The purpose of the timing chain and its length
To understand the purpose of the timing chain, it is necessary to outline what the engines of classic VAZ models are. All these engines are overhead engines. That is, the timing shaft (aka timing) is located in the upper part of the engine, above the crankshaft and above the oil pump shaft.
The timing chain is the main connecting link in the VAZ 2107 engine
All these shafts are equipped with sprockets, onto which the timing chain is placed. The chain's job is simple: it must transmit torque from the timing shaft to the crankshaft and to the oil pump shaft. From the crankshaft, torque is transmitted to the chassis, and from there to the drive wheels. They begin to rotate and the car moves forward. Thus, the timing chain is the most important connecting link between the three engine shafts, and any breakdown of this link will inevitably lead to either serious problems in the operation of the motor or to its complete jamming if the chain breaks.
Find out about the VAZ 2107 belt drive: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/metki-grm-vaz-2107-inzhektor.html
Timing chain length for VAZ engines
If the driver decides to replace the timing chain on his “seven”, he will go to the spare parts store, where he will inevitably be faced with the question: which chain to choose?
You should know a simple rule: all engines on the VAZ “classic” are equipped only with chains. The only difference is in the length of the chains, or more precisely, in the number of links:
- chains with 114 links. They are installed on VAZ 2102, VAZ 2101 and VAZ 21011 (these short chains are designed for small engines - from 1.2 to 1.3 liters);
- chains with 116 links. They are installed on VAZ models from 2103 to 2107 inclusive. The same chains are installed on the Niva (VAZ 21213). The need for a longer chain is due to the increased volume of engines, which varies from 1.5 to 1.7 liters.
Based on all of the above, the driver in the store will have to determine what kind of chain he is buying - short or long. There are two ways to do this:
- The first way is obvious: simply count the number of links. If there are 116 of them, the chain for the VAZ 2107 has been found;
- the second method is simpler: you need to fold the chain in half, and then look at the pair of end links. If these links are symmetrical, then the chain has 116 links. If not, the chain is short, 114 links.
It should also be noted here that recently counterfeit timing chains have often been found on store shelves. Fortunately, the fakes are made rather carelessly, so an attentive car enthusiast can immediately suspect something is wrong.
Video: how to recognize a fake timing chain
VAZ 2107 injector device - Do-it-yourself car repair
“Seven” is the latest representative of the VAZ series of rear-wheel drive cars. The seventh model was developed on the basis of the VAZ 2105 and differs in the shape of the seats, interior trim, shape of lighting devices and engine power.
Initially, the VAZ 2107 was equipped with a one and a half liter engine from the VAZ 2103. Subsequently, the range of engines installed on the “seven” was expanded. Cars with engine sizes ranging from 1.45 to 1.7 liters were produced for different markets. It was the 1.7 liter engine that was the first to be equipped not with a carburetor, but with an injection power system. Subsequently, the VAZ 2107 injector completely removed carburetor cars from the assembly line.
The principle of operation of the VAZ 2107 injection engine
Unlike carburetor systems, where the preparation of the air-fuel mixture occurs in the carburetor chambers, the injection system involves injecting fuel directly into the cylinders. Therefore, such a system is called a “distributed injection system”.
Injection systems are qualified depending on the principle of operation and the number of injectors. “Seven” is equipped with a separate injection system with 4 nozzles (one per cylinder). VAZ 2107 injectors are controlled by a microcontroller of the electronic engine control unit. It regulates the flow of fuel into the cylinders depending on the operating mode, the position of the gas pedal and other parameters read by special sensors.
The ECU (electronic control unit) controls the amount of fuel and air entering the engine combustion chambers. In addition, it controls the formation of a spark on the spark plugs, changing the timing depending on the speed. The ECU also turns the fuel pump on and off, regulates idle speed, controls the amount of CO in the exhaust gases, and the temperature of the coolant in the cylinder block. It all works as follows.
Gasoline from the tank, passing through the fuel filter, is supplied by a pump to the fuel rail. The latter has a pressure regulator that regulates the flow of fuel to the injectors. A pressure of 300 MPa is maintained in the fuel rail, and excess fuel is sent to the gas tank through the return pipe.
The electronic control unit opens and closes the injectors, ensuring that gasoline is supplied to the intake manifolds with each engine revolution. The amount of fuel entering the cylinder depends on the time during which the injector is open.
The ECU calculates this time based on the readings of many sensors. The main indicators that affect the injector opening time are information from the mass air flow sensor and the throttle position sensor.
The opening moment of the injector is determined based on the position of the pistons in the cylinder, which is transmitted to the ECU by the crankshaft sensor.
Other parameters are also taken into account:
- coolant temperature, which affects the combustion process of the fuel mixture;
- on-board network voltage, on which the injector response time depends;
- engine speed;
- exhaust gas composition.
Ignition system VAZ 2107 injector
The VAZ 2107 injection engine is equipped with an electronic ignition module, consisting of an electronic board and a pair of coils. Due to the absence of moving parts, the system is highly reliable and does not require regular maintenance. The moment of spark formation is determined by the engine ECU and depends on the crankshaft speed.
Advantages of VAZ 2107 injection models
- Due to the optimal formation of the fuel mixture, the efficiency of an injection engine is higher than that of a carburetor. Accordingly, the VAZ 2107 injector engine consumes less fuel and is at the same time more powerful than a carburetor engine with the same volume.
- Electronics regulate engine speed, thanks to which it idles more steadily, stalls less often when starting from a standstill, and starts better in cold weather.
- Unlike a carburetor engine, an injection engine does not require frequent adjustment of the fuel supply and ignition systems.
- The optimal composition and quantity of the fuel-air mixture entering the cylinders, as well as the presence of a catalyst, ensure a minimum content of harmful substances in the exhaust. This is an important point from an environmental and health perspective.
- Hydraulic chain tensioner and hydraulic valve clearance compensators eliminate the need for manual adjustment of the mechanism and ensure quieter engine operation.
- The torque curve is smoother - high torque is achieved over a wider rpm range.
Disadvantages of the injection model of the VAZ engine
In addition to its advantages, the injection VAZ 2107 has some disadvantages:
- The location of the engine and other units in the engine compartment remains the same as in the old-style “classic”. This makes it difficult to access some parts. However, the injection system is quite reliable, so it does not require frequent maintenance during operation.
- The injection “seven” is equipped with a catalyst, which is easily damaged when driving through obstacles. Therefore, you need to be careful when driving on uneven roads.
- An engine with an injector is more demanding on fuel quality than a carburetor variation. When using low-quality gasoline, the system may become contaminated, requiring unscheduled maintenance of the unit.
- If the injection system breaks down, it will not be possible to repair it and adjust it “on the knee” in a garage. You'll have to go to a service station.
THIS IS INTERESTING: Replacing Mazda 6 gh pads
Malfunctions of the VAZ 2107 injection engine
Problems with the 7 injection engine usually manifest themselves as follows:
- The engine is running erratically.
- Fuel consumption of the VAZ 2107 has been increased.
- There is an increased CO content in the exhaust gases.
- Dips when pressing the accelerator pedal.
- The engine “does not pull” (reduced power).
- To diagnose injection system faults, special equipment is required. In particular, in order to read error codes and check sensor readings and the operation of the engine ECU, a special computer (tester) is required. Therefore, repairs and diagnostics of the VAZ 2107 injector are carried out at specialized service stations. The most common cause of injector failure is clogged injectors.
Causes of injector clogging
Typically, problems with the injection system occur when using low-quality gasoline. Heavy paraffins contained in such fuel settle on the walls of the system, cutting off the fuel supply. Manufacturers of high-quality gasoline add detergent to it - a special additive that dissolves deposits. Low-quality gasoline contains too much paraffin, which forms deposits faster than detergents can remove them.
Deposits form more intensively at low temperatures, so when the car is frequently driven with a cold engine, the injector becomes clogged more often.
Deposits can accumulate not only in the injectors. Often vapors settle on the throttle valve, which leads to a change in the proportions of the air-fuel mixture entering the cylinders.
Deposits of substances contained in low-quality gasoline may also appear on the back of the intake valve plates. This can lead to valve burnout or fuel detonation.
To clean the injection system of deposits, it is necessary to use special flushing fluid and equipment. You can wash the injector in a garage. To do this, you need a syringe and washing liquid.
The latter is mixed with gasoline and poured into the injection system through the hose of the vacuum brake booster. First, the operation is performed with the engine turned off, then with the engine running. The mixture is fed into the running engine gradually, in small portions.
As a result, the deposits dissolve, enter the engine cylinders and burn there. In this case, clouds of smoke may briefly appear coming out of the muffler.
Source: https://avto-voshod.ru/ekspluatatsiya/ustrojstvo-vaz-2107-inzhektor.html
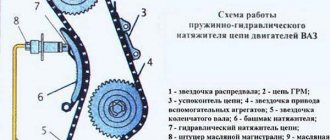
Main elements of the timing chain tensioning system
The timing chain in the engine is supported not only by the three sprockets mentioned above. It is supported by several other important devices.
The timing chain tensioning system consists of several critical elements
Let's look at them in more detail.
Timing chain stop pin
The timing chain in the VAZ 2107 engine is supported by a complex tensioning system. One of the elements of this system is the limiting finger. This is a small cylindrical part screwed into the wall of the cylinder block. The pin is located next to the crankshaft sprocket. The purpose of the pin is as follows: if the timing chain tension suddenly weakens, the pin will prevent the chain from jumping off the crankshaft sprocket.
The design of the restrictive pin is extremely simple - it is a regular bolt with a head truncated on the sides
At the same time, the chain will begin to touch the limiter with a characteristic ringing sound, which will certainly attract the driver’s attention, since this sound will be heard even in the cabin. If the chain breaks, the limiter will not allow it to completely fly off the sprocket and break the nearby oil pump and timing shaft sprockets. If the timing chain is tensioned normally, it does not touch the limiting pin, since in this case there is a constant gap of about 1.5 cm between it and the pin.
About timing chain tensioners
The purpose of the timing chain tensioner is easy to guess from its name. He must constantly tension the chain, preventing it from sagging. If the chain sags by even half a centimeter, it may fly off one of the sprockets (although this happens quite rarely, much more often there are situations when the chain remains on the sprocket, but at the same time jumps several teeth forward, as a result of which the uniformity of its tension is completely disrupted , and the sagging increases even more). At different times, different types of tensioners were installed on the VAZ 2107.
Mechanical tensioners
In a mechanical tensioner, the force required for the tension shoe to press on the chain is created by a conventional spring. It presses on the rod, it moves out of the body and presses on the shoe. And the shoe, in turn, puts pressure on the chain, constantly dampening its vibrations.
The main element of the mechanical tensioner is the plunger spring
The spring in such a tensioner is adjusted with a conventional plunger nut. If the driver needs to tighten the chain a little, he simply tightens the nut slightly, eliminating any slack.
Mechanical tensioners for VAZ 2107 are reliable and simple in design
Automatic tensioners
Automatic tensioners were installed on later models of the VAZ 2107. Unlike mechanical devices, the design of this tensioner includes a toothed bar with a ratchet.
The main element of the automatic timing chain tensioner is a toothed bar
The plunger spring presses on this bar, and the bar transmits this force to the shoe. The ratchet prevents the bar from returning to its original position. This keeps the timing chain tension constant.
Finding automatic tensioners for VAZ 2107 on sale has become increasingly difficult lately.
Hydraulic tensioners
These tensioners were installed in the latest VAZ 2107 models. The main difference between these devices is the principle of their operation. The force in the hydraulic tensioner is created not by a spring, but by oil pressure. It is supplied to the tensioner through a reinforced high-pressure hose.
Oil is supplied to the hydraulic tensioner through a special reinforced hose
Read about installing hydraulic compensators on the VAZ 2107: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/gidrokompensatoryi-na-vaz-2107.html
Timing chain tensioner
The timing chain tensioner is another indispensable element of the tension system, without which uniform operation of the timing chain is impossible. The damper is a metal plate that is attached to the wall of the cylinder block.
The timing chain adjuster on the “seven” is a simple metal plate held on by two bolts
This plate is located opposite the tensioner, that is, the damper acts on the second half of the chain. Since the tensioner presses the chain very sharply, the opposite side of the chain inevitably begins to vibrate. To dampen this vibration, a damper is needed. The chain, touching the damper plate, loses some of its energy and the amplitude of its oscillations decreases significantly. Without the restraining effect of the guide, the chain will stretch much faster.
Design of the VAZ 2106, 2107 chain drive
To drive the VAZ 2106/2107 with a carburetor, a double-row roller chain is used. It transmits force from a sprocket mounted on the crankshaft to another sprocket mounted on the end of the camshaft. The chain is a structure that develops large inertia, so a chain drive requires vibration damping. Even a well-tensioned chain retains the property of “playing” in those places where there are no sprockets or tensioners.
The chain has virtually zero ability to stretch and compress, and fairly limited flexibility. Therefore, in order to provide it with constant tension while working in its place at any speed, it has to be literally shackled, using a system of tensioners and dampers.
This problem on the VAZ 2106/2107 is solved by a damper - an additional spring-loaded clamping bar. It has a steel frame covered with a layer of durable rubber. Tensioners and dampers dampen vibration and noise quite effectively. The chain is prevented from falling off by a stop pin that is screwed into the block or cylinder head. During normal operation the chain does not touch it.
Timing chain jump and its symptoms
The chain, like any other part of the car, wears out over time. Wear usually shows up as chain stretching. The cause of stretching is the so-called metal fatigue, which affects almost all parts that experience cyclic loads. Having stretched, the chain begins to sag significantly. If the driver does nothing, then sooner or later a situation will arise when the chain on one of the sprockets jumps one or two teeth forward. After this, all valve timing in the engine will be disrupted, as will its operation. Here are the main signs of a skipped timing chain:
- the engine runs intermittently, and they occur even at idle;
- while driving, power dips appear, which most often occur during the acceleration of the car;
- the engine starts very poorly, and this does not depend on the outside temperature;
- A characteristic jingling sound is heard from under the hood, which intensifies as the engine speed increases.
All these signs indicate that the timing chain has not only weakened, but also jumped. And the driver needs to replace it as soon as possible. If this is not done, the engine will sooner or later seize, after which you will have to make expensive major repairs.
About assembling the timing belt and installing the chain according to the marks
As mentioned above, the timing system has a marking system that allows you to correctly install the guide sprockets and timing chain after replacement.
- If the timing chain was changed on a carburetor “seven”, then the oil pump sprocket, which was loosened above, is tightened first. In this case, the mark on the sprocket is aligned with the protrusion on the body (and if the “seven” is injection, this point does not play a big role).
- The chain guide and tension shoe are returned to their place.
- Now the crankshaft sprocket is put in place. It also has a recessed mark, which also needs to be aligned with the protrusion on the timing case, and only after that tighten the fastening nut on the sprocket and install the cotter pin in place.
- After aligning the crankshaft sprocket according to the marks, a new timing chain is put on it.
- Now all that remains is to install the camshaft sprocket in place. The asterisk does not tighten. The timing chain is put on it. In this case, the sprocket must be turned so that the mark on it coincides with the mark on the cylinder block. If there is no match, the chain should be removed from the teeth and the sprocket should be turned in the desired direction until the marks completely coincide.
Before tightening the sprocket on the camshaft, the marks must be carefully aligned - When the risks coincide, it is necessary to check the coincidence of the marks on the remaining sprockets. If there is no discrepancy between the marks, you can tighten the camshaft sprocket and install a cotter pin on it.
- Now all that remains is to return the timing cover to its place, and then replace the previously removed radiator.
More about the design and replacement of the timing chain damper: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/uspokoitel-tsepi-vaz-2107.html