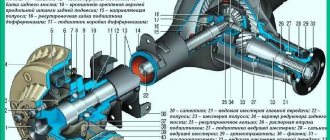
Differential device
The differential on a vehicle's axle is designed to ensure that the vehicle's wheels travel different distances when turning or on uneven sections of the road surface. The disadvantage of this mechanism becomes noticeable when used off-road, when its operation is ensured by the load of one of the 4 wheels, while the main part of it must be carried out by the other wheel. In practice, this manifests itself when the car gets stuck in the mud: one of the wheels continues to slip, while the other remains motionless.
UAZ 469 › Logbook › Differential lock: what is it and what is it for
To increase the vehicle's cross-country ability, the differential mechanisms are made lockable (differential lock).
A differential is a mechanism that allows the wheels of a car to rotate at different speeds relative to each other, this is necessary for the tires to roll without slipping when cornering. Moreover, if the differential is installed between the wheel drives (half-axles), it is called inter-axle, and if between different axles - inter-axle. What, you ask, does this give?
Imagine this situation: one of the wheels of the drive axle has fallen into a hole with clay, and the other is standing on solid ground. What happens in the case of a conventional, so-called free differential? That's right, a wheel that falls into a hole will skid helplessly, while a wheel standing on solid ground will be at rest, not transmitting any torque. As you already understand, differential locks serve precisely to eliminate this glaring injustice. There are different types of differential locks, but basically the locks are divided into two large groups: differentials that are locked rigidly, 100% (so-called lockers, from the English locker - “lock”), and limited slip differentials (in the English version - “limited”) slippage", or LSD - Limited Slip Differential).
Each of these options has its own advantages and disadvantages. The main disadvantage of “hard” differential locks is their amazing ability to destroy the transmission, gearbox and tire wear.
Although, if you think about it, there is nothing unexpected in this. After all, even wheels on very slippery surfaces constantly either run over bumps, or fall into holes and slip in turns. In short, the transmission is constantly affected by alternating forces.
In order to overcome the inherent disadvantage of conventional differentials and rigid differentials, intermediate differential lock designs have been created. This design was developed in 1965 by the English and refers to cylindrical self-locking limited slip differentials (or, as they are called abroad, limited slip differentials) or simply a self-locking differential lock.
The principle of its operation is simple. If you “press” the satellites with some force, not allowing them to rotate between the side gears at relatively high speeds, then the differential, on the one hand, will be able to perform its main work in turns, allowing the wheels to rotate at different angular speeds, and on the other hand, will distribute torque under difficult conditions in such a way that it will allow the wheel in better traction conditions to realize greater traction force.
The indisputable advantage of the Quaife self-locking differential is its simplicity. Two housing parts, two side gears, ten satellite gears (cylindrical gears), a cage - and that’s it! When the car is moving in a straight line, the Quif lock works like a regular differential. The side gears rotate at the same speeds, and the satellites only transmit torque equally to both wheels, rotating with the housing and side gears as one unit. And in a turn, when there is a mismatch in wheel speeds, the differential lock begins to work - the satellites rotate between the body and the semi-axial gears, allowing the outer wheel to run forward. A self-locking differential can better utilize engine torque on slippery surfaces or when there is excess traction.
Types of locks
If something happens to such a design or the differential begins to work incorrectly, it is better to repair the part. And since the mechanism is located in the gearbox, to remove it it is necessary to remove the entire assembly.
The first thing to do is to remove the side gears by turning them around the pinions. To be able to remove the satellites, it is necessary to remove the retaining ring from their axis. Then the driven gear should be released, for which the bolts in the differential mount must be unscrewed. The entire part is disconnected from the body using a chisel and hammer.
Disassembling the unit
All detached parts may have minor defects, which can be easily removed using fine-grained sandpaper. If they cannot be corrected manually, it is better to put the differential up for sale and purchase a new one. The normal operation of the differential may be hampered by a defect on the driven gear in the gearbox. It is advisable to replace this part to prevent further damage to the entire assembly.
Bearings can quickly become unusable and are best replaced immediately. The differential housing itself is replaced if the bearing seats are quite worn.
How does he work?
If specialized devices were not installed on cars, wheels located on the same axle would constantly rotate at the same speed, as a result of which a lot of different operational problems would arise that relate to handling. Thus, among the side effects that could arise in the absence of a differential and differential locks on the UAZ, it is worth noting an inflated and at the same time completely uneven tire consumption, a significant increase in the load on various suspension elements, and insignificant steering. With the help of a differential, it became possible to unevenly distribute the rotation speed received by each wheel from the driveshaft.
Tips for using forced locking on UAZ vehicles
When using a differential lock, the car is less susceptible to corner swings, and it is possible to overcome sandy or snowy obstacles. But on loose soil there is a danger of landing the car on the bottom and axle housings. In this case, the vehicle is pulled out by a winch or towed. After overcoming a difficult section, the forced locking is turned off.
It is prohibited to block the axle shafts when driving on paved roads. It is not allowed to drive a vehicle with locked wheel drives at a speed of more than 10 km/h. When installing a lock on vehicles with larger rims or tires, it is necessary to use reinforced axle shafts. Increased loads occurring in the transmission can damage the crankcases or gears.
When using self-locking devices on the front axle, you should take into account the possibility of changes in the vehicle's behavior when driving on the highway. When accelerating a car in a turn on a slippery surface, the tires begin to slip, which is perceived by the mechanism as a signal to lock.
A locked differential will not allow the car to move along the curve of the highway, but will straighten the trajectory (driving the car into the oncoming lane or into a ditch).
Source
When is it needed?
Not everyone understands that in real operating conditions, wheels can rotate at different speeds in a variety of situations, namely:
All the features mentioned above are not too important for the driven axle shafts for the reason that in fact they are not connected to each other and rotate completely independently. However, the drive pair receives power directly from the gearbox, and each wheel has a rigid connection with the transmission, as a result of which curved movement becomes quite difficult.
Which self-locking differential to choose
It all depends on the operating conditions of the machine. The fact is that the Patriot is a heavy car and with its help you can’t take deep snow covers from acceleration - you’ll end up on bridges. As a rule, all this is done by coasting without gas (back and forth). In this case, the blockages can even interfere, especially hard ones - they will break the track. At the same time, with blocking, the patriot will be less susceptible to extreme corner hangings (small corner patrols are not scary anyway) and it will be possible to storm the snow while moving. But also without fanaticism. Let’s not forget about “sitting on bridges.” After all, without blocking and without acceleration, a patriot simply does not drag himself to an ambush, but with blocking it is easy. In short, this is still a jungle. Let's shorten it a little. I decided for myself to have a self-block in the back. Because we have winter for half a year. I wanted to ride in the rear as much as possible during the winter half of the year. I spent a long time scouring the internet and chose Val Racing because I found almost nothing negative about them. I installed a 50% self-block with a preload of 4-6, this is a purely urban option. In principle, people put up 70% of self-blocks for the city and even in front and don’t complain. What we get with a self-locking unit in the rear is a more predictable drift of the rear when the gas is exceeded while accelerating in a straight line. (When turning at speed on a Patriot, I don’t recommend accelerating at all with or without locking). Cross-country ability improves slightly. There is not much point in putting the forced link back because the rear is light and in strong corners, and even when going uphill it will simply slip with both wheels. Now about the self-block on the front. Installing self-controlled locks on the front is fraught with a sharp change in the behavior of the car at the moment the self-lock is activated. Simply put, let’s imagine the situation: there is a turn, a 2-lane road, a little slippery, we are going to overtake. We notice an oncoming car. There is no choice to slow down and backing into the tail of the overtaken is not an option, we are Russian people and it is dangerous. It remains to speed up a little, especially since we seem to have time. We press on the gas and the wheels begin to slip a little. Slipping? - which means the automatic block turns on and we suddenly stop turning as we were turning and start driving straight, straight into the oncoming traffic. Therefore, having placed the self-block on the front, you must always be prepared for the unpredictability of a patriot who is sometimes not predictable even without it. In the beginning, it would still be better to use coercion. In addition, a more loaded muzzle will better stretch the entire body in corner hangings. What kind of coercion? I'm not entirely experienced here. The air doesn't last long. The differential cuffs are starting to etch. And the installation is complicated and expensive (compressor, hoses). Hydraulics are a problem in installation, but not like with pneumatic ones. Pneumatic is more reliable. Mechanical is cheaper than the first two. Both in terms of installation and cost. She needs a second handbrake in the cabin. Not in demand among people and sellers. Electro. Electric locks for Patriot are sold by one company called Simbad. Eaton electric lock. The rest of the companies buy from Simbad. Simbad itself also does not produce these locks, but is an assembly intermediary. They order the kit components, assemble them and send them to people. Things were not going well for Simbad; deliveries to customers were delayed for up to six months. But now they seem to be improving. The blocking is not cheap, about 24 thousand rubles. but due to the fact that the kit includes reinforced axle shafts. Also a controversial issue. Because as I understand it, this excuse is “REINFORCED” axle shafts and not a useful quality. It's just that the splines of the standard axle shafts are not suitable for locking. Because blocking is carried out, as I understand it, specifically for gazelles. And to fit it into the vehicle, you need adaptive axle shafts and adaptive axle covers. All this was called reinforced axle shafts. Nevertheless, for 24 thousand rubles. we get forced locking, which is as easy to install as a self-locking lock or a standard differential. You just need to drill a hole for the wire in the bridge. And attach a button in the cabin for connection. The lock works at speeds up to 30 km/h and is automatically disabled when this speed is exceeded. She has a minus. When changing the direction of movement, the self-block is re-blocked. There is a risk of breaking the self-block in harsh extreme conditions when rocking. There already seem to be precedents.
Where is it used?
The differential today is installed on both trucks and passenger vehicles, regardless of whether we are talking about all-wheel drive or single-wheel drive models. In all-wheel drive vehicles, the distribution gear also provides control of the balance of forces that is formed between the axles. In the vast majority of cases, it is located in the rear of the car and is directly connected to the driveshaft.
How to enable locking on UAZ Bukhanka
The website UAZ-Buhanka.ru is dedicated to UAZ loaf or tablet cars, as the car is popularly called.
Loaf salon photo
This page contains photos of the interior of the UAZ Bukhanka car:
Location of controls
1 - steering wheel. The steering wheel of UAZ-31512, UAZ-3153 and the UAZ-3741 family vehicles has a central horn button. The steering wheel of UAZ-31514 and UAZ-31519 cars is equipped with an energy-intensive pad and has two horn buttons located in the wheel spokes. 2 — rear view mirror (internal). Adjustable by turning around the articulated head. 3 - instrument panel. 4 — sun visors. 5 — windshield blower pipes. 6 — passenger handrail. 7 — lamp (plafond) lighting. 8 - battery ground switch. Switching the “mass” on and off is done by turning the knob 90°. 9 — lever for engaging the front drive axle. It has two positions: front - the axle is on, rear - the axle is off. Before engaging the front axle, engage the front wheels. Turn on the axle while the vehicle is moving. 10 - heater. 11 — transfer case control lever. It has three positions: forward - direct gear is engaged, middle - neutral, reverse - downshift is engaged. Before downshifting, engage the front axle. Engage the downshift with the clutch disengaged and only when the car is completely stopped. 12 — gear shift lever. The switching pattern is shown on the handle. Shift gears by smoothly pressing the lever without jerking. If you cannot engage the required gear before moving off, lightly release the clutch pedal, and then disengage the clutch a second time and engage the gear. When switching from a higher gear to a lower one, it is recommended to disengage the clutch twice and briefly press the throttle pedal. Engage reverse gear only after the vehicle has come to a complete stop. When you engage reverse, the reversing light turns on. 13 — lever of the parking brake system. To turn the lever on, move it back; to turn it off, press the button at the end of the lever and move the lever forward until it stops. When the parking brake is engaged, the red warning lamp on the instrument panel lights up. 14- handle for driving the hatch cover for ventilation and heating of the body. 15 — valve handle for switching fuel tanks. The handle is turned forward - the valve is closed, turned to the left - the left tank is on, turned to the right - the right tank is on. The valve is not installed on vehicles with one fuel tank. 16 — carburetor throttle control pedal. 17 — pedal of the service brake system. Brake the car smoothly, gradually increasing pressure on the pedal. When braking, do not let the wheels slide, as in this case the braking effect is significantly reduced (compared to rolling braking) and tire wear increases. In addition, strong and sudden braking on a slippery road can cause the car to skid. 18 — clutch pedal. When changing gears and starting from a stop, the clutch pedal should be pressed quickly and fully, and released smoothly. Depressing the pedal slowly or incompletely causes the clutch to slip, making it difficult to shift gears and causing increased wear on the clutch plate. When the pedal is suddenly released (especially when starting from a standstill), the load on the transmission increases, which can lead to deformation of the clutch driven disc and other transmission parts. When driving the car, do not keep your foot on the clutch pedal, as this leads to partial disengagement of the clutch and the disc slipping. 19 — foot switch for headlights. By pressing the button, with the headlights on, the low beam or high beam headlights are turned on. Not installed on vehicles with multifunctional left-hand stalks. 20 - portable lamp socket. 21 — radiator shutter control handle. Under certain operating modes and climatic conditions, in order to maintain the temperature of the engine coolant within 70-80 ° C, it is necessary to regulate the amount of air cooling the radiator using blinds. When the handle is pulled, the blinds close. 22 — rear view mirror (external). 23 — direction indicator switch handle. The handle automatically returns to the neutral position when the steering wheel is turned in the opposite direction (when the car enters a straight line). Some cars are equipped with multifunction steering column switches. 24 - carburetor throttle control knob. The extended handle is fixed by turning 90° in any direction. 25 - carburetor choke control handle. The extended handle is fixed by turning 90° in any direction.
Console:
1 — alarm switch. When you press the switch button, the lamps of all indicators and turn signal indicators, the signal lamp for turning on the turn indicators (item 6) and the indicator lamp inside the switch button simultaneously operate in a flashing mode. 2 — speedometer. It shows the speed of the car in km/h, and the counter installed in it shows the total mileage of the car in km. 3 — fuel level indicator in the tank. Each tank has its own indicator sensor (except for additional tanks). 4 — warning lamp for emergency condition of the brake system (red). Lights up when the tightness of one of the hydraulic drive circuits to the brake mechanisms is broken. 5 - warning light for turning on the parking brake (red). 6 — signal lamp for turning on the direction indicators (green). Operates in flashing mode when the turn signal switch or hazard warning light switch is turned on. 7-signal lamp for emergency overheating of the coolant in the radiator. 8 — signal lamp for turning on the high beam headlights (blue). 9 — coolant temperature indicator in the engine cylinder block. 10-signal lamp for emergency oil pressure. Lights up when the oil pressure in the engine lubrication system drops to 118 kPa (1.2 kgf/cm2) 11 - oil pressure indicator in the engine lubrication system. 12 - voltmeter. Shows the voltage in the vehicle's on-board network. 13 - cigarette lighter. To heat the cigarette lighter coil, press the handle of the insert, push it in until it locks into the body and release the handle. When the required heating temperature of the spiral is reached, the insert automatically returns to its original position. Forced holding of the insert in a recessed position is not allowed. 14 — lighting lamp (installed on UAZ-31512, on other models a courtesy lamp is installed) 15 — lighting lamp (plafond) switch. On some models the switch is located next to the lampshade. 16 — carburetor throttle control knob. 17 — switch for fuel level sensors in tanks. 18 — rear fog lamp switch with built-in warning light 19 — fog lamp switch. 20 - combined ignition and starter switch (see Fig. 1.22 and 1 23). The key from the ignition switch of UAZ-31514, UAZ-31519, UAZ-3153 vehicles is removed only in position III, and the locking mechanism is activated, blocking the steering shaft. To lock the steering when parked, set the key to position III, remove it and turn the steering wheel in any direction until you hear a click, indicating that the tongue of the locking device coincides with the groove of the steering wheel shaft locking sleeve. When unlocking the steering, insert the key into the ignition switch and, rocking the steering wheel left and right, turn the key clockwise to position 0. In order to eliminate cases of erroneous activation of the starter while the engine is running (key position II), a lock is used in the design of the ignition switch mechanism , making it possible to restart the engine only after returning the key to position 0.
What is it like?
There are three main categories worth noting:
Depending on what type of design is considered, the nature of the technology for transmitting forces to the wheels also changes. In the event that one wheel loses normal traction with the road, the gearbox will direct all the torque to this axle shaft, as a result of which the wheel that has lost reliable support will begin to slip. It is then that the need arises to block the differentials on the UAZ in order to temporarily disable the unit and distribute the rotating force equally between the axle shafts. Thus, blocking provides much better passability in some situations.
Self-locking differential on UAZ: from A to Z
A self-locking differential on an UAZ is a device that is responsible for distributing the torque of the transmission driveshaft between the wheels of the vehicle, the rear or front axle.
The main function of this mechanism is to ensure wheel rotation without slipping.
So, if a car moves in a straight line, on a flat road with a good and clean surface, its wheels are equally loaded, and their rotation speed is the same. In this case, the differential acts as a transmission link from the driveshaft.
If driving conditions begin to change, such as turning or slipping, then the load on the vehicle’s wheels is uneven. To continue the controlled movement of the machine, there is a need to distribute the resulting torque from the driveshaft between the wheels in different ratios. In this case, the differential performs this task and ensures safe maneuvering of the vehicle.
The machine differential can be located in the transmission in three options, which depend on the type of drive, namely:
- in front-wheel drive cars - in the gearbox housing;
- rear-wheel drive cars have differentials in the drive axle housing;
- All-wheel drive vehicles are equipped with differentials in the front and rear axle housings, or in the transfer case.
History of the differential
Differentials on cars were not introduced immediately. Their birth is due to the fact that at the dawn of the automotive industry, designers were faced with the problem of maneuverability of the first cars. The wheels were spinning at the same angular speed. This led to loss of controllability when cornering and maneuvering on slippery roads. It was not destined to be a reliable means of transportation.
The first mechanism, which was responsible for the distribution of torque between the axes, was invented by the Frenchman Peccoeur. He presented his invention to the world in 1825. The inventor is also known for creating the world's first four-wheeled steam truck.
The mechanism invented by the Frenchman was a device consisting of shafts and gears. They contributed to the transmission of torque from the engine to the wheels. However, the unit failed to completely solve the problem of slipping when turning. The shortcomings especially manifested themselves when driving in icy conditions, when the wheels lost grip on the road. This led to frequent accidents. Crashing a car in off-road conditions was common.
The designers were forced to start looking for a solution to the problem. This process took quite a long time. Ferdinand Porsche managed to make a workable device and eliminate the problem by inventing a cam mechanism in the differential that prevents slipping of the axle wheels.
Porsche completed his research in 1935. The first successful examples of the new differential were installed on Volkswagen models (Ture B-70).
How does the differential work?
The standard differential has a gear operating principle, ensuring the transfer of power from the crankshaft to the wheels. Its device includes a number of main components, which include:
- axle gears with satellites, located in a cup (housing). Each axle shaft has a bearing;
- a cup rigidly connected to the driven gear, designed to transmit torque from the main gear.
The work of the differential is reduced to transmitting rotation to the axle shaft, providing torsion and rotation of the wheels. The satellites are designed to create different angular speeds with a constant amount of torque.
Self-locking differential
An autonomous self-locking differential is an independent unit that does not require any external control systems. The device is intended exclusively for wheeled vehicles; tracked vehicles do not use it.
It is customary to divide “self-blocks” into 2 groups:
- Torque-driven differentials.
- Differentials that begin to work when there is a difference in angular speeds from the driven gears.
Group 1 includes devices with worm, screw, and disk locking.
The 2nd group is represented by mechanisms with a centrifugal automatic switch, having a viscous coupling, a gerotor hydraulic pump, and overrunning clutches.
Self-blocks for UAZ Krasikova, etc. Cam differentials are usually classified as intermediate types.
The principle of operation of a self-locking differential on a UAZ
The standard self-locking differential on an UAZ is a symmetrical inter-wheel (otherwise known as center) differential. Its operation is carried out in three modes:
- linear motion mode;
- maneuvering around corners;
- driving on slippery roads.
In the first mode (straight-line), the UAZ wheels operate under conditions of equal road surface resistance. The thrust to the differential easily enters its body, along with which the satellites move. They ensure the normal operation of the axle gears, transmitting draft forces to the wheel in equal proportions. The rotation speed of the axle shaft gears is equal to the rotation speed of the main gear.
In the second mode, at the beginning of maneuvering, when turning, the inner wheel of the axle begins to experience more resistance than the outer one. At the same time, the inner gear of the axle shaft begins to slow down, which leads to rotation of the satellites, which increase the frequency of torsion of the outer gear of the axle shaft. The drive wheels begin to spin at different angular speeds. This allows you to maneuver without slipping. The differential device provides uniform traction, regardless of the angular velocity, in an equal ratio to each wheel.
When a UAZ moves on a slippery road surface, one of the wheels, as a rule, is under conditions of greater resistance, while the second one slips and skids. In this situation, the limited slip differential allows the towing wheel to rotate at a higher speed. The second wheel, on the contrary, begins to stop. Since the torque on the towing wheel is insignificant, due to low adhesion, the traction of the wheel is also small. This differential operation makes it possible to overcome slippery areas quite successfully.
However, there is a deadlock situation on a UAZ equipped with a standard symmetrical differential, when the car is unable to move.
In the standard, factory configuration, the differential lock on a UAZ, including those equipped with Spicer axles, can, when entering a turn on a slippery road, create the effect of so-called “oversteer.” When the car accelerates strongly, which is carried out in mixed road conditions, the car may begin to drift away from the trajectory along which the driver is directing it.
Features of the “self-block” device
The solution to the above problem led to the emergence of various types of self-locking mechanisms. By design they are automatic and manual.
Blocking options
Depending on the characteristics of the car, different operation limitation schemes are used - manual or automatic.
When the lock is engaged, the car's wheels will completely ignore the traction force and equal force will be transmitted from the engine to them. In this regard, more efficient vehicle cross-country ability is ensured, which is impossible if an open differential is installed on the vehicle. That is why it is not surprising that differential locking of the UAZ military axle and other options for improving the cross-country ability of this vehicle have recently become widespread.
Types of differentials for UAZ Patriot
UAZ Patriot is a car that is designed not only to win the hearts of those who like to ride in such a jeep, but also to overcome various kinds of obstacles that arise in the path of the iron horse. The SUV copes with these obstacles with a bang, which some foreign analogues may even envy. But to truly be the best rogue, the SUV lacks such an element as a limited-slip differential. Everyone knows what a differential is, but let’s take a closer look at what self-locking means, as well as what its advantages are.
What is a locking differential?
Structurally, a differential equipped with a lock is arranged in exactly the same way as standard open-type units, but in this case, a mechanism is added to limit the difference in the rotation speed of a pair of output gears. This mechanism can be based on a pneumatic, hydraulic or electrical system.
The most popular recently has become the electric differential lock of the UAZ, in which the locking is carried out fully automatically or by pressing a button. The driver can decide when it is best to disengage the differential in order to take advantage of completely uniform wheel rotation.
Self-locking differential
An autonomous self-locking differential is an independent unit that does not require any external control systems. The device is intended exclusively for wheeled vehicles; tracked vehicles do not use it.
It is customary to divide “self-blocks” into 2 groups:
- Torque-driven differentials.
- Differentials that begin to work when there is a difference in angular speeds from the driven gears.
Group 1 includes devices with worm, screw, and disk locking.
The 2nd group is represented by mechanisms with a centrifugal automatic switch, having a viscous coupling, a gerotor hydraulic pump, and overrunning clutches.
Self-blocks for UAZ Krasikova, etc. Cam differentials are usually classified as intermediate types.
Where to install?
In any case, the UAZ center differential lock is a useful device that you can install yourself even if the design of your car does not initially provide for it. In the vast majority of cases, experts advise installing it in the rear of the car, since a correctly installed lock will give you the opportunity to make the traction between the rear and front wheels extremely even. This arrangement is much safer and more efficient. If we talk about the features of installation work, then in themselves they are not extremely complex, and, if necessary, can be carried out both in a standard inspection pit and on a lift.
Features of the “self-block” device
The solution to the above problem led to the emergence of various types of self-locking mechanisms. By design they are automatic and manual.
The manual type of locking involves forced locking of the differential on the UAZ by the driver.
Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The manual self-block on a UAZ car is controlled by the driver. You have to turn it on and off yourself. This leads to distraction from control of the car while driving. Moreover, the cable used in this process continues to be a rather weak link.
Automatic ones do not require attention from the driver; they will lock the differential independently. However, the devices are expensive.
But in most cases, UAZ owners decide to replace the standard limited-slip differential with automatic units.
It should be noted that automatic self-locking differentials, despite certain disadvantages, are the most popular devices installed in SUV axles. Their design allows them to be mounted in any bridge. However, the greatest efficiency will be achieved when installing a “self-block” in the rear axle.
You can install the device at home, in the garage. The advantage of this solution is cost savings. But it is worth remembering that this process is complex and time-consuming. Assembly requires increased attention and strict adherence to the instructions. Careful adjustment of the gaps is necessary (a special washer is used). The adjustment process is described in sufficient detail in the attached instructions, as well as in the installation information for a specific device, which is available on the Internet. The disadvantage of self-installation is that there is a high probability of disrupting the normal operation of the drive axle.
The advantage of installing self-locking devices by special organizations (carrying out disassembly and assembly of bridges under special technological conditions) is obvious. Why spend a lot of your time on installation when you can entrust it to specialists. Moreover, these structures are obliged to provide guarantees and provide technical support for their work.
Full
In this case, the difference in wheel rotation speed is eliminated completely, but you need to understand the fact that such locking of the UAZ rear differential can ultimately lead to certain side effects, such as slipping on off-road and dirt roads, as well as increased load on the wheels. parts of wheels and transmission while driving on hard surfaces. It is best to fully lock the differential only manually.
What are the options for diff locks for UAZ - a brief overview and cost
The most common differential locking schemes for UAZ Patriot:
- A self-locking mechanism (when disabled), developed by Val Racing for installation on axles with a “spicer” design. For activation, a power pneumatic drive is used, powered by a separate electric compressor (not included in the kit). The cost of the set intended for the front axle is 22.3 thousand rubles. A set of parts for the rear axle drive will cost another 22.3 thousand rubles; in addition, you need to buy a pump and air lines.
- The product of the Sprut company is intended for installation on bridges of the “spicer” circuit. Control is carried out by compressed air, which is pumped by a compressor. Additionally, gas supplied to the gearbox housings prevents the ingress of water, which causes leaching of lubricant and corrosion of gears. The cost of parts for 1 bridge is 22 thousand rubles, the set includes an electronic air distributor powered by the vehicle’s on-board network.
- The electric locking drive is supplied by Eaton; there are versions with a transfer case control unit. The design of the unit does not require maintenance during operation; when the lock is turned off, the differential operates as a standard unit. The blocker is driven by an electrically driven magnet; the control button is located on the instrument panel or center console. The cost of the set starts from 41 thousand rubles, the use of reinforced axle shafts is recommended.
- A mechanical drive from the Nirfi company will cost the buyer 20.4 thousand rubles. (per set for 1 bridge). The design is reliable because it consists of a rod and a shift lever located inside the car. To install the device, you need to cut a hole in the axle housing, which makes it difficult to install the lock yourself. Used differential housings are used to make the kits.
- Screw blocker supplied by Val Racing. The device costs about 20 thousand rubles, and turns on automatically when the load on the transmission increases. The DAK self-locking unit (Krasnikov’s design), which uses screws and balls, has a similar design. Under standard motion conditions, the balls move freely; when slippage is detected, the device automatically locks. After equalizing the rotation speeds of the wheels, the block is removed.
- A homemade design in which the opposite teeth of a gear (at 90°) located on the axle shaft are welded. The use of such a device worsens the controllability of the machine and increases the load on the transmission. The cost of such a design is minimal, but the consequences of use will exceed the price of factory devices.
Features of manual blocking
This option is the most understandable and convenient. Simply press the switch, as a result of which the limiter assembly starts working and completely prevents the distribution of force between the wheels.
Selective locking is quite complex, and it is often necessary to completely stop the vehicle in order to adjust the differential on such SUVs, including the UAZ Hunter. The differential is often also locked using a limited slip unit or traction control system.
Types of products
Currently, there are quite a number of different types of self-locking differentials on the market for the UAZ vehicle. The main ones include the following:
- Self-block for UAZ screw, increased friction. It has been known on the market for a long time. It is distinguished by its simplicity of design. Drivers note that it works most effectively when the engine power is increased before overcoming obstacles with the gas pedal, which eliminates slipping. However, the disadvantages of such devices include situations where a car gets into a hole, hangs out with one wheel, and gets out of it with great difficulty.
Important ! It is not recommended to install and use this type of self-locking differential on a UAZ if you are going to operate the vehicle in severe off-road conditions.
- Differential with cam self-locking method. Experts believe that this is a reliable device that can solve absolutely all problems in overcoming various obstacles. It refers to limited slip differentials. The principle of operation is mechanical, allowing you to easily get out of a situation where one wheel is hanging out, the second will always do everything possible to “pull out” the car.
- Forced self-locking differential device. Appeared on the market quite recently. These mechanisms are equipped with an axle shaft on which there are additional splines. The main distinctive feature of a forced “self-block” is that it is pneumatic and works with a pneumatic drive.
- Self-locking differential on UAZ DAK (Krasikova automatic differential). This device is distinguished by high performance characteristics. It can be mounted in both front and rear axles of UAZ. High performance is ensured by special screws that overtake special balls in space, influencing the free-wheeling characteristics. So, when the wheel is suspended, the balls expand, clamping the augers. The differential is locked. Unlocks when the same angular rotation of the axle shafts is established.
The main enterprise in the Russian Federation specializing in the production of UAZ self-locking devices is the IZH plant. Typically, units are sold through the IZHTEKHNO dealer. The Tolyatti enterprise AVTOSPRINTER is also popular.
The American company EATON is known for its solutions, which has developed and applies the electrical blocking principle. The electronic type of products of which (self-blocks operating on the principle of electric differential locks) is gaining more and more popularity. The main control unit in it is the electric drive.
Experienced drivers, professionals, state that the above-described unpleasant situations that arise when installing a standard differential on a UAZ are mainly private unpleasant moments. However, the self-locking differentials offered for installation, if installed correctly, can significantly increase the vehicle’s cross-country ability, allowing you to drive confidently on any off-road terrain.
Homemade differential lock
Made following the example of Inventor Adventure. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b-wmfBzYUp4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=okPYjAvjxeg. My new development, differential lock VAZ, Moskvich, NIVA, at home.
Channel support. Homemade forced differential locking Moskvich. Second attempt. Channel support: https://www.donationa. Help the Yandex money channel 410014183299611 Sberbank 4276842018995071.
Guys, don't be stupid. This is an Experiment! Read the story of this diff! Previously, such a system was installed on a car.
At the industrial site of the famous DAK.
Operation of a self-locking differential. A little about the running results.
Our website - https://www.autoproduct.biz/ Buy Differential Lock Autoproduct - https://autoproduct.biz/catalog/group/3 - Obstacle. Forced hydraulic locking in the rear axle of Timken UAZ-469.
Rear and front differential lock
In any case, the wheels equipped with the system will have the same rotation speed when activated, making it easier for the vehicle to move.
You can install either a manual or automatic system yourself.
The main thing is that the process will not take much time. Any car enthusiast with basic car repair skills can handle it. If the car is rear-wheel drive, it is better to install the lock on the rear wheel drive.
But what to do if the SUV has all-wheel drive.
Experts say that in this case, the locking will be more appropriate on the rear axle.
But to increase wheel grip on the road surface in the most difficult conditions, rear and front differential locks are installed.
The Chevrolet Niva is one of the few Russian-made SUVs that, in addition to excellent cross-country ability, can also boast a relatively modern design. Therefore, it still enjoys well-deserved popularity in the market.
The Chevrolet Niva owes its good off-road characteristics to its predecessors - the VAZ2121, namely permanent all-wheel drive, with the possibility of forced differential locking. But before setting up the transfer case and using the gearshift levers correctly, you must first understand how this mechanism works and what happens during its operation.
The transmission of this type of car consists of several main components: cardan, gearbox, transfer case and axles. The main component in the bridge structure is the differential. If it were not there, the wheels would rotate at the same speed, which would lead to wheel slipping and excessive load on the axle. The presence of a differential allows you to avoid destruction of the axle due to the fact that when turning, torque is transmitted to one of the wheels.
The design itself provides for the transmission of torque to the wheel, which experiences less traction with the surface. Therefore, for example, a wheel that stands on ice or sand will spin faster than one that stands on asphalt.
The Niva design provides for the presence of three differentials. This is due to the presence of permanent all-wheel drive in the car. If the same force were transmitted to all wheels, then the car could only move in a straight line. But when turning, the forces between the wheels are distributed unevenly. Accordingly, two bridges connected to each other will invariably experience increased loads that can destroy the structure. There are some SUV models that do not have a center differential installed, but they use other technical solutions, such as clutches or all-wheel drive is not permanent.
DIY car differential lock
If a car has one drive axle, then it also has one differential - between the wheels of this axle.
- automatic;
- forced, activated by the driver.
By blocking control method:
- mechanical;
- electromechanical;
- hydraulic;
- pneumatic
The answer to this question depends on what kind of car you have and where you drive it.
How to make a differential lock
That's why it needs to be adjusted to suit your driving style.
That's why many drivers don't accept it.
- It should be noted that this kind of differential locking with your own hands is simpler than with the manual method.
- blocking will work whenever you need it. This way you can focus solely on driving and keep both hands on the wheel at all times;
- There is a clicking sound when the gears engage, which some drivers find annoying and difficult to get used to.
- this type of restriction is felt on the road. Tire noise is especially noticeable when cornering, as well as resistance on sharp turns;
There are two types of partial restrictions:
- using helical gears (the most famous are Quaife and Torsen).
- using friction discs;
The task is quite difficult, given the wide variety.
History of the differential
Differentials on cars were not introduced immediately. Their birth is due to the fact that at the dawn of the automotive industry, designers were faced with the problem of maneuverability of the first cars. The wheels were spinning at the same angular speed. This led to loss of controllability when cornering and maneuvering on slippery roads. It was not destined to be a reliable means of transportation.
The first mechanism, which was responsible for the distribution of torque between the axes, was invented by the Frenchman Peccoeur. He presented his invention to the world in 1825. The inventor is also known for creating the world's first four-wheeled steam truck.
The mechanism invented by the Frenchman was a device consisting of shafts and gears. They contributed to the transmission of torque from the engine to the wheels. However, the unit failed to completely solve the problem of slipping when turning. The shortcomings especially manifested themselves when driving in icy conditions, when the wheels lost grip on the road. This led to frequent accidents. Crashing a car in off-road conditions was common.
The designers were forced to start looking for a solution to the problem. This process took quite a long time. Ferdinand Porsche managed to make a workable device and eliminate the problem by inventing a cam mechanism in the differential that prevents slipping of the axle wheels.
Porsche completed his research in 1935. The first successful examples of the new differential were installed on Volkswagen models (Ture B-70).