Author: newavtomaster News
We will find out what the Chevrolet Niva exhaust system looks like in the material below. Initially, Chevrolet Niva cars were developed exclusively from the point of view of an inexpensive alternative to a significant number of cars. By and large, the developers succeeded, since in society this model has a strong opinion about its high performance. The car has excellent practicality, since in addition to movement, it allows you to transport small loads. The high level of practicality is explained by the special suspension design. Its height allows you to avoid most problems associated with the road surface. In this case, we will talk about the exhaust system and possible options for improving it.
Drivers who use the car for a long time note that during engine operation, a sound appears that is reminiscent of a “roar” or “growling” in its content. This behavior is explained by the formation of sound vibrations, which are caused by gas that has been processed and is under pressure. Due to this, the speed of gas movement is quite high, which determines the appearance of the characteristic sound. Thus, a system with affected areas produces a huge amount of noise during operation, which is not typical for a complete structure.
As gases escape, the temperature decreases and a cooling process occurs. According to environmental requirements, modern cars are equipped with special cleaning filters that help retain and remove harmful impurities. Chevrolet Niva cars are no exception. For proper operation of the injector and electronic control unit, a lambda probe must be used.
In general, if the exhaust gas exhaust system is disassembled into elements, then at the end you will get the following sequence: muffler; muffler for additional purposes; catalyst; Lambda probe; receiving tube. The elements are connected through auxiliary tubes and fastening clamps.
Main elements of the exhaust system
The design of the exhaust system becomes more complex, but with each new car model it includes all the same elements.
Collector
The exhaust pipe is an intermediate link between the car engine and the converter (catalyst). The collector is responsible for the removal of gases. Since in this case there is a very strong mechanical and temperature load, which can reach up to 1000 degrees, quite strict requirements are imposed on this part of the muffler. Therefore, in the manufacture of the intake pipe, only the best alloys of cast iron and steel are used.
Also, a vibration compensator (corrugation) is sometimes installed on this part, thanks to which engine vibration is damped and does not pass further through the exhaust system.
Neutralizer
The catalytic converter (or catalyst) “afterburns” unburned fuel residues and processes carbon monoxide. This element of the exhaust system is a special chamber or tank in which a ceramic or metal element in the form of a honeycomb is located. Thanks to these honeycombs, gas mixtures are purified through chemical reactions.
Now manufacturers have begun to produce multi-section neutralizers that meet all international standards, which process a wider range of harmful substances.
Front muffler (resonator)
The resonator is, in fact, one of those parts that are commonly called mufflers. This element performs the function of reducing noise, but not cleaning exhaust gases. When gases pass through the resonator, a lot of noise is created. Therefore, the internal “filling” of the front muffler consists of numerous grilles and holes that reduce the speed of escaping gases, as well as vibration. By and large, a resonator is a tank with a perforated pipe.
Front mufflers are:
- Active. Such mufflers are made of special sound-absorbing materials, and their design is simple.
- Reactive. Silencers of this type use combinations of expansion and resonator chambers.
Do not confuse the resonator with the rear muffler, as their design is very different.
Rear muffler
When we say “muffler,” we most often mean the rear part of the exhaust system. This element provides the final absorption of noise and also carries out the final removal of gases.
Unlike the resonator, the internal “filling” of the rear muffler is heterogeneous. Several chambers with special fillers are installed inside it. Thanks to the porous structure, the system of partitions and air ducts, it is possible not only to get rid of strong noise, but to reduce the temperature in the system.
Speaking of noise reduction, we cannot ignore another type of system that reduces excessive noise in the exhaust pipe.
We knock out the Chevrolet Niva catalyst
For those who want to save as much as possible, this method will be ideal. What is its essence? First, the old catalyst is removed. Then, using a grinder, its body is cut out. After this, the ceramic filling will be removed using a rough method. This is done using a hammer and chisel.
Thus, the element body remains empty. After this, the cover is welded back into place using a welding machine. The part is installed in its original place. Some people modify the design - install a perforated pipe and install insulation (for example, glass wool or crumpled thin wire) in the layer between the pipe and the body. Thus, an analogue of a flame arrester is obtained.
The cost of such removal is less than 300 rubles, but this requires a grinder, a disk, electrodes and a welding machine. Therefore, this method is not always relevant for motorists - it will be easier and faster to use the services of a service station, where they will install a ready-made flame arrester in a couple of hours.
Advantages and disadvantages of removal
Car exhaust system.
types and features Before talking about its disadvantages and advantages, you should first of all pay attention to the conditions under which it is used. Since if, for example, the ignition is faulty or the fuel is of insufficient quality, then all this is not applied affects its operation and leads to failure
Therefore, if the car has problems with dynamics, or gasoline consumption has increased, the first thing you should pay attention to is the condition of the exhaust system. The normal operation of the element, or as it is called CAT, is designed for 50-150 thousand kilometers, and its service life directly depends on the conditions under which it is operated.
Therefore, before resorting to a complete replacement of a part, pay attention to how the ignition system is adjusted, what fuel is used, this all directly affects its operation. It is also important to use high-quality oils, this is also an important aspect related to how long the catalyst will last
As for repair work, this procedure is not complicated, you can do it yourself, without the help of specialists, this will help you save money, since a new part is not cheap, and if you entrust this work to a specialist, it will be quite expensive. Of course, if you do not have free time and you do not have problems with money, then you can resort to the help of a specialist.
Removing the catalyst: the correct procedure
The device cannot be repaired. The catalytic converter is a disposable honeycomb ceramic structure. The material is fragile, so it is difficult to remove it yourself. It is better to trust the professionals at the service station. Technicians with equipment will remove the damaged structure from the exhaust system.
Repair sequence:
- Removing the exhaust system.
- Removing ceramic elements from the muffler.
- Installation of flame arresters when removing the upper catalyst.
- Installation of a decoy for a lambda probe.
- Making corrections to the engine ECU.
The procedure for replacing the catalyst on a Chevy Niva must be accompanied by the installation of a lambda probe emulator. The trick is required to eliminate an error in the operation of the engine ECU. In the absence of a catalyst, the lambda probe will send incorrect data, which will lead to a richer fuel mixture.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Owners of the new Chevrolet Niva will be asked about the possible consequences of removing the catalytic system. After all, this is a direct interference with the operation of the car. However, the procedure also has its advantages, which were appreciated by owners of used Chevrolet Niva.
Advantages:
- Saving on car maintenance.
- Replacement will no longer be required.
- Factors that could disable the catalyst are reduced as negative. This applies to prolonged driving on a faulty engine, low-quality fuel, or impacts on the muffler while driving off-road.
- It is easier for the engine to release exhaust gases. Accordingly, the power will increase slightly.
The procedure for replacing a catalytic converter is similar to cutting out an appendix. They did it and forgot, that’s the principle. This procedure will not affect the driving performance of the car.
Flaws:
- The engine noise becomes more audible.
- The negative impact on the environment is increasing.
- The risk of getting caught during testing for compliance with CO2 emission standards increases significantly. Sometimes regulatory authorities do such checks, especially during special events.
- It will be difficult to pass the inspection.
- Additional costs for engine ECU exchange. It will continue to believe that the catalyst is present and working. The device readings will have to be corrected for the motor to operate correctly.
Owners must independently determine the risks of device removal procedures. Often you can’t do without it. The problem is the high cost of a new catalyst. Because of this, it is not practical to install a new device on an old car.
Watch this video on YouTube
Direct flow muffler
Where is the camshaft position sensor in the Chevrolet Niva and signs of its malfunctions
In conventional mufflers, in the process of resisting exhaust gases, part of the engine power is lost. Although this consumption is insignificant, many car enthusiasts are looking for ways to make the muffler quieter without losing engine power. For these purposes, manufacturers have developed special direct-flow models.
The design of such a muffler differs from the usual design. Unlike standard models, in direct-flow units the engine power is not only reduced, but also increased by using the energy of the exhaust gases.
The essence of the operation of “forward flows” is that when gases exit the collector, less resistance is required. Thanks to this, the motor does not have to expend extra energy to overcome the pressure. The resulting difference is converted into useful driving power.
The direct-flow muffler itself is a straight pipe with a perforated surface. By and large, it is enclosed in an outer casing. There are also separators and chambers inside the muffler, just fewer of them than in standard systems. Thanks to this design, the exhaust gases move in a straight line and do not encounter strong resistance. At the same time, thanks to the perforated surface, they expand and come out freely.
The outer casing of the direct-flow muffler is coated with a special absorbent composition, due to which the gases inside do not resonate, and the sound of the engine does not exceed permissible limits. This way noise levels are kept to a minimum.
Chevrolet Niva: car exhaust system and its design
Since the start of production, the Chevrolet Niva has enjoyed the reputation of being a relatively inexpensive workhorse. Many car enthusiasts chose it specifically for work. Convenient and practical, it is suitable for both transportation and traveling without cargo. The high seating position perfectly protects against many surprises that our roads are so rich in. What is an exhaust system and what tuning options are there?
Where does the engine “roar” come from? Exhaust gases move at high speed, and they create sound waves. The flow speed is quite high, and the speed of sound vibrations is even higher.
This is why a car with a burned out muffler makes so much noise.
What does the system consist of?
Car exhaust system: device diagram, possible malfunctions and diagnostic methods
The Chevrolet Niva gas exhaust system is very different from its predecessor, the VAZ 2121. New system components were added that affected the efficiency, quality and ecology of the exhaust. So, the components of the system are:
- Downpipe or elbow;
- Lambda probe;
- Resonator;
- Muffler;
- Suspensions;
- Outlet pipe;
- Catalyst.
Let's consider each element separately, what functional actions they perform and what they consist of.
Reception pipe. The exhaust outlet pipe or elbow is used to receive direct exhaust from the vehicle's engine. It has a curved shape, hence the name, and consists of two tubes attached to the exhaust manifold. After bending, these tubes flow into one and are connected to the next element. The intake pipe is fixed with special pins and the joint is sealed using a heat-resistant gasket. During engine operation, not only exhaust gases pass through the elbow, but also sparks of unburned fuel, so this design experiences high temperatures. At the junction of two pipes into one, there is an innovation, which consists of a special sensor that is screwed into the exhaust pipe. This sensor is called an oxygen or lambda probe.
Lambda probe. The sensor is used to determine the composition of oxygen in exhaust gases. This composition depends on the amount of fuel and air supplied to the engine cylinders. The sensor provides a signal in the form of electrical voltage, which is received in the control unit and transmitted to the dashboard in a form understandable to the driver.
Catalyst. The catalyst or converter is connected directly to the other end of the exhaust pipe, and at the junction it is sealed with a heat-resistant gasket. It serves to prevent exhaust from passing through at the junction. The catalyst has the shape of a barrel, which is not dismountable. Performs a converting function; when exhaust comes from the engine, it cleans it to the lowest content of harmful substances and passes it on to the next element. Inside, the neutralizer consists of different cleaning substances arranged in series. The catalytic converter on a Chevrolet Niva car lasts about 100 - 120 thousand kilometers, after which it needs to be replaced.
Resonator. It is also called an auxiliary muffler, as it resembles the appearance of the main muffler, only small. Performs the function of ensuring optimal exhaust flow throughout the entire system, that is, it smoothes out this passage. Many people believe that the primary reduction in exhaust volume occurs in the resonator, but in fact this is not the case. Inside the auxiliary muffler there is a set of mesh tubes through which the exhaust passes and smoothes the flow of gases.
Muffler. It performs the function of reducing exhaust volume. It is the final element of the system and is connected to the resonator via a clamp and a heat-resistant ring. Silencers are made from the following materials:
- Aluminized steel;
- Stainless steel;
- Galvanized with aluminum;
- Black metal.
Improving the model
To improve the model, you can use methods of externally changing the design. One such example is a dual outlet exhaust system. During operation, an additional pipe is welded to the end of the muffler. Depending on the quality of the pipe and its shape, the sound vibrations may change. Of course, not every car enthusiast is interested in this type of activity.
More serious changes relate directly to the functionality of the unit and increase the power characteristics. To increase power performance, the Chevrolet Niva exhaust system must get rid of the converter and lambda probe. Instead of the latter, a snag is installed. When working with a resonator, there are two options, which involve removing it completely or replacing it with a new one. Also, a new pipe with a larger diameter should be installed. In order for gases to be extracted at a higher speed, the installation of an additional element called a “spider” is required.
The above is a system change diagram that can be used as a whole, however, selective changes are also acceptable. Everything is determined by the goals of the car owner. By performing these manipulations, you can achieve an increase in power characteristics by 15 hp. However, it is worth considering the fact that the sound of the engine will change greatly, and the amount of harmful emissions will also increase, which is not welcome in society and on the roads.
The Chevrolet Niva exhaust system undergoes profound changes extremely rarely. This is due to a number of reasons, primarily the high cost of work. The Chevrolet Niva is a relatively cheap model, not intended for racing, so creating a powerful system does not meet the common sense of the design of this car.
Adviсe
Whatever method is used, it is important to know that after removing the catalyst, the electronic unit will still show an error. This is accompanied by a yellow "Check Engine" light.
And all because the oxygen sensor will record incorrect data about the amount of oxygen remaining in the catalyst. How to solve this issue? To get rid of the yellow lamp once and for all, you need to use a fake oxygen sensor. This is a kind of mechanical plug that has the same thread and dimensions as a standard lambda probe. It is the snag that is capable of adjusting the values of the lambda probe.
Another method is flashing the electronic unit. However, it is better to do this operation at a service station. The essence of the process is to install software for Euro-2. Thus, the ECU will not have information about the catalyst, and the engine will operate normally without additional interference. This method is relevant if the catalyst is removed at a service station. After all, in the service, the installation of a flame arrester is carried out in conjunction with the firmware of the electronic unit.
Also note that the length of the common exhaust system pipe does not change. Therefore, you should not install a new rear bumper on the Chevrolet Niva (whether it is restyling or pre-restyling, it does not matter). The system will operate normally. The only thing that will change for the worse is the smell of gas.
Reasons for carrying out restoration work
To determine the condition of the exhaust system, no serious equipment is required. Here, it is enough to catch the changes in the work of changing sound vibrations. The exhaust gas removal mechanism is not complicated, however, it is subject to a huge impact in terms of high temperature, so some elements may fail.
If the problem is with the muffler, then there is a high probability of holes appearing as a result of burnout, the source of which is high temperature. In the case of a catalyst, a crack can be detected, which is not always detectable by visual inspection. Quite often you can find a damaged clamp or a failed gasket.
When buying a used car, you should keep in mind that some unscrupulous owners install special devices instead of a worn lambda probe. Among car owners, such devices are called decoys. When purchasing a vehicle, this should be taken with particular seriousness.
Replacing an additional muffler and catalyst
As mentioned above, the additional muffler and catalyst are a non-separable unit, which is replaced entirely in the event of failure of one or another element.
Let's consider the procedure for removing this unit. We drive the car into the inspection pit and wait some time until all elements of the exhaust system have completely cooled down. It should be remembered that the catalyst heats up to a much higher temperature than the mufflers, and accordingly it takes longer to cool down.
After the car's exhaust system has cooled down, you can begin to remove the catalyst and additional muffler. First of all, we clean the bolted joints with a wire brush, and then treat them with VD-40.
Then, using two “17” keys, unscrew the bolts securing the unit to the exhaust pipe of the exhaust manifold. Remove the bolts and spring washers.
Now we need to disconnect the resonator and catalyst from the main muffler. To do this, use two “13” keys to unscrew the bolts of the coupling clamp, remove the clamp and remove the graphite ring-spacer.
We remove the rubber suspension clamps from the corresponding brackets on the body and remove the entire assembly. Installing a new part is performed in the reverse order.
It should be noted: of course, if any of the elements fail, the car owner does not always have the opportunity to replace the entire assembly. In such a situation, you can go a slightly different way: use a grinder to cut off the element that has become unusable and install a new one in its place by welding. This solution is especially advisable in the event of failure of the additional muffler. The fact is that it costs slightly less than a catalyst, and often it will be much more profitable to purchase and install it separately (without touching the converter).
Replacement of exhaust system elements
Often, every motorist encounters the problem of burning out a muffler, resonator or other elements on a Chevrolet Niva, which entails an unpleasant sound from under the bottom. If elements burn out, it is better not to try to weld on steel linings, but to immediately replace the part.
Muffler replacement
Although the Chevrolet Niva car has decent ground clearance, replacement of exhaust parts is carried out from the inspection hole, because strong physical effort is required to unscrew the fasteners. The muffler on Shnivy is removed in the following order:
Using two keys set to “13”, you need to unscrew the nuts connecting the muffler to the resonator and remove the clamp. The auxiliary muffler is lowered down and the graphite sealing ring is removed from the connection point. The muffler brackets are removed from the hangers on both sides and the muffler is removed. If the suspensions have visible defects, it is recommended to replace them as well. Install the new muffler in reverse order. It is the muffler that is the most common element of the system that becomes unusable.
Replacing the resonator paired with a catalyst
The catalytic converter has a one-piece design with a resonator, which is a disadvantage in the Niva Chevrolet. The neutralizer has a service life much longer than the resonator, but if the latter fails, both elements must be replaced. Due to the long service life, the connections oxidize and therefore it is necessary to treat them with VD-40 lubricant before removing them. Next, we move on to the removal and replacement process:
The connection to the receiving pipe is unscrewed with two keys “17” and disconnected. The connection between the resonator and the muffler, which was described above, is disconnected. The rubber suspensions are removed from the brackets and the resonator and neutralizer are removed. Reinstallation of new elements is carried out in the reverse order of removal. But the cost of a pair of neutralizer and resonator will cost a considerable amount, so it is advisable, if the catalyst is not damaged, to separate the part with a grinder. Then weld the new resonator and install it in the seat.
Peculiarities
So what is this element? This is a catalytic converter, the main task of which is to reduce the emission of harmful substances and a three-component type catalyst is installed. It consists of:
- Cases.
- Carrier block.
- Thermal insulation.
The main element of the Chevrolet Niva catalyst is the carrier block. It is made from special, fire-resistant ceramics. This block is a set of numerous honeycomb cells designed to increase the contact area with exhaust gases. These honeycombs are coated with special catalyst substances. These are palladium, rhodium and platinum. These metals are capable of accelerating chemical reactions in the Chevrolet Niva catalyst-resonator. Thus, harmful gas particles that pass through these components are converted into harmless oxide, nitrogen and carbon dioxide. We also note that a catalyst sensor is installed in the element housing. The Chevrolet Niva is equipped with the simplest oxygen sensor - there is only one for the entire element. For comparison, modern Japanese and Korean cars are equipped with two such sensors.
Among the features of the catalyst, it is worth noting the fact that the element operates at temperatures from 400 degrees Celsius. Therefore, when the engine warms up, this element does not work. Only at high temperatures is it possible to remove up to 90 percent of harmful substances in the honeycombs of the carrier block.
Knock out the contents of the Niva Chevrolet catalyst
In this case, there is no need to cut anything out, the contents of the catalyst are simply knocked out and all the ceramics spill out. Unscrew the catalyst mount and lower it as far as possible.
Next, I inserted a long drill bit from a hammer drill into a drill and drilled holes in the catalyst, then a spray bottle reinforced with the spell “your mother” was used. By the way, the cat was probably not clogged. This is what came out of him.
There was nothing left inside. There are a lot of pictures on the Internet with comments about what needs to be cut and then cooked, but in the shnivy it turns out you can get by with some kind of pin. Putting everything back together was no problem. To push the rubber bands in, I use silicone lubricant for motorcycle chains - they fly into the seats without tension. Then I thought that right now there would be a rare hemorrhoid with unscrewing the stuck lambda because it was inconvenient at first glance, I mentally prepared myself and hop, but it wasn’t even really tightened. Now I wonder if they changed it or tried to clean it with phosphoric acid?
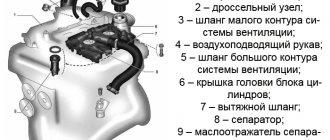
Cylinder head structure of VAZ engines
The block head performs all the functions described above using parts and entire assemblies built into it. The head is based on a solid cast part made of durable aluminum alloy, which has high thermal conductivity, as well as some viscosity - it is necessary for a firm fit of the head through the gasket to the cylinder block.
The cylinder head has a number of holes, cavities and recesses of various shapes and purposes:
- Combustion chambers;
- The cavities of the water cooling jacket (in heads of modern types, stiffeners are also located there);
- Inlet and outlet channels;
- Channels for installing valves;
- Shaft for the timing chain (in the cylinder head of VAZ “Classic” engines);
- Holes for installing spark plugs, sensors (temperature, phases, oil pressure) and other parts;
- Holes for bolts with which the head is screwed to the block;
- Oil channels;
- Oil bath for lubrication of timing parts;
- Place for installing a pencil case with a camshaft (on VAZ “Classic” models);
- Bed for installing the camshaft (on later VAZ models).
A number of parts and entire assemblies are installed on the cylinder head in one way or another, including:
- Valve guides are pressed into special channels;
- Valve seats are installed in the upper part of the combustion chambers (in early models - cast iron, in later models - cermet);
- Valves, springs, valve drive levers, etc.;
- A camshaft (or two shafts in modern models) with bearings, seals and plugs, in VAZ “Classic” models - a shaft with a pencil case, in later models - an aluminum camshaft bearing housing (in VAZ-2108, 2109, 21099 and some models of the tenth family there are two such cases, in the engines of current Lada models there is one, but of a large size);
- Intake manifold or throttle body;
- An exhaust manifold;
- Tee for connecting the cylinder head to the cooling system;
- Spark plug;
- Sensors for coolant temperature, emergency drop in oil pressure, timing and others;
- Timing chain or timing belt tensioner and tensioner;
- Ground wire;
- Fuel line;
- On many models of heads there is a distributor, a generator and other parts.
From above, the cylinder head is closed with a cover that performs protective functions - it protects timing parts from external influences. The cover has a neck for filling oil, as well as holes for bolts with which the cover is attached to the cylinder head. The cover is installed through the gasket.
The VAZ block head itself is installed on the cylinder block through a gasket, installation is carried out with ten bolts (in all models), many heads also have an eleventh bolt, screwed on the side. The gasket ensures the necessary tightness of the combustion chambers, and also regulates their volume within certain limits.
In general, the cylinder heads of VAZ cars, especially the early models (“Classics”), have a fairly simple design, and therefore are highly reliable and durable. And thanks to their design, they can be serviced and repaired independently, without the help of specialists. This is used by many owners of old Zhiguli, Samara, Sputnik, VAZ of the tenth family, modern Kalin, Prior and Grant, as well as Niv equipped with the same engines.
Exhaust gas exhaust system design
Main purpose
design - ensuring normal engine operation, environmental friendliness of exhaust and acoustic comfort of passengers and others. The device converts the energy of sound vibrations into thermal activity. Due to their exposure to high temperatures and moisture, some components, including the muffler of the Niva Chevrolet
, need complete replacement.
Main units of the gas exhaust system:
- neutralizer;
- main acoustic filter;
- additional acoustic filter;
- intake pipes;
- oxygen sensor;
- fasteners.
The catalytic converter and the additional resonator form a single unit, which is attached to the main one on a movable hinge. In turn, the main filter is suspended from the floor of the machine using two pillows. The intake pipes are attached to the manifold on studs through a special gasket.
Exhaust system
Components
The exhaust of a Chevrolet Niva car is made by analogy with the previous model - VAZ 2121. But some units and components were also added to it, which increased efficiency and reduced the amount of harmful emissions. Main nodes:
- Downpipe
- Catalyst
- Lambda probe
- Resonator
- Muffler
- Fastenings
- Outlet pipe
Let's try to take a closer look at each component and understand their purpose.
Reception pipe. Sometimes also called the knee. It is made of durable materials, resistant to high temperatures, since it is exposed to the hottest gases and sparks of incompletely burned fuel. It has a curved shape, which is how it got its name. Studs and heat-resistant gaskets are used to connect to the engine. The main purpose is to remove gases from the engine and direct them down under the bottom to other components.
Lambda probe. It is installed at the junction of the exhaust pipes and screwed into the system. This is a sensor that measures the oxygen content in exhaust gases. These parameters are affected by the ratio of the fuel and air mixture that enters the cylinder.
Catalyst. Connects to the exhaust pipe. This is a non-separable structure made in the shape of a barrel. The function of the catalyst is to transform the exhaust and clean it of harmful substances. The neutralizer, which is located inside, consists of sequentially arranged elements whose task is to minimize the amount of particle emissions. The component is designed to last 100-120 thousand kilometers, after which it can become clogged with combustion products or its filler begins to crumble, rendering it unusable. As a result, the car's power is significantly reduced and it begins to stall at idle. Therefore, the most preferable is the Chevrolet Niva exhaust system without a catalyst, the percentage of contamination of which is not much higher, but at the same time the reliability is much higher.
Resonator. It has a shape that makes it look like an aftermarket muffler, but it's not. Combustion products enter the exhaust system after the exhaust valves open, which means this occurs unevenly. Therefore, its task is to distribute the exhaust in the system and smooth out the flow. For this purpose, a system of meshes is used, passing through which the speed of air movement is reduced. Some people believe that it also reduces the volume of the system, but this is not so.
Muffler. It is this component that affects the exhaust volume. It is the final element. The connection to the resonator is made using heat-resistant rings and a clamp. The muffler can be made of several materials:
- Aluminum
- Stainless steel or galvanized
- Black metal.
Suspensions. The task of these components is to mount the system to the body and dampen vibration so that noise is not transmitted to the body and makes staying in the cabin as comfortable as possible.
Sequence of work when replacing faulty Niva Chevrolet mufflers with new ones
Unlike the exhaust pipes, the noise reduction device is located at the lowest point of the ground clearance and is constantly in contact with various mixtures in the form of snow and salt, which are aggressive towards metal. Over time, the unit receives through holes, which leads to disruption of acoustic comfort and environmental conditions. Let's consider all the ways to replace such parts.
Removing and installing the main exhaust filter
- Unscrew the nuts of the pipe clamp.
- Disconnect the filter and remove the O-ring.
- Remove the suspension cushions from the brackets.
- Remove the muffler.
- Install a new node.
Replacing the neutralizer and additional filter
- Unscrew the 2 bolts securing the catalyst to the exhaust pipe.
- Unscrew the nuts of the clamp securing the additional filter to the main filter pipe.
- Remove the faulty unit.
- Install a new part.
Changing the exhaust pipe
- Remove the anti-roll bar.
- Disconnect the wires to the oxygen sensor and unscrew it from the pipe.
- Unscrew the bracket bolts.
- Unscrew the top mounting bolt.
- Bend the locking plates and unscrew the 4 nuts on the exhaust manifold.
- Remove the 2 neutralizer mounting bolts.
- Dismantle the pipe by turning it along its axis.
- Install a new part and carry out installation work in reverse order.
The high temperature of the exhaust system elements requires the use of special thermal screens, which are also susceptible to corrosion and require immediate replacement.
Basics of safe repair work
Despite the fact that the work is carried out with the engine turned off, there is a high probability of suffocation from exhaust gases. Therefore, the work room must be equipped with excellent ventilation or be easily blown to allow oxygen to enter. Before performing any activity, ensure that sufficient time has passed for the system to completely cool down. Otherwise, you may get severe burns. It is worth noting that the cooling of the catalyst in relation to other elements is longer. It is strictly prohibited to carry out repairs in close proximity to fire. When performing work, you should not use a jack; it is dangerous and can lead to undesirable consequences.
4.25.1 Design features of the exhaust system
Details Category: 4.25 Exhaust gas system Updated 08/07/2014 09:21
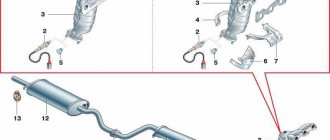
Exhaust gases are removed from the engine through the exhaust manifold, exhaust pipe 15 (Fig. 4.25.1-1), neutralizer 13, additional muffler 12 and main muffler 11.
There are two designs of the exhaust pipe and converter with an additional muffler assembly to meet Euro-2 and Euro-3 toxicity standards.
The receiving pipe meets Euro-2 standards and has a built-in control sensor 5 for oxygen concentration and is connected to the neutralizer flange using a movable hinge. A metal-graphite sealing ring 7 with a spherical surface is placed between the flanges.
The exhaust pipe meets Euro-3 standards in its design and has a control sensor 5 for oxygen concentration and a compensator for vibrations that occur during engine operation and while the vehicle is moving, and is connected to the converter flange using three bolts and nuts. A gasket 18 is installed between the flanges of the receiving pipe and the converter. A diagnostic sensor 19 for oxygen concentration is installed in the pipe behind the converter.
The exhaust pipe 15 is fastened with nuts to the studs of the exhaust manifold, and a sealing gasket 3 is installed between them. Locking plates 1 are placed under the nuts fastening to the manifold. The second end of the intake pipe is attached to the bracket 6 mounted on the gearbox cover using a clamp 14.
The neutralizer 13 and the additional muffler 12 form a non-separable unit, which is attached to the main muffler with a clamp, and are suspended together with the main muffler 11 to the body floor using two pillows 10. The mufflers, together with the pipes, form non-separable units and are replaced with new ones during repairs.
Rice. 4.25.1-1. Exhaust system: 1 – plate; 2 – hairpin; 3 – gasket; 4 – nut; 5 – control oxygen concentration sensor; 6 – bracket; 7 – sealing ring; 8 – front body floor protection screen; 9 – rear body floor protection screen; 10 – muffler suspension cushion; 11 – main muffler; 12 – additional muffler; 13 – neutralizer; 14 – clamp; 15 – exhaust pipe; 16 – conical spring; 17 – bolt; 18 – gasket; 19 – diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor.
HELPFUL ADVICE Check the exhaust system periodically. If there is an increased noise level from the exhaust system, check its tightness. To do this, start the engine and inspect the entire system. By running your hand over possible leaks without touching the nodes, you will immediately feel the leak of gases. If necessary, replace rusted and burnt-out components.
WARNING Before repairing the exhaust system, allow it to cool down as it becomes very hot when the engine is running. Exhaust gases are poisonous and poisoning occurs unnoticed, so be sure to open the garage door before starting the engine!
USEFUL ADVICE If it is impossible to replace the defective unit with a new one, you can temporarily restore its functionality by applying a metal patch to the damaged area and securing it with clamps or wire. It is recommended to place a sheet of asbestos under the patch.
Chevrolet Niva Manual
Exhaust systems: 1 — exhaust pipe; 2 - sealing gasket; 3 - control oxygen concentration sensor; 4 — metal compensator; 5 - sealing gasket; 6 — neutralizer with additional muffler; 7 — main muffler; 8 — system suspension cushion; 9 — diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor. The exhaust system consists of an exhaust manifold, a downpipe, a catalytic converter with an additional muffler and a main muffler. The exhaust pipe flange is attached to the exhaust manifold flange using four studs. The connection is sealed with a heat-resistant metal-reinforced gasket. The fastening nuts are brass or copper-plated and are secured against unscrewing by locking plates (one per two nuts), the edges of which are bent at the edges of the nuts. A threaded bushing for the control oxygen concentration sensor (lambda probe) is welded into the exhaust pipe. The exhaust pipe is additionally attached with a clamp to the gearbox bracket. A bellows-type metal compensator is welded into the rear part of the exhaust pipe, allowing the power unit to oscillate on the supports without transmitting them to the exhaust system. The exhaust gas catalytic converter flange is attached to the rear flange of the exhaust pipe with three bolts and nuts. A sealing gasket is installed between the flanges. The neutralizer serves to reduce emissions of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. It consists of ceramic blocks with many pores, coated with so-called afterburning catalysts: rhodium, palladium, platinum. Passing through the pores of the neutralizer, toxic carbon monoxide (CO) is converted into low-toxic dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen oxides are reduced to harmless nitrogen. The degree of gas purification in a working neutralizer reaches 90–95%. For normal operation of the converter, the composition of the exhaust gases (in particular, the oxygen content in them) must be within strictly specified limits. This function is performed by the controller, changing the amount of fuel supplied depending on the readings of the control oxygen concentration sensor. A sleeve for a diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor is welded into the pipe connecting the converter to the additional muffler (see Engine management system). The neutralizer and sensors are very sensitive to lead compounds - if they are “poisoned” by them, they stop working. Therefore, it is strictly prohibited to operate a car (even for a short time) on leaded gasoline. Another reason for the failure of the converter is interruptions in the ignition system: unburnt fuel burns out in the converter, damaging its blocks. This can cause the exhaust system to become clogged and the engine to stall (or severely lose power). The main muffler is located at the rear of the body. The pipes of the additional and main mufflers are suspended from the body brackets on two rubber cushions. To protect the body floor from excessive heating, protective screens are installed above the converter and additional muffler. Maintenance of the exhaust system consists of inspecting pipes and mufflers for corrosion, replacing failed parts, tightening connections and periodically replacing sensors.