a distance of 1-2 cm from each other.
This is labor-intensive work, so you can use an alternative method - using a grinder with a 1.6 - 3.2 mm disc, cut holes in the pipe in the shape of a herringbone at a distance of 1-2 cm from each other.
Weld a pipe with holes to the sections in the muffler and fill the entire space with metal pipe cleaners.
On the reverse side, the electrode may be missing, no problem, the hole left will be additional to the rest drilled or sawn. But if you go by principle, you will have to cut out the other side of the muffler.
Weld the outer part back and, if necessary, update the pipe running from the forward flow towards the exhaust.
Completely clean the device, prime it with primer and paint, this will extend its service life.
It’s worth taking a closer look at the filler. In the example described above, a metal mesh was used, but still the best option would be expanded clay (in the middle), and put fire-resistant mineral wool on top.
We make direct flow from scratch
To do this you will need to use the services of a turner. We order two pipes:
- One made of steel 2 mm thick with a diameter of 130 mm and a length of 42 mm.
- The second is made of steel with a thickness of 2.5 mm, a diameter of 52 mm and a length of 42 mm with holes with a diameter of 8-10 mm, every 2 cm;
Two flanges with a diameter of 130 mm with an internal hole of 52 mm, metal thickness 2-2.5 mm can be ordered separately.
Prepared:
- Asbestos rope;
- Glass wool or mineral wool.
Asbestos rope is wrapped around the inner pipe. This is done in order to protect the mineral wool, which will be the top layer, from overheating.
We fill the top layer, assemble and scald the structure. We weld the fasteners and attach the forward flow to its regular place. For beauty, you can put a muffler attachment on it.
Another design of the device is shown below.
Blueprints
There are a lot of ways to make a direct-flow muffler; the main thing here is to understand the principle of operation of the device and use your imagination. And for car owners who find it difficult to do this, use the methods and drawings described above, they are simple and accessible to many.
Also tell us in the comments what type of forward flow is installed on your car and how you can do it yourself, this will help many people understand this topic.